Abstract
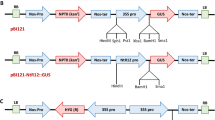
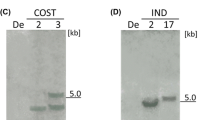
The maize b-32 protein is a functional ribosome-inactivating protein (RIP), inhibiting in vitro translation in the cell-free reticulocyte-derived system and having specific N-glycosidase activity on 28S rRNA. Previous results indicated that opaque-2 (o2) mutant kernels, lacking b-32, show an increased susceptibility to fungal attack and insect feeding and that ectopic expression in plants of a barley and a pokeweed RIP leads to increased tolerance to fungal and viral infection. This prompted us to test whether b-32 might functi on as a protectant against pathogens. The b32.66 cDNA clone under the control of the potato wun1 gene promoter was introduced into tobacco by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. Out of 23 kanamycin resistant regenerated shoots, 16 contained a PCR fragment of the corrrect size spanning the boundary between the promoter used and the coding region of the b-32 gene. Eight independently transformed tobacco lines were randomly chosen for protein analysis: all of them expressed b-32 protein. The data presented indicate that transgenic tobacco plants expressing b-32 show an increased tolerance against infection by the soil-borne fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, N.A. (1982) The genetics and pathology of Rhizoctonia solani. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 20, 327–9.
Barbieri, L., Stirpe, F. (1982) Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants: properties and possible uses. Cancer Surv. 1, 489–520.
Bass, H.W., Webster, C., O'Brian, G.R., Roberts, J.K.M., Boston, R.S. (1992) A maize ribosome-inactivating protein is controlled by the transcriptional activator Opaque-2. Plant Cell 4, 225–34.
Bonness, M.S., Ready, M.P., Irvin, J.D., Mabry, T.J. (1994) Pokeweed antiviral protein inactivates pokeweed ribosomes; implications for the antiviral mechanism. Plant J. 5, 173–83.
Bowles, R.J. (1990) Defense related proteins in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59, 873–907.
Bradford, M.M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–54.
Broekaert, W.F., Terras, F.R.G., Cammue, B.P.A., Osborn, R.W. (1976) Plant defensins: novel antimicrobial peptides as components of the host defense system. Plant Physiol. 108, 1353–8 (1995).
Broglie, K., Chet, I., Holliday, M., Cressman, R., Biddle, P., Knowlton, S., Mauvais, C.J., Broglie, R. (1991) Transgenic plants with enhanced resistance to the fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani. Science 254, 1194–7.
Chaudhry, B., Muller-Uri, F., Cameron-Mills, V., Gough, S., Simpson, D., Skriver, K., Mundy, J. (1994) The barley 60 kDa jasmonate-induced protein (JIP60) is a novel ribosome-inactivating protein. The Plant J. 6, 815–24.
Coleman, W.H., Roberts, W.K. (1994) Inhibitors of animal cell-free protein synthesis from grains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 696, 239–44 (1982).
Corazza, L., Luongo, L., Chilosi, G. (1992) Characterization of a strain of Rhizoctonia solani Kuèhn from melon in Italy. Phytopath. Medit. 31, 121–2.
Di Fonzo, N., Hartings, H., Brembilla, M., Motto, M., Soave, C., Navarro, E., Palau, J., Rhode, W., Salamini, F. (1988) The b-32 protein from maize endosperm, an albumin regulated by the O2 locus: nucleic acid (cDNA) and amino acid sequences. Mol. Gen. Genet. 212, 481–7.
Di Fonzo, N., Manzocchi, L., Salamini, F., Soave, C. (1986) Purification and properties of an endospermic protein of maize associated with the Opaque-2 and Opaque-6 genes. Planta 167, 587–94.
Dixon, R.A., Lamb, C.J. (1990) Molecular communication in interactions between plants and microbial pathogens. Annu. Rev. Plant Phys. 41, 339–67.
Donini, G., Albano, M., Forlani, F., Maddaloni, M., Stasse, L., Motto, M. (1996) A novel dual-component promoter in plant tissues. Maydica 41, 91–5.
