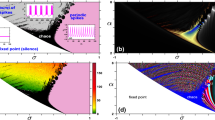
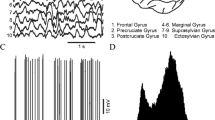
Abstract
We develop a new computationally efficient approach for the analysis of complex large-scale neurobiological networks. Its key element is the use of a new phenomenological model of a neuron capable of replicating important spike pattern characteristics and designed in the form of a system of difference equations (a map). We developed a set of map-based models that replicate spiking activity of cortical fast spiking, regular spiking and intrinsically bursting neurons. Interconnected with synaptic currents these model neurons demonstrated responses very similar to those found with Hodgkin-Huxley models and in experiments. We illustrate the efficacy of this approach in simulations of one- and two-dimensional cortical network models consisting of regular spiking neurons and fast spiking interneurons to model sleep and activated states of the thalamocortical system. Our study suggests that map-based models can be widely used for large-scale simulations and that such models are especially useful for tasks where the modeling of specific firing patterns of different cell classes is important.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott LF, Varela JA, Sen K, Nelson SB (1997) Synaptic depression and cortical gain control. Science 275: 220–224.
Bazhenov M, Stopfer M, Rabinovich M, Abarbanel HD, Sejnowski TJ, Laurent G (2001a) Model of cellular and network mechanisms for odor-evoked temporal patterning in the locust antennal lobe. Neuron. 30: 569–581.
Bazhenov M, Stopfer M, Rabinovich M, Huerta R, Abarbanel HD, Sejnowski TJ, Laurent G (2001b) Model of transient oscillatory synchronization in the locust antennal lobe. Neuron. 30: 553–567.
Bazhenov M, Timofeev I, Steriade M, Sejnowski T (2000) Patterns of spiking-bursting activity in the thalamic reticular nucleus initiate sequences of spindle oscillations in thalamic network. J. Neurophysiol. 84: 1076–1087.
Bazhenov M, Timofeev I, Steriade M, Sejnowski TJ (1998) Computational models of thalamocortical augmenting responses. J. Neurosci. 18: 6444–6465.
Bazhenov M, Timofeev I, Steriade M, Sejnowski TJ (1999) Selfsustained rhythmic activity in the thalamic reticular nucleus mediated by depolarizingGABAAreceptor potentials. Nat. Neurosci. 2: 168–174.
Bazhenov M, Timofeev I, Steriade M, Sejnowski TJ (2002) Model of thalamocortical slow-wave sleep oscillations and transitions to activated states. J. Neurosci. 22: 8691–8704.
Calvin WH, Stevens CF (1968) Synaptic noise and other sources of randomness in motoneuron interspike intervals. J. Neurophysiol. 31: 574–587.
Cang J, Friesen WO (2002) Model for intersegmental coordination of leech swimming: central and sensory mechanisms. J. Neurophysiol. 87: 2760–2769.
Casti AR, Omurtag A, Sornborger A, Kaplan E, Knight B, Victor J, Sirovich L (2002) A population study of integrate-and-fire-orburst neurons. Neural Comput. 14: 957–986.
Chagnac-Amitai Y, Connors BW (1989) Horizontal spread of synchronized activity in neocortex and its control byGABA-mediated inhibition. J. Neurophysiol. 61: 747–758.
Chervin RD, Pierce PA, Connors BW (1988) Periodicity and directionality in the propagation of epileptiform discharges across neocortex. J. Neurophysiol. 60: 1695–1713.
Connors BW, Gutnick MJ (1990) Intrinsic firing patterns of divers neocortical neurons. Trends Neurosci. 13: 99–104.
Contreras D, Destexhe A, Sejnowski, TJ, Steriade M (1996). Control of spatiotemporal coherence of a thalamic oscillation by corticothalamic feedback. Science 274: 771–774.
Corchs S, Deco G (2001) A neurodynamical model for selective visual attention using oscillators. Neural. Netw. 14: 981–990.
Crook SM, Ermentrout GB, Vanier MC, Bower JM (1997) The role of axonal delay in the synchronization of networks of coupled cortical oscillators. J. Comput. Neurosci. 4: 161–172.
Delaney KR, Gelperin A, Fee MS, Flores JA, Gervais R, Tank DW, Kleinfeld D (1994) Waves and stimulus-modulated dynamics in an oscillating olfactory network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 669–673.
Destexhe A, Bal T, McCormick DA, Sejnowski TJ (1996) Ionic mechanisms underlaying synchronized and propagating waves in a model of ferret thalamic slices. J. Neurophysiol. 76: 2049–2070.
Destexhe A, Contreras D, Sejnowski TJ, SteriadeM(1994a)Amodel of spindle rhythmicity in the isolated thalamic reticular nucleus. J. Neurophysiol. 72: 803–818.
Destexhe A, Mainen ZF, Sejnowski TJ (1994b) Synthesis of models for excitable membranes, synaptic transmission and neuromodulation using a common kinetic formalism. J. Comput. Neurosci. 1: 195–230.
Ermentrout B (1998) Linearization of F-I curves by adaptation. Neural Comput. 10: 1721–1729.
Ermentrout B, Wang JW, Flores J, Gelperin A (2001) Model for olfactory discrimination and learning in Limax procerebrum incorporating oscillatory dynamics and wave propagation. J. Neurophysiol. 85: 1444–1452.
Ermentrout GB, Kleinfeld D (2001) Traveling electrical waves in cortex: Insights from phase dynamics and speculation on a computational role. Neuron. 29, 33–44.
Gais S, Plihal W, Wagner U, Born J (2000) Early sleep triggers memory for early visual discrimination skills. Nat. Neurosci. 3: 1335–1339.
Galarreta M, Hestrin S (1998) Frequency-dependent synaptic depression and the balance of excitation and inhibition in the neocortex. Nat. Neurosci. 1: 587–594.
Gestrin G, Masterbroek HAK, Zaagman WH (1980) Stochastic constancy, variability and adaptation of spike generation: Performance of a giantneuron in the visual system of the fly. Biol. Cybern. 38: 31–40.
Golomb D (1998) Models of neuronal transient synchrony during propagation of activity through neocortical circuitry. J. Neurophysiol. 79: 1–12.
Golomb D, Amitai Y (1997) Propagating neuronal discharges in neocortical slices: Computational and experimental study. Journal of Neurophysiology. 78: 1199–1211.
Golomb D, Ermentrout GB(1999) Continuous and lurching traveling pulses in neuronal networks with delay and spatially decaying connectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 13480–13485.
Golomb D, Ermentrout GB (2001) Bistability in pulse propagation in networks of excitatory and inhibitory populations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86: 4179–4182.
Golomb D, Ermentrout GB (2002) Slow excitation supports propagation of slow pulses in networks of excitatory and inhibitory populations. Phys. Rev. E. Stat. Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 65: 061911.
Golomb D, Wang XJ, Rinzel J (1994) Synchronization properties of spindle oscillations in a thalamic reticular nucleus model. J. Neurophysiol. 72: 1109–1126.
Golomb D, Wang X-J, Rinzel J (1996) Propagation of spindle waves in a thalamic slice model. Journal of Neurophysiology. 75: 750–769.
Golowasch J, Marder E (1992) Ionic currents of the lateral pyloric neuron of the stomatogastric ganglion of the crab. J. Neurophysiol. 67: 318–331.
Gray CM, McCormick DA (1996) Chattering cells: Superficial pyramidal neurons contributing to the generation of synchronous oscillations in the visual cortex. Science 274: 109–113.
Gutkin BS, ErmentroutGB(1998) Dynamics of membrane excitability determine interspike interval variability: A link between spike generation mechanisms and cortical spike train statistics. Neural. Comput. 10: 1047–1065.
Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF (1952) A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. Lond. 117: 500–544.
Hoppensteadt FC, Izhikevich EM (1996) Synaptic organizations and dynamical properties of weakly connected neural oscillators. II. Learning phase information. Biol. Cybern. 75: 129–135.
Hoppensteadt FC, Izhikevich EM (1998) Thalamo-cortical interactions modeled by weakly connected oscillators: Could the brain use FM radio principles? Biosystems. 48: 85–94.
Houweling AR, Bazhenov M, Timofeev I, Grenier F, Steriade M, Sejnowski TJ (2002) Frequency-selective augmenting responses by short-term synaptic depression in cat neocortex. J. Physiol. 542: 599–617.
IzhikevichEM(2003) Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks. 14: 1569–1572.
Izhikevich EM (2004) Which model to use for cortical spiking neurons? IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks (in press).
Jahnsen H, Llinás R (1984) Electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones: An in vitrostudy. Journal of Physiology 349: 205–226.
Kawahara S, Toda S, Suzuki Y, Watanabe S, Kirino Y (1997) Comparative study on neural oscillation in the procerebrum of the terrestrial slugs Incilaria bilineata and J. Exp. Biol. 200: 1851–1861.
Knight BW (1972a) Dynamics of encoding in a population of neurons. J. Gen Physiol. 59: 734–766.
Knight BW (1972b) The relationship between the firing rate of a single neuron and the level of activity in a population of neurons. Experimental evidence for resonant enhancement in the population response. J. Gen. Physiol. 59: 767–778.
Kuramoto Y (1984) Chemical oscillations, waves, and turbulence. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York-Tokyo.
Longtin A, Doiron B, Bulsara AR (2002) Noise-induced divisive gain control in neuron models. Biosystems. 67: 147–156.
Lytton WW, Destexhe A, Sejnowski TJ (1996) Control of slow oscillations in the thalamocortical neuron: A computer model. Neuroscience. 70: 673–684.
Mainen ZF, Sejnowski TJ (1996) Influence of dendritic structure on firing pattern in model neocortical neurons. Nature 382: 363–366.
Mason A, Larkman A (1990) Correlations between morphology and electrophysiology of pyramidal neurons in slices of rat visual cortex. II. Electrophysiology. J. Neurosci. 10: 1415–1428.
McCormick DA, Connors BW, Lighthall JW, Prince DA(1985) Comparative electrophysiology of pyramidal and sparsely spiny stellate neurons of the neocortex. J. Neurophysiol. 54: 782–806.
Nenadic Z, Ghosh BK, Ulinski P (2003) Propagating waves in visual cortex: A large-scale model of turtle visual cortex. J Comput Neurosci. 14: 161–184.
Nenadic Z, Ghosh BK, Ulinski PS (2002) Modeling and estimation problems in the turtle visual cortex. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 49: 753–762.
Noda H, Adey WR (1970) Firing of neuron pairs in cat association cortex during sleep and wakefulness. J. Neurophysiol. 33: 672–684.
Pinsky PF, Rinzel J (1994) Intrinsic and network rhythmogenesis in a reduced Traub model for CA3 neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 1: 39–60.
Prechtl JC, Cohen LB, Pesaran B, Mitra PP, Kleinfeld D (1997) Visual stimuli induce waves of electrical activity in turtle cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 7621–7626.
Roelfsema PR, Engel AK, Konig P, SingerW(1997) Visuomotor integration is associated with zero time-lag synchronization among cortical areas. Nature 385: 157–161.
Rulkov NF (2002) Modeling of spiking-bursting neural behavior using two-dimensional map. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 65: 041922.
Shilnikov AL, Rulkov NF (2003), Origin of chaos in a twodimensional map modeling spiking-bursting neural activity. Int. J. Bif. and Chaos. 13: 3325–3340.
Sigvardt KA, Miller WL (1998) Analysis and modeling of the locomotor central pattern generator as a network of coupled oscillators. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 86: 250–265.
