Abstract
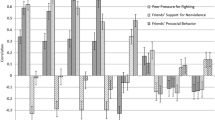
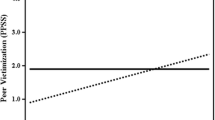
This study describes the development and initial validation of the Peer-report Measure of Internalizing and Externalizing Behavior (PMIEB), a peer-nomination inventory that assesses internalizing (anxiety, depression, somatic complaints) and externalizing (aggression, delinquency, hyperactivity/attentional problems) psychopathology in school-aged children. Peer nomination inventories such as the PMIEB can provide an important perspective on children's behavioral and emotional functioning, for purposes ranging from descriptive psychopathology to outcome assessments of school-based treatment programs. However, although there currently are peer-nomination inventories for several specific domains of behavioral and emotional problems, the PMIEB represents the first broadband peer-nomination assessment instrument that can efficiently provide peer-report information across a wide range of child emotional and behavioral problems. Results of this study provide support for the reliability and validity of both broadband PMIEB subscales, as well as 5 of the 6 narrowband PMIEB subscales.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Integrative guide for the 1991 CBCL/4–18, YSR, and TRF profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. (1983). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist and revised Child Behavior Profile. Burlington, London: Queen City Printers.
Achenbach, T. M., McConaughy, S. H., & Howell, C. T. (1987). Child/adolescent behavioral and emotional problems: Implications of cross-informant correlations for situational specificity. Psychological Bulletin, 101(2), 213–232.
American Guidance Service. (1992). The behavior assessment system for children. Circle Pines, MN: Author.
American Psychiatric Association. (1987). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (3rd ed., Rev.). Washington, DC: Author.
Barkley, R. A. (1998). Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A handbook for diagnosis and treatment (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford.
Bollen, K. A. (1989). Structural equations with latent variables. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
Browne, M. W., & Cudeck, R. (1993). Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In K. A. Bollen & J. S. Long (Eds.), Testing structural equation models. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Catron, T., & Weiss, B. (1994). The Vanderbilt school-based counseling program. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 2, 247–253.
Cicchetti, D., & Toth, S. L. (1991). A developmental perspective on internalizing and externalizing disorders. In D. Cicchetti & S. L. Toth (Eds.), Internalizing and externalizing expressions of dysfunction: Rochester symposium on developmental psychopathology (pp. 1–20). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Clark, L. A., & Watson, D. (1995). Constructing validity: Basic issues in objective scale development. Psychological Assessment, 7, 309–319.
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika, 16, 297–334.
Eron, L. D., Walder, L. O., & Lefkowitz, M. M. (1971). Learning of aggression in children. Boston: Little, Brown & Co.
Floyd, F. J., & Widaman, K. F. (1995). Factor analysis in the development and refinement of clinical assessment instruments. Psychological Assessment, 7, 286–299.
Foster, S. L., Inderbitzen, H. M., & Nangle, D. W. (1993). Assessing acceptance and social skills with peers in childhood: Current issues. Behavior Modification, 17, 255–286.
Garber, J., & Hilsman, R. (1992). Cognitions, stress, and depression in children and adolescents. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 1, 129–167.
Howell, D. C. (1982). Statistical methods for psychology. Boston: Duxbury.
Huesmann, L. R., Eron, L. D., Guerra, N. G., & Crawshaw, V. B. (1994). Measuring children's aggression with teachers' predictions of peer nominations. Psychological Assessment, 6, 329–336.
Jöreskog, K. G., & Sörbom, D. (1999). LISREL 8.3. Chicago: Scientific Software.
Kline, R. B. (1998). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. New York: Guilford.
Krehbiel, G. G., & Milich, R. (1986). Issues in the assessment and treatment of socially rejected children. Advances in Behavioral Assessment of Children and Families, 2, 249–270.
Lefkowitz, M. M., & Tesiny, E. P. (1980). Assessment of childhood depression. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 48(1), 43–50.
Masten, A., Morison, P., & Pelligrini, D. (1985). A revised class play method of peer assessment. Developmental Psychology, 21, 523–533.
Ollendick, T. H. (1995). Assessment of anxiety and phobic disorders in children. In K. D. Craig & K. S. Dobson (Eds.), Anxiety and depression in adults and children (pp. 99–124). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Panak, W. F., & Garber, J. (1992). Role of aggression, rejection, and attributions in the prediction of depression in children. Development and Psychopathology, 4, 145–165.
Patterson, G. R., & Yoerger, K. (1997). A developmental model for late-onset delinquency. In O. D. Osgoode (Ed.), Motivation and delinquency (pp. 119–177). Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press.
Pekarik, E. G., Prinz, R. J., Liebert, E. D., Weintraub, S., & Neale, J. M. (1976). The pupil evaluation inventory: A sociometric technique for assessing children's social behavior. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 4, 83–97.
Prinz, R. J., Swan, G., Weintraub, S., & Neale, J. (1978). ASSESS: Adjustment scales for sociometric evaluation of secondary school students. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 6, 493–501.
Quiggle, N. L., Garber, J., Panak, W. F., & Dodge, K. A. (1992). Social information processing in aggressive and depressed children. Child Development, 63, 1305–1320.
Realmuto, G. M., August, G. J., & Hektner, J. M. (2000). Predictive power of peer behavioral assessment for subsequent maladjustment in community samples of disruptive and nondisruptive children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 41, 181–190.
Sabornie, E. J., & Ellis, E. S. (1987). Sociometry for teachers of behaviorally disordered students. In R. B. Rutherford & C. M. Nelson (Eds.), Severe behavior disorders of children and youth (pp. 28–40). Boston: Little, Brown & Co.
Safran, S. P. (1995). Peer perceptions of emotional and behavioral disorders: What are students thinking? Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 3, 66–75.
Schaughency, E. A., McCone, D., & Covey, A. (1989). A preliminary evaluation of peer assessment of inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. Paper presented at the 23rd annual meeting of the Association for the Advancement of Behavior Therapy, Washington, DC.
Schaughency, E. A., & Rothlind, J. (1991). Assessment and classification of attention deficit hyperactive disorders. School Psychology Review, 20(2), 187–202.
Shaffer, D., Lucas, C. P., & Richters, J. E. (1999). Diagnostic assessment in child and adolescent psychopathology. New York: Guilford.
Weiss, B., & Catron, T. (1994). The specificity of comorbidity of aggression and depression in children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 22, 389–401.
Weiss, B., Catron, T., Harris, V., & Phung, T. (1999). The effectiveness of traditional child psychotherapy. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 67, 82–94.
Williams, B. T. R., & Gilmour, J. D. (1994). Sociometry and peer relationships. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 35, 997–1013.
Younger, A. J., Schneider, B. H., & Daniels, T. (1991). Aggression and social withdrawal as viewed by children's peers: Conceptual issues in assessment and implications for intervention. Journal of Psychiatry and Neuroscience, 16, 139–145.
Younger, A. J., Schwartzman, A. E., & Ledingham, J. E. (1986). Age-related differences in children's perceptions of social deviance: Changes in behavior or perspective? Developmental Psychology, 22, 531–542.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiss, B., Harris, V. & Catron, T. Development and Initial Validation of the Peer-Report Measure of Internalizing and Externalizing Behavior. J Abnorm Child Psychol 30, 285–294 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015158930705
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015158930705