Abstract
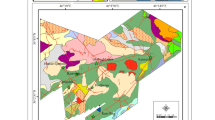
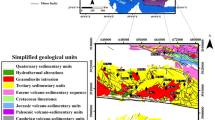
In this paper, we describe new fuzzy models for predictive mineral potential mapping: (1) a knowledge-driven fuzzy model that uses a logistic membership function for deriving fuzzy membership values of input evidential maps and (2) a data-driven model, which uses a piecewise linear function based on quantified spatial associations between a set of evidential evidence features and a set of known mineral deposits for deriving fuzzy membership values of input evidential maps. We also describe a graphical defuzzification procedure for the interpretation of output fuzzy favorability maps. The models are demonstrated for mapping base metal deposit potential in an area in the south-central part of the Aravalli metallogenic province in the state of Rajasthan, western India. The data-driven and knowledge-driven models described in this paper predict potentially mineralized zones, which occupy less than 10% of the study area and contain at least 83% of the “model” and “validation” base metal deposits. A cross-validation of the favorability map derived from using one of the models with the favorability map derived from using the other model indicates a remarkable similarity in their results. Both models therefore are useful for predicting favorable zones to guide further exploration work.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agterberg, F. P., 1989, Systematic approach to dealing with uncertainty of geoscience information in mineral exploration: Proc. 21st APCOM Symp. (Las Vegas, Nevada), p. 165–178.
Agterberg, F. P., and Bonham-Carter, G. F., 1990, Deriving weights-of-evidence from geoscience contour maps for prediction of discrete events: Proc. 22nd APCOM Symp. (Berlin, Germany), v.2, p. 381–395.
An, P., Moon, W. M., and Rencz, A., 1991, Application of fuzzy set theory for integration of geological, geophysical and remote sensing data: Can. Jour. Exploration Geophysics, v.27, no.1, p. 1–11.
Bonham-Carter, G. F., 1994, Geographic Information Systems for geoscientists: Modelling with GIS: Pergamon Press, Oxford, 398p.
Carranza, E. J. M., and Hale, M., 2001, Geologically constrained fuzzy mapping of gold mineralization potential, Baguio district, Philippines: Natural Resources Research, v.10, no.2, p. 125–136.
Cheng, Q., and Agterberg, F. P., 1999, Fuzzy weights of evidence and its application in mineral potential mapping: Natural Resources Research, v.8, no 1, p. 27–35.
Cox, D. P., and Singer, D. A., 1986, Mineral deposit models. U.S. Geol. Survey Bull. 1693, US Govt Printing Office, Washington, 379p.
Deb, M., 1986, Sulfur and carbon isotope compositions in the stratiform Zn-Pb-Cu sulfide deposits of the Rajpura-Dariba belt, Rajasthan: a model of ore genesis: Mineral. Deposita, v.21, no.4, p. 313–321.
Deb, M., 1999, Metallic mineral deposits of Rajasthan, in Kataria, P., ed., Proc. Seminar on Geology of Rajasthan-Status and Perspective, (Udaipur, India) p. 213–237.
Deb, M., 2000, VMS deposits: geological characteristics, genetic models and a review of their metallogenesis in the Aravalli range, NW India, in Deb, M., ed., Crustal Evolution and Metallogeny in the Northwestern Indian Shield: Narosa Publ. House, New Delhi, p. 217–239.
Deb, M., and Sarkar, S. C., 1990, Proterozoic tectonic evolution and metallogenesis in the Aravalli-Delhi orogenic complex, NW India: Precambian Res., v.46, no. 1–2, p. 115–137.
Deb, M., and Thorpe, R. I., 2001, Geochronological constraints in the Precambrian geology of northwestern India and their metallogenic implications: Proc. Inter. Workshop on Sediment-hosted Lead-Zinc Deposits in the Northwestern Indian Shield (New Delhi and Udaipur, India), p. 137–152.
Deb, M., Thorpe, R. I., Cumming, G. L., and Wagner, P. A., 1989, Age, source and stratigraphic implications of Pb isotope data for conformable, sediment hosted base metal deposits in the Proterozoic Aravalli-Delhi orogenic belt, NW India: Precambrian Res., v.43, no.1, p. 1–22.
