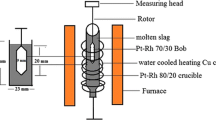
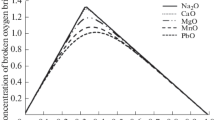
Abstract
In view of the urgent need for an extrapolation of the thermochemical and thermophysical properties of multicomponent metallurgical slags, a semiempirical slag model has been developed at the Department of Metallurgy, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm. In this model, Temkin's description of ionic melts is coupled with Lumsden's total dissociation of polymerized silicate and aluminate species. The excess Gibbs energies are described by means of Redlich–Kister polynomials. The model parameters that correspond to binary silicate systems are generated from available experimental data and used consequently to describe systems of higher order. The model is successful in extrapolating the thermodynamic data for a number of ternary and higher-order silicate systems. In view of the uncertainties in the literature data in the case of the Al2O3–SiO2system, Knudsen cell mass spectrometric measurements are conducted and the model parameters are assigned on the basis of these results. This enables reasonable predictions of the thermodynamic properties of multicomponent aluminosilicate slags. The model description is also used in linking thermodynamic data with slag viscosities. The viscosities of ternary silicates could be predicted from the binary viscosities and the thermodynamic data.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Masson, C.R., Thermodynamics and Constitution of Silicate Slags, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1972, vol. 210, pp. 89-96.
Hillert, M., Jansson, B., Sundman, B., and Ågren, J., A Two-Sublattice Model Molten Solutions with Different Tendency for Ionization, Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16, pp. 261-266.
Gaye, H. and Welfringer, J., Modeling of the Thermodynamic Properties of Complex Metallurgical Slags, in Second Int. Symp. on Metallurgical Slags and Fluxed, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, Nevada: AIME, 1984, pp. 357-375.
Lumsden, J., The Thermodynamics of Liquid Iron Silicates, Physical Chemistry Proceedings: Metallurgy, Part 1, Pittsburgh: Interscience, 1959, pp. 165-205.
Temkin, M., Mixtures of Fused Salts as Ionic Solutions, Zh. Fiz. Khim., 1945, vol. 20, pp. 411-420.
Richardson, F.D., The Solutions of Metallurgist-Retrospect and Prospect, Physical Chemistry Proceedings: Metallurgy, Part 1, Pittsburgh: Interscience, 1959, pp. 1-26.
Bygdén, