Abstract
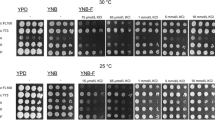
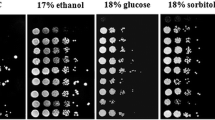
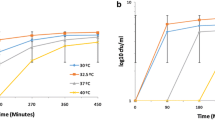
Mg2+ at 3.5 mM increased the tolerance of a self-flocculating fusant of Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae to ethanol. After 9 h of exposure to 20% (v/v) ethanol at 30 °C, all cells died whereas over 50% remained viable for the cells grown with Mg2+. The effect of Mg2+ is closely related to its ability to decrease plasma membrane permeability of cells subjected to ethanol stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai FW, Jin Y, Feng PS, He XL (1999) Studies of ethanol fermentation using a fusant SPSC flocs – description of flocs, growth and ethanol fermentation kinetics. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 15: 455–460.
Casey GP, Ingledew M (1986) Ethanol tolerance in yeasts. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 13: 219–290.
D'Amore T, Stewart GG (1987) Ethanol tolerance of yeast. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 9: 322–330.
Hayashida S, Feng DD, Hongo M (1975) Physiological properties of yeast cells grown in the proteolipid supplemented media. Agric. Biol. Chem. 39: 1025–1031.
Hayashida S, Feng DD, Ohta K, Chaitiumvong S, Hongo M (1976) Compositions and a role of Aspergillus oryzae proteolipid as a high concentration alcohol-producing factor. Agric. Biol. Chem. 40: 73–78.
Ingram LO, Buttke TM (1984) Effects of alcohols on microorganisms. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 25: 253–300.
Mizoguchi H, Hara S (1996) Effect of fatty acid saturation in membrane lipid bilayers on simple diffusion in the presence of ethanol at high concentrations. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 81: 406–411.
Rosa MF, Sá-Correia I, Novais JM (1987) Production of ethanol at high temperatures in the fermentation of Jerusalem artichoke juice and a simple medium by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biotechnol. Lett. 9: 441–444.
Rosa MF, Sá-Correia I, Novais JM (1988) Improvements in the ethanol tolerance of Kluyveromyces fragilis in Jerusalem artichoke juice. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 31: 705–710.
Thomas DS, Hossack JA, Rose AH (1978) Plasma membrane lipid composition and ethanol tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch. Microbiol. 17: 239–245.
Yang JY, Park KH, Pek UH, Yu JH (1990) Screening and characterization of the high alcohol producing Saccharomyces cerevisiae D 1. Korean J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 18: 511–516.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, CK., Bai, FW. & An, LJ. Enhancing ethanol tolerance of a self-flocculating fusant of Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae by Mg2+ via reduction in plasma membrane permeability. Biotechnology Letters 25, 1191–1194 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024583503274
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024583503274