Abstract
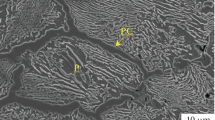
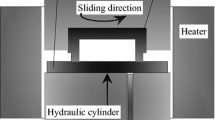
Ball-on-flat friction experiments between two austenitic stainless steel antagonists in sliding contact are carried out under very low loads and in two liquid environments, namely demineralized water and methanol. The wear debris produced during long-duration tests are characterized by different techniques such as X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and Mössbauer spectroscopy. Martensite is observed as a dominant phase in the wear debris but other phases have been also identified. In the debris produced under demineralized water, there is significant contribution of a second phase, which is poorly crystallized and which was identified as the hydrous iron oxide called ferrihydrite. In the debris produced under methanol, there is a remaining amount of austenite that is not transformed into martensite, and the presence of ferrihydrite has been also detected in very small quantities. The formation of the martensitic debris which occurs from the beginning of the wear tests supports the fact that under our experimental conditions the main damaging mode is abrasive wear by hard particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Fayeulle and D. Treheux, Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 19/20 (1987) 216.
R. Wei, P.J. Wilbur, W.S. Sampath, D.L. Williamson, Y. Qu and L. Wang, J. Tribol. 112 (1990) 27.
A. Van Herpen, B. Reynier and C. Phalippou, J. Phys. IV (France) 8 (1998) 181.
S. Fayeulle, in: Wear of Materials, ASME Proc., ed. K.C. Ludema (New York, 1987) p. 3.
S. Fayeulle, in: Defect and Diffusion Forum, Vol. 57-58, ed. F.H. Wöhlbier (Aedermannsdorf, 1988) p. 327.
C. Brin, Thesis, University of Poitiers, France (1999).
J.P. Rivière, C. Brin, J.P. Villain and R. Cauvin, J. Phys. IV (France), accepted.
S. Herjo, Y. Tomata and M. Ono, in: The 5th Int. Conf. on Residual Stresses, Vol. 1, eds. T. Ericsson, M. Odén and A. Andersson (Linköping, 1997) p. 46.
P. Goudeau, K.F. Badawi, A. Naudon, M. Jaulin, N. Durand, L. Bimbault and V. Branger, J. Phys. IV (France) 6 (1996) 187.
J.P. Eymery, J. Phys. IV (France) 2 (1992) 211.
G.W. Simmons and H. Leidheiser, in: Applications of Mössbauer Spectrometry, Vol. 1, ed. R.L. Cohen (New York, 1976) p. 85; E. Murad and J.H. Johnson, in: Mössbauer Spectroscopy Applied to Inorganic Chemistry, Vol. 2, ed. G.L. Long (Plenum, New York, 1987) p. 507.
F.V. Chukhov, B.B. Zvyagrin, A.I. Gorshkov, L.P. Yernilova and V.V. Balaskova, Int. Geology Rev. 16 (1974) 1131.
B. Cho, K. Fujita, K. Oda and H. Ino, Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 76 (1993) 415; E. Murad and U. Schwertmann, Am. Mineral. 65 (1980) 1044.
N. Bergeon, C. Esnouf, G. Guénin, Y. Robach and L. Porte, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 16 (1997) 1135; W. Shiao and W. Shunhua, Prog. Natural Sci. 7 (1997) 469.
J.F. Marco, M. Gracia, J.R. Gancedo, M.A. Martin-Luengo and G. Joseph, Corros. Sci. 42 (2000) 753.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brin, C., Rivière, JP., Eymery, JP. et al. Structural Characterization of Wear Debris Produced During Friction Between Two Austenitic Stainless Steel Antagonists. Tribology Letters 11, 127–132 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016612718139
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016612718139