Smith GD, Cox CL, Sherman SM, Rinzel J (2000). Fourier analysis of sinusoidally driven thalamocortical relay neurons and a minimal integrate-and-fire-or-burst model. J. Neurophysiol. 83: 588–610.
Smith GD, Sherman SM (2002) Detectability of excitatory versus inhibitory drive in an integrate-and-fire-or-burst thalamocortical relay neuron model. J. Neurosci. 22: 10242–10250.
Softky WR, Koch C 1993. The highly irregular firing of cortical cells is inconsistent with temporal integration of random EPSPs. J. Neurosci. 13: 334–350.
Stein RB (1967) The frequency of nerve action potentials generated by applied currents. Proc. R. Soc. Lond B. Biol. Sci. 167: 64–86.
Steriade M, McCormick DA, Sejnowski TJ (1993a) Thalamocortical oscillations in the sleeping and aroused brain. Science 262: 679–685.
Steriade M, Nunez A, Amzica F (1993b) A novel slow (<1 Hz) oscillation of neocortical neurons in vivo: Depolarizing and hyperpolarizing components. J. Neurosci. 13: 3252–3265.
Steriade M, Timofeev I, Durmuller N, Grenier, F (1998) Dynamic properties of corticothalamic neurons and local cortical interneurons generating fast rhythmic (30-40 Hz) spike bursts. J. Neurophysiol. 79: 483–490.
Steriade M, Timofeev I, Grenier F (2001) Natural waking and sleep states: A view from inside neocortical neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 85: 1969–1985.
Stickgold R, James L, Hobson JA(2000)Visual discrimination learning requires sleep after training. Nat. Neurosci. 3: 1237–1238.
Timofeev I, Bazhenov M, Sejnowski T, Steriade M (2001a) Contribution of intrinsic and synaptic factors in the desynchronization of thalamic oscillatory activity. Thalamus and related systems. 1: 53–69.
Timofeev I, Grenier F, BazhenovM, Sejnowski TJ, Steriade M(2000) Origin of slow cortical oscillations in deafferented cortical slabs. Cer. Cortex 10: 1185–1199.
Timofeev I, Grenier F, SteriadeM(2001b) Disfacilitation and active inhibition in the neocortex during the natural sleep-wake cycle: An intracellular study. PNAS 98: 1924–1929.
Topolnik L, Steriade M, Timofeev I (2003) Partial cortical deafferentation promotes development of paroxysmal activity. Cereb. Cortex 13: 883–893.
Traub RD, Jefferys JG, Whittington MA (1997) Simulation of gamma rhythms in networks of interneurons and pyramidal cells. J. Comput. Neurosci. 4: 141–150.
Traub RD, Whittington MA, Colling SB, Buzsaki G, Jefferys JG (1996) Analysis of gamma rhythms in the rat hippocampus in vitro and in vivo. J. Physiol. 493 (Pt 2): 471–484.
Troyer TW, Miller KD (1997) Physiological gain leads to high ISI variability in a simple model of a cortical regular spiking cell. Neural Comput. 9: 971–983.
Tsodyks MV, Markram H (1997) The neural code between neocortical pyramidal neurons depends on neurotransmitter release probability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 94: 719–723.
Tuckwell HC (1988) Introduction to Theoretical Neurobiology. Vol. 2, Nonlinear and Stochastic Theries. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Wang XJ (1998) Calcium coding and adaptive temporal computation in cortical pyramidal neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 79: 1549–1566.
Williams TL, Bowtell G (1997) The calculation of frequency-shift functions for chains of coupled oscillators, with application to a network model of the lamprey locomotor pattern generator. J. Comput. Neurosci. 4: 47–55.
Winfree A (1987) When Time Breaks Down. Springer-Verlag, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rulkov, N., Timofeev, I. & Bazhenov, M. Oscillations in Large-Scale Cortical Networks: Map-Based Model. J Comput Neurosci 17, 203–223 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JCNS.0000037683.55688.7e
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JCNS.0000037683.55688.7e