Endo, Y., Mitsui, K., Motizuchi, M., Tsurugi, K. (1996) The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 5908–12 (1987).
Endo, Y., Tsurugi, K. (1987) RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 8128–30.
Garcia-Olmedo, F., Salcedo, G., Sanchez-Monge, R., Hernandez-Lucas, C., Carmona, M.J., Lopez-Fando, J.J., Fernandez, J.A., Gomez, L., Royo, J., Garcia-Maroto, F., Castagnaro, A., Carbonero, P. (1992) In: Shewry, P.R. (ed) Barley, genetics, biochemistry, molecular biology and biotechnology, pp 335–50. CAB International.
Gupta, S.C., Asnani, V.L., Khare, B.P. (1970) Effect of the Opaque-2 gene in maize on the extent of infestation by Sitophylus orizae L. J. Stored Prod. Res. 6, 191–4.
Hain, R., Reif, H.J., Krause, E., Langebartels, R., Kindl, H., Vornam, B., Wiese, W., Schmeltzer, E., Schreier, P.H., Stoècker, R.H., Stenzel, K. (1993) Disease resistance results from foreign phytoalexin expression in a novel plant. Nature 361, 153–6.
Hartings, H., Lazzaroni, N., Marsan, P.A., Aragay, A., Thompson, R., Salamini, F., Di Fonzo, N., Palau, J., Motto, M. (1990) The b-32 protein from maize endosperm: characterization of genomic sequences encoding two alternative central domains. Plant Mol. Biol. 14, 1031–40.
Hartings, H., Lazzaroni, N., Rossi, V., Riboldi, G.R., Thompson, R., Salamini, F., Motto, M. (1995) Molecular analysis of opaque-2 alleles from Zea mays L. reveals the nature of mutational events and a presence of a hypervariable region in the 59 part of the gene. Genet. Res. Camb. 65, 11–19.
Hey, T.D., Hartley, M., Walsh, T.A. (1995) Maize ribosomeinactivating protein (b-32). Plant Physiol. 107, 1323–32.
Jach, G., Go rnhardt, B., Mundy, J., Logemann, J., Pinsdorf, E., Leah, R., Schell, J., Maas, C. (1995) Enhanced quantitative resistance against fungal disease by combinatorial expression of different barley antifungal proteins in transgenic tobacco. Plant J. 8, 97–109.
Kataria, H.R., Verma, P.R. (1992) Rhizoctonia solani damping-off and root rot in oilseed rape and canola. Crop Prot. 11, 8–13.
Lamb, C.J., Lawton, M.A., Dron, M., Dixon, R.A. (1989) Signal and transduction mechanisms for activation of plant defense against microbial attack. Cell 56, 215–24.
Lamb, C.J., Ryals, J.A., Ward, E.R., Dixon, R.A. (1992) Emerging strategies for enhancing crop resistance to microbial pathogens. Bio/Technology 10, 1436–45.
Leah, R., Tommerup, H., Svendsen, I.B., Mundy, J. (1991) Biochemical and molecular characterization of three barley seed proteins with antifungal properties. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 1564–73.
Lodge, J.K., Kaniewski, W.K., Tumer, N.E. (1991) Broad-spectrum virus resistance in transgenic plants expressing pokeweed antiviral protein. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 90, 7089–93 (1993).
Loesch, J.R., Foley, P.J., Cox, D.F. (1976) Comparative resistence of o2 and normal inbred lines of maize to ear-rotting pathogens. Crop Sci. 16, 841–2.
Logemann, J., Jach, G., Tommerup, H., Mundy, J., Schell, J. (1992) Expression of a barley ribosome-inactivating protein leads to increased fungal protection in transgenic tobacco plants. Bio/Technology 10, 305–8.
Lohmer, S., Maddaloni, M., Motto, M., Di Fonzo, N., Hartings, H., Salamini, F., Thompson, R. (1991) The maize regulatory locus Opaque-2 encodes a DNA-binding protein which activates the transcription of the b-32 gene. EMBO J. 10, 617–24.
