Abstract
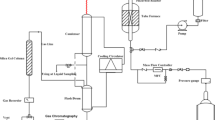
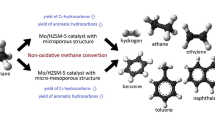
Well-controlled treatment with alkali solution causes the etching of HZSM-5 framework, which results in the formation of the new porosity and channel structure with the coexistence of micropores and mesopores, as evidenced by nitrogen adsorption experiments. The dissolution of the zeolite framework, as revealed by the investigation of solid-state NMR, begins from the crystalline site with Si–O–Si linkages. The inertness of the alkali treatment toward Si–O–Al bond in the framework preserves the specific Brønsted acid site that is defined to be the bridging OH species over Si–O–Al units in zeolite. The Mo-modified catalysts derived from the alkali treatments showed a very high catalytic performance in the conversion of methane to aromatics (MDA) when compared with the conventional Mo/HZSM-5 catalyst. The unique selectivity to aromatics and stability of the catalysts derived from the alkali-treated ZSM-5 are attributed to the coexistence of mesopores and inherent micropores in the zeolites, which optimizes an environment for catalytic reaction and mass transfers. The channel with mainly 3–5 nm in diameters in the zeolites serves as the “aisle” to enhance the diffusion of molecules, especially the aromatics molecules, while the micropores have been identified to be the active cavities for the aromatics formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Wang, T. Li, M. Xie and G. Xu, Catal. Lett. 21 (1993) 35.
Y. Xu and L. Lin, Appl. Catal. A188 (1999) 53.
Y. Shu and M. Ichikawa, Catal. Today 71 (2001) 55.
Y. Xu, X. Bao and L. Lin, J. Catal. 216 (2003) 386.
D. M. Bibby, N. B. Milestone, J. E. Patterson and L. P. Aldridge, J. Catal. 97 (1986) 493.
M. Guisnet and P. Magnoux, Appl. Catal. 54 (1989) 1.
M. Guisnet and P. Magnoux, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 88 (1994) 53.
A. de Lucas, P. Canizares and A. Duran, Appl. Catal. A206 (2001) 87.
D. Wang, G. D. Meitzner and E. Iglesia, J. Catal. 206 (2002) 14.
Y. Lu, D. Ma, X. Bao and L. Lin, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commum. (2002) 2048.
D. Ma, Y. Lu, L. Su, Z. Xu, Z. Tian, Y. Xu, L. Lin and X. Bao, J. Phys. Chem. B106 (2002) 8524.
W. Richard, H. Young and E. Iglesia, J. Phys. Chem. B103 (1999) 5787.
B. Sharifah, H. Derouane-Abd, A. J. Ross and E. G. Derouane, Catal. Today 63 (2000) 461.
C. Bouchy, I. Schmidt, J. R. Anderson, C. J. H. Jacobsen, E. G. Derouane and S. B. Derouane-Abd Hamid, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 163 (2000) 283.
C. Zhang, S. Li, Y. Yuan, W. Zhang, T. Wu and L. Lin, Catal. Lett. 56 (1998) 207.
M. Ogura, S. Shinomiya, J. Tateno, Y. Nara and M. Matsukata, Chem. Lett. (2000) 882.
M. Ogura, S. Shinomiya, J. Tateno, Y. Nara, M. Nomura, E. Kikuchi and M. Matsukata, Appl. Catal. A219 (2001) 33.
T. Suzuki and T. Okuhar, Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 43 (2001) 83.
J. C. Groen, J. Perez-Ramirez and L. A. Peffer, Chem. Lett. (2002) 9.
Y. Shu, D. Ma, X. Bao and Y. Xu, Catal. Lett. 66 (2000) 161.
W. Liu, Y. Xu, S. Wong, J. Qiu and N. Yang, J. Mol. Catal. A120 (1997) 257.
D. Ma, Y. Shu, W. Zhang, X. Han, Y. Xu and X. Bao, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 39 (2000) 2928-2931.
J. Shu, A. Adnot and B. P. Grandjean, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 38 (1999) 3860.
D. Wang, M. Rosynek and J. H. Lunsford, Top. Catal. 3 (1996) 289.
J. E. DeVries, H. C. Yao, R. J. Baird and H. S. Gandhi, J. Catal. 84 (1983) 8.
P. E. Dai and J. H. Lunsford, J. Catal. 64 (1980) 173.
T. Yang and J. H. Lunsford, J. Catal. 103 (1987) 55.
Y. Shu, D. Ma, L. Xu, Y. Xu and X. Bao, Catal. Lett. 70 (2000) 67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, L., Liu, L., Zhuang, J. et al. Creating Mesopores in ZSM-5 Zeolite by Alkali Treatment: A New Way to Enhance the Catalytic Performance of Methane Dehydroaromatization on Mo/HZSM-5 Catalysts. Catalysis Letters 91, 155–167 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CATL.0000007149.48132.5a
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CATL.0000007149.48132.5a