Abstract
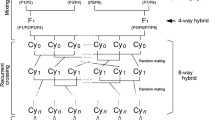
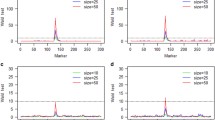
Simple line crosses, for example, backcross and F2, are commonly used in mapping quantitative trait loci (QTL). However, these simple crosses are rarely used alone in commercial plant breeding; rather, crosses involving multiple inbred lines or several simple crosses but connected by shared inbred lines may be common in plant breeding. Mapping QTL using crosses of multiple lines is more relevant to plant breeding. Unfortunately, current statistical methods and computer programs of QTL mapping are all designed for simple line crosses or multiple line crosses but under a regular mating system. It is not straightforward to extend the existing methods to handle multiple line crosses under irregular and complicated mating designs. The major hurdle comes from irregular inbreeding, multiple generations, and multiple alleles. In this study, we develop a Bayesian method implemented via the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm for mapping QTL using complicated multiple line crosses. With the MCMC algorithm, we are able to draw a complete path of the gene flow from founder alleles to their descendents via a recursive process. This has greatly simplified the problem caused by irregular mating and inbreeding in the mapping population. Adopting the reversible jump MCMC algorithm, we are able to simultaneously search for multiple QTL along the genome. We can even infer the posterior distribution of the number of QTL, one of the most important parameters in QTL study. Application of the new MCMC based QTL mapping procedure is demonstrated using two different mating designs. Design I involves two inbred lines and their derived F1, F2, and BC populations. Design II is a half-diallel cross involving three inbred lines. The two designs appear different, but can be handled with the same robust computer program.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bink, M.C.A.M., L.L.G. Janss &; R.L. Quaas, 2000. Markov chain Monte Carlo for mapping a quantitative trait locus in outbred populations. Genet. Res. Camb. 75: 231-241.
Brooks, S.P. &; P. Giudici, 1998. Convergence assessment for reversible jump MCMC simulations. Manuscript available at http://www.statslab.cam.ac.uk/~mcmc/pages/list.html.
Green, P.J., 1995. Reversible jump Markov chain Monte Carlo computation and Bayesian model determination. Biometrika 82: 711-732.
Gelman, A., J.B. Carlin, H.S. Stern &; D.B. Rubin, 1995. Bayesian Data Analysis. Chapman &; Hall, London, UK.
Geman, S. &; D. Geman, 1984. Stochastic relaxation, Gibbs distributions, and the Bayesian restoration of images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Machine Intell. 6: 721-741.
Haley, C.S. &; S.A. Knott, 1992. A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity 69: 315-324.
Hoeschele, I., P. Uimari, F.E. Grignola, Q. Zhang &; K.M. Gage, 1997. Advances in statistical methods to map quantitative trait loci in outbred populations. Genetics 147: 1445-1457.
Heath, S.C., 1997. Markov chain Monte Carlo segregation and linkage analysis for oligogenic models. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 61: 784-760.
Hastings, W.K., 1970. Monte Carlo sampling methods using Markov chains and their applications. Biometrika 57: 97-109.
Jansen, R.C. &; P. Stam, 1994. High resolution of quantitative traits into multiple loci via interval mapping. Genetics 136: 1447-1455.
Kao, C.H., Z.-B. Zeng &; R.D. Teasdale, 1999. Multiple interval mapping for quantitative trait loci. Genetics 152: 1203-1216.
Lander, E.S. &; D. Botstein, 1989. Mapping Medelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121: 185-199.
Lynch, M. &; B. Walsh, 1998. Genetics and Analysis of Quantitative Traits. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts.
Liu, Y. &; Z.-B. Zeng, 2000. A general mixture model approach for mapping quantitative trait loci from diverse cross designs involving multiple inbred lines. Genet. Res. Camb. 75: 345-355.
Lee, J.K. &; D.C. Thomas, 2000. Performance of Markov chain Monte Carlo approaches for mapping genes in oligogenic models with an unknown number of loci. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67: 1232-1250.
Muranty, H., 1996. Power of tests for quantitative trait loci detection using full-sib families in different schemes. Heredity 76: 156-165.
Nobile, A. &; P.J. Green, 2000. Bayesian analysis of factorial experiments by mixture modeling. Biometrika 87: 15-35.
Rebai, A. &; B. Goffinet, 1993. Power of tests for QTL detection using replicated progenies derived from a diallel cross. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86: 1014-1022.
Rebai, A. &; B. Goffinet, 2000. More than QTL mapping with diallel designs. Genet. Res. Camb. 75: 243-247.
Satagopan, J.M., B.S. Yandell, M.A. Newton &; T.G. Osborn, 1996. A Bayesian approach to detect quantitative trait loci using Markov chain Monte Carlo. Genetics 144: 805-816.
Satagopan, J.M. &; B.S. Yandell, 1998. Bayesian model determination for quantitative trait loci. Manuscript available at ftp://ftp.stat.wisc.edu/pub/yandell/revjump.html/.
Stephens, D.A. &; R.D. Fisch, 1998. Bayesian analysis of quantitative trait locus data using reversible jump Markov chain Monte Carlo. Biometrics 54: 1334-1347.
Sillanpää, M.J. &; E. Arjas, 1998. Bayesian mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci from incomplete inbred line cross data. Genetics 148: 1373-1388.
Sillanpää, M.J. &; E. Arjas, 1999. Bayesian mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci from incomplete outbred offspring data. Genetics 151: 1605-1619.
Sobel, E. &; K. Lange, 1996. Descent graphs in pedigree analysis: applications to haplotyping, location scores, and marker-sharing statistics. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 58: 1323-1337.
Thompson, E.A., 1994. Monte Carlo likelihood in genetic mapping. Statist. Sci. 9: 355-366.
Uimari, P. &; I. Hoeschele, 1997. Mapping linked quantitative trait loci using Bayesian analysis and Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms. Genetics 146: 735-743.
Uimari, P. &; M.J. Sillanpää, 2001. Bayesian oligogenic analysis of quantitative and qualitative traits in general pedigrees. Genet. Epidemiol. 21: 224-242.
Xu, S., 1995. A comment on the simple regression method for interval mapping. Genetics 141: 1657-1659.
Xu, S., 1998. Mapping quantitative trait loci using multiple families of line crosses. Genetics 148: 517-524.
Xu, S. &; N. Yi, 2000. Mixed model analysis of quantitative trait loci. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 14542-14547.
Yi, N. &; S. Xu, 2000a. Bayesian mapping of quantitative trait locifor complex binary traits. Genetics 155: 1391-1403.
Yi, N. &; S. Xu, 2000b. Bayesian mapping of quantitative trait loci under the identity-by-descent-based variance component model. Genetics 156: 411-422.
Yi, N. &; S. Xu, 2001. Bayesian mapping of quantitative trait loci under complicated mating designs. Genetics 157: 1759-1771.
Zeng, Z.-B., 1994. Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136: 1457-1468.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, N., Xu, S. Linkage Analysis of Quantitative Trait Loci in Multiple Line Crosses. Genetica 114, 217–230 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016296225065
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016296225065