Abstract
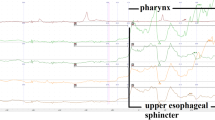
The aim of this study was to characterize the motion, morphology, and pressure of the upper esophageal sphincter (UES). The UES and its surrounding structures were evaluated in seven normal subjects and four human cadavers, using simultaneous high-resolution endoluminal sonography and manometry. The UES musculature on ultrasound is a C-shaped structure with an angle of 107 ± 19°. The mean peak resting UES pressure was 74 mm Hg, with a total cross-sectional area (CSA) of 0.87 ± 0.33 cm2. During swallowing, the UES moved in an orad direction. Localizing the UES sonographically, the peak UES pressure in the cadavers was 19.7 ± 10.0 mm Hg. The UES has a greater muscular CSA and resting pressure than the upper esophageal body. In the cadaver studies, the UES was imaged in conjunction with a significant increase in pressure, indicating that the pressure is due to passive mechanical conformational changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Miller LS, Liu J-B, Colizzo FP, Ter H, Marzano J, Barbarevech C, Hedwig K, Leung L, Goldberg BB: Correlation of high-frequency esophageal ultrasonography and manometry in the study of esophageal motility. Gastroenterology 109:832–837, 1995
McCray Jr. VM, Chung C, Parkman HP, Miller LS: Use of simultaneous high-resolution endoluminal sonography and manometry to characterize high pressure zone of distal esophagus. Dig Dis Sci 45(8):1660–1666, 2000
Wong RF, Bonapace ES, Chung CY, Liu J-B, Parkman HP, Miller LS: Simultaneous endoluminal sonography and manometry to assess the anal sphincter complex in normal subjects. Dig Dis Sci 43:2362–2372, 1998
Sobin J, Nathanson A, Engstrom C-F: Endoluminal ultrasonography: A new method to evaluated dysphagia. J Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Related Spec 58(2):105–109, 1996
Pehlivanov N, Liu J, Kassab GS, Puckett JL, Mittal RK: Relationship between esophageal muscle thickness and intraluminal pressure: An ultrasonographic study. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 280(6):G1093–G1098, 2001
Sivarao DV, Goyal RK: Functional anatomy and physiology of the upper esophageal sphincter. Am J Med 108(4A):27S–37S, 2000
Kahrilas PJ: Upper esophageal sphincter function during antegrade and retrograde transit. Am J Med 103:56S–60S, 1997
Cook IJ, Dodds WJ, Dantas RO, et al.: Opening mechanisms of the human upper esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol 257:G748–G759, 1989
Castell JA, Dalton CB, Castell DO: Pharyngeal and upper esophageal sphincter manometry in humans. Am J Physiol 258: G173–G178, 1990
Castell JA, Castell DO: Modern solid state computerized manometry of the pharyngoesophageal segment. Dysphagia 8:270–275, 1993
Massey BT: The use of intraluminal manometry to assess upper esophageal sphincter function. Dysphagia 8:339–344, 1993
Asoh R, Goyal RK: Manometry and electromyography of the upper esophageal sphincter in the opossum. Gastroenterology 74:514–520, 1978
Doty RW: Neural organization of deglutition. In Handbook of Physiology, Alimentary Canal, Sect 6, Vol 4. CF Code (ed).Washington, DC, American Physiological Society, 1968, pp. 1861–1902
Jacob P, Kahrilas PJ, Herzon G, McLaughlin B: Determinants of upper esophageal sphincter pressure in dogs. Am J Physiol 259:G245–G251, 1990
Grimm AF, Whitehorn WV: Characteristics of resting tension of myocardium and localization of its elements. Am J Physiol 210:1362–1368, 1966
Spiro D, Sonenblick EH: Comparison of ultrastructural basis of the contractile process in heart and skeletal muscle. Circ Res15 (Suppl 11):14–37, 1964
Welch RW, Luckmann K, Ricks PM, Drake ST, Gates GA: Manometry of the normal upper esophageal sphincter and its alterations in laryngectomy. J Clin Invest 63:1036–1041, 1979
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, L.S., Dai, Q., Sweitzer, B.A. et al. Evaluation of the Upper Esophageal Sphincter (UES) Using Simultaneous High-Resolution Endoluminal Sonography (HRES) and Manometry. Dig Dis Sci 49, 703–709 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DDAS.0000030077.15625.69
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DDAS.0000030077.15625.69