Gettings, M. E., and Bultman, M. W., 1993, Quantifying favorableness for occurrence of a mineral deposit type-an example from Arizona: U.S. Geol. Survey, Open-File Rept. 93–392, 23 p.
Goguen, J. A., 1969, The logic of inexact concepts: Synthese, v.19, p. 325–373.
Goodfellow, W. D., 1987, Anoxic stratified oceans as a source of sulphur in sediment-hosted stratiform Zn-Pb deposits (Selwyn Basin, Yukon, Canada): Chemical Geology, v.65, no. 3–4, p. 359–382.
Goodfellow, W. D., 2001, Attributes of modern and ancient sediment-hosted, sea-floor hydrothermal deposits: Proc. Intern. Workshop on Sediment-hosted Lead-Zinc Deposits in the Northwestern Indian Shield, (New Delhi and Udaipur, India), p. 1–35.
GSI, 1981, Total intensity aeromagnetic map and map showing the magnetic zones of the Aravalli region, southern Rajasthan and northwestern Gujarat, India (1:253,440): Geol. Survey India, Hyderabad, India.
Gupta, S. N., Arora, Y. K., Mathur, R. K., Iqballuddin, Prasad, B., Sahai, T. N., and Sharma, S. B., 1995a, Lithostratigraphic map of Aravalli region (2nd ed.) (1:250,000): Geol. Survey India, Calcutta, India.
Gupta, S. N., Arora, Y. K., Mathur, R. K., Iqballuddin, Prasad, B., Sahai, T. N., and Sharma, S. B., 1995b. Structural map of the Precambrian of Aravalli region (2nd edn.) (1:250,000): Geol. Survey India, Calcutta, India.
Gupta, S. N., Arora, Y. K., Mathur, R. K., Iqballuddin, Prasad, B., Sahai, T. N., and Sharma, S. B., 1997, The Precambrian geology of the Aravalli Region, Geol. Survey India, Mem, v.123, GSI, Hyderabad, India, 262p.
Haldar, S. K., 2001, Grade-tonnage model for lead-zinc deposits of Rajasthan, India: Proc. Intern. Workshop on Sediment-hosted Lead-Zinc Deposits in the Northwestern Indian Shield (New Delhi and Udaipur, India, p. 153–160.
Hellendoorn, H., and Thomas, C., 1993, Defuzzification in fuzzy controllers: Jour. Intell. Fuzzy Syst., v.1, p. 109–123.
Helson, H., 1964, Adaption-level theory: Harper and Row, New York. 732p.
Heron, A.M., 1953, The geology of central Rajputana: Geol. Survey India Mem., v.79, no.1, 389p.
Kemp, L. D., Bonham-Carter, G. F., and Raines, G. L., 1999, Arc-WofE: ArcView extension for weights of evidence mapping http: //gis.nrcan.gc.ca/software/arcview/wofe.
Knox-Robinson, C. M., 2000, Vectorial fuzzy logic: a novel technique for enhanced mineral prospectivity mapping with reference to the orogenic gold mineralisation potential of the Kalgoorlie Terrane, Western Australia. Australian Jour. Earth Sciences, v.47, no.5, p. 929–942.
Large, D. E., 1983. Sediment-hosted massive sulfide lead-zinc deposits: an empirical model, in Sangster, D. F., ed., Sediment-hosted Stratiform Lead-Zinc Deposits, Mineralogical Assoc. Canada, Short Course Handbook, v.8, p. 1–29.
Lydon, J. W., 2001, Exploration criteria and genetic models for SEDEX deposits: the Belt-Purcell Basin and the Sullivan deposit: Proce. Intern. Workshop on Sediment-hosted Lead-Zinc Deposits in the Northwestern Indian Shield (New Delhi and Udaipur, India), p. 197–223.
Pan, G. C., and Harris, D. P., 2000, Information synthesis for mineral exploration: Oxford Univ. Press, New York, 461p.
Pettijohn, F. J., 1975, Sedimentary rocks: Harper and Row, New York, 628p.
Porwal, A., and Hale, M., 2000, GIS-based weights-of-evidence analysis of multiclass spatial data for predictive mineral mapping: a case study from Aravalli province, western India: Proc. XIV Intern. Con. Applied Geologic Remote Sensing, (Las Vegas, Nevada), p. 377–384.
Porwal, A., and Sides, E. J., 2000, A predictive model for base metal exploration in a GIS environment: Intern. Archives of Photogrammetry. and Remote Sensing, v.XXXIII, p. B7 (Amsterdam), p. 1178–1184.
Raja Rao, C. S., Poddar, B. C., and Basu, K. K., and Dutta, A. K., 1971, Precambrian stratigraphy of Rajasthan: a review: Rec. Geol. Survey India, v.101, no.2, p. 60–79.
Roy, A. B., 1988, Stratigraphic and tectonic frame work of the Aravalli Montain Range, in Roy, A. B., ed., Precambrian of the Aravalli Mountain Rajasthan, India: Geol. Soc. India Mem., v.7, p. 3–31.
Roy, A. B., and Paliwal, B. S. 1981, Evolution of lower Proterosoic epicontinental deposits: stromatolite bearing Aravalli rocks of Udaipur, Rajasthan, India: Precambrian Res., v.14, p. 49–71.
Roy, A. B., Paliwal, B. S., Shekhawat, S. S., Nagori, D. K., Golani, P. R., and Bejarniya, B. R., 1988, Stratigraphy of the Aravalli Supergroup in type area, in Roy, A. B., ed., Precambrian of the Aravalli Mountain Rajasthan: India: Geol. Soc. India Mem., v.7, p. 121–131.
Roy, A. B., Sharma, B. L., Paliwal, B. S., Chauhan, N. K., Nagori, D. K., Golani, P. R., Bejarniya, B. R., Bhu, H, and Ali Sabah, M., 1993, Lithostratigraphic and tectonic evolution of the Aravalli Supergoup: a protogeosynclinal sequence, in Cassyap A.M. ed., Rift Basins and Aulacogens, Gyanodaya Prakashan: Nainital, p. 73–90.
Sarkar, S. C., 2000, Geological setting, characteristics, origin and evolution of sediment-hosted sulfide ore deposits of Rajasthan: a critique with comments on their implications for future exploration, in Deb, M., ed., Crustal Evolution and Metallogeny in the Northwestern Indian Shield: Narosa Publ. House, New Delhi, p. 240–292.
Singer, D. A., and Kouda, R., 1999, A comparison of the weights of evidence method and probabilistic neural networks: Natural Resources Research, v.8, no.4, p. 287–298.
Sinha-Roy, S., 2000, Precambrian metallotects and mineralisation types in Rajasthan: their relation to crustal evolution, in Deb, M., ed., Crustal Evolution and Metallogeny in the Northwestern Indian Shield: Narosa Publ. House, New Delhi, p. 217–239.
Sinha-Roy, S., Malhotra, G., and Guha, D. B., 1995, A transect across Rajasthan Precambrian terrane in relation to geology, tectonics and crustal evolution of south-central Rajasthan, in Sinha-Roy, S., and Gupta, K. R., eds., Continental Crust of NW and Central India: Geol. Soc. India Mem., v.31, p. 63–90.
Sugden, T. J., Deb, M., and Windley, B. F., 1990, The tectonic setting of mineralisation in the Proterozoic Aravalli-Delhi orogenic belt, NW India, in Naqvi, S.M., ed., Precambrian Continental Crust and its Economic Resources: Developments in Precambrian Geology 8, Elsevier Sci. Publ., Amsterdam, p. 367–390.
Thole, U., Zimmermann, H. J., and Zysno, P., 1979, On the suitability of minimum and product operators for intersection of fuzzy sets: Fuzzy Sets and Systems, v.2, p. 167–180.
Zimmermann, H. J., 1991, Fuzzy set theory-and its applications (2nd edn.): Kluwer Acad. Publ. Dordrecht, 99p.
Zadeh, L. A., 1965, Fuzzy sets: IEEE Information and Control, v.8, no.3, p. 338–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porwal, A., Carranza, E.J.M. & Hale, M. Knowledge-Driven and Data-Driven Fuzzy Models for Predictive Mineral Potential Mapping. Natural Resources Research 12, 1–25 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022693220894
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022693220894