Maddaloni, M., Barbieri, L., Lohmer, S., Motto, M., Salamini, F., Thompson, R. (1991) Characterization of an endospermspecific developmentally regulated protein synthesis inhibitor from maize seeds. J. Genet. Breed. 45, 377–80.
McKinney, H.H. (1923) Influence of soil temperature and moisture on infection on wheat seedling by Helmintosporium sativum. J. Agric. Res. 26, 195–217.
Mett, V.D., Lochhead, L.P., Reynolds, P.H.S. (1993) Coppercontrollable gene expression system for whole plants. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 90, 4567–71.
Murashige, T., Skoog, F. (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol. Plant 15, 473–97.
Ogoshi, A. (1987) Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and intraspecific groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 25, 125–43.
Oppenheim, A.B., Chet, I. (1992) Cloned chitinase in fungal plantpathogen control strategies. Trends Biotechnol. 10, 392–4.
Pastam, I., Fitzgerald, D. (1991) Recombinant toxins for cancer treatment. Science 254, 1173–6.
Roby, D., Broglie, K., Cressman, R., Biddle, P., Chet, I., Broglie, R. (1990) Activation of a bean chitinase promoter in transgenic tobacco plants by phytopathogenic fungi. Plant Cell 2, 999–1007.
Rogers, S.G., Horsch, R.B., Fraley, R.T. (1985) Gene transfer in plants: Production of transformed plants using Ti-plasmid vectors. Methods Enzymol. 118, 627–40.
SAS Institute (1985) SAS user's guide: Statistics. 5th Edition. SAS Inst., Inc., Raleigh, NC, USA.
Siebertz, B., Logemann, J., Willmitzer, L., Schell, J. (1989) Cis-Analysis of the wound-inducible promoter wun1 in transgenic tobacco plants and histochemical localization of its expression. Plant Cell 1, 961–8.
Soave, C., Tardani, L., Di Fonzo, N., Salamini, F. (1981) Zein level in maize endosperm depends on a protein under control of the opaque-2 and opaque-6 loci. Cell 27, 403–10.
Spooner, R.A., Lord, M.J. (1990) Immunotoxins: status and prospects. Trends Biotechnol. 8, 189–93.
Stirpe, F., Barbieri, L., Battelli, M.G., Soria, M., Lappi, D.A. (1992) Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants: present status and future prospects. Bio/Technology 10, 405–12.
Taylor, S., Massiah, A., Lomonossoff, G., Roberts, L.M., Lord, J.M., Hartley, M. (1994) Correlation between the activities of five ribosome-inactivating proteins in depurination of tobacco ribosomes and inhibition of tobacco mosaic virus infection. Plant J. 5, 827–35.
Walsh, T.A., Morgan, A.E., Hey, T.D. (1991) Characterization and molecular cloning of a proenzyme form of a ribosome inactivating protein from maize. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 23422–7.
Woloshuk, C.P., Meulenhoff, J.S., Sela-Burlage, M., van der Elzen, P.J.M., Cornelissen, B.J.C. (1991) Pathogen induced proteins with inhibitory activity toward Phytophtora infestans. Plant Cell 3, 619–28.
Wu, G., Shortt, B.J., Lawrence, E.B., Levine, E.B., Fitzsimmons, K.C., Shah, D.M. (1995) Disease resistance conferred by expression of a gene encoding H2O2-generating glucose oxidase in transgenic potato plants. Plant Cell 7, 1357–68.
Zhu, Q., Maher, E.A., Masoud, S., Dixon, R.A., Lamb, C.J. (1994) Enhanced protection against fungal attack by constitutive coexpression of chitinase and glucanase genes in transgenic tobacco. Bio/Technology 12, 807–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MADDALONI, M., FORLANI, F., BALMAS, V. et al. Tolerance to the fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani AG4 of transgenic tobacco expressing the maize ribosome-inactivating protein b-32. Transgenic Res 6, 393–402 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018435417740
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018435417740