Abstract
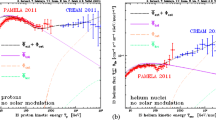
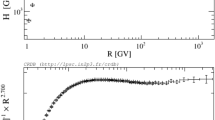
The isotopic abundances of the Galactic cosmic radiation measured in the Heliosphere provide unique information on acceleration, propagation modes and containment times in the Galactic magnetic fields. Nuclear interactions with interstellar matter lead to observable γ-radiation production and, thus, to direct information on cosmic ray distribution throughout the Galaxy and its magnetic halo. The COSPIN High Energy Telescope (HET) has excellent isotopic resolution from hydrogen to nickel over the ten year period of Ulysses in space. Based on our recent work, we discuss the implications for modeling the acceleration and propagation of the cosmic radiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders, E. and Grevesse, N.: 1989, ‘Abundances of the Elements: Meteoritic and Solar’, Cosmochim. Acta 53, 197–214.
Cassé, M. and Paul, J. A.: 1982, ‘On the Stellar Origin of the 22Ne Excess in Cosmic Rays’, Astrophys. J. 258, 860–863.
Connell, J. J.: 1998, ‘Galactic Cosmic Ray Confinement Time: Ulysses HET Measurements of the Secondary Radio-Nuclide 10Be’, Astrophys. J. Lett. 502, L59–62.
Connell, J. J.: 2001, ‘Cosmic Ray Composition as Observed by Ulysses’, Space Sci. Rev., in press.
Connell, J. J., DuVernois, M. A., and Simpson, J. A.: 1998, ‘Galactic Cosmic Ray 36Cl Clock: Ulysses HET Results’, Astrophys. J. Lett. 509, L97–100.
Connell, J. J. and Simpson, J. A.: 1997a, ‘High Resolution Measurements of the Isotopic Composition of Galactic Cosmic Ray C N O Ne Mg and Si from the Ulysses HET’, Proc. 25th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf., Durban 3, 381–384.
Connell, J. J. and Simpson, J. A.: 1997b, ‘Isotopic Abundances of Fe and Ni in Galactic Cosmic Ray Sources’, Astrophys. J. Lett. 475, L61–64.
Connell, J. J. and Simpson, J. A.: 1999, ‘Ulysses HET Measurements of Electron-capture Secondary Isotopes: Testing the Role of Cosmic Ray Reacceleration’, Proc. 26th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf., Salt Lake City 3, 33–36.
DuVernois, M. A.: 1997, ‘Galactic Cosmic-Ray Manganese: Ulysses High Energy Telescope Results’, Astrophys. J. 481, 241–252.
DuVernois, M. A., Simpson, J. A., and Thayer, M. R.: 1996, ‘Interstellar Propagation of Cosmic Rays: Analysis of the Ulysses Primary and Secondary Elemental Abundances’, Astron. Astrophys. 316, 555–563.
Silberberg, R., Tsao, C. H., and Shapiro, M. M.: 1998, in M. M. Shapiro, R. Silverberg, and J. P. Wefel (eds), ‘A Weak Reacceleration Model for Cosmic Rays that Fits both Heavy Ions and Electrons’, Towards the Millennium in Astrophysics, (World Scientific, Singapore) pp. 227–240.
Simpson, J. A. et al.: 1992, ‘The Ulysses Cosmic Ray and Solar Particle Investigation’, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 92, 365–399.
Simpson, J. A. and Connell, J. J.: 1998, ‘Cosmic Ray 26Al and Its Decay in the Galaxy’, Astrophys. J. Lett. 497, L85–88.
Strong, A. W. and Moskalenko, I. V: 1998, ‘Propagation of Cosmic Ray Nucleons in the Galaxy’, Astrophys. J. 509, 212–228.
Truran, J. W. and Arnett, W. D.: 1971, ‘Explosive Nucleosynthesis and the Composition of Metal-Poor Stars’, Astron. Space Sci. 11, 430–442.
Wuosmaa, A. H. et al.: 1998, ‘The β + Decay Partial Half Life of 54Mn and Cosmic Ray Chronometry’, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2085–2088.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simpson, J., Connell, J. Cosmic Ray Isotopic Composition Studies with the Ulysses High Energy Telescope: Implications for Origin and Distribution in the Galaxy. Space Science Reviews 97, 337–341 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011897521750
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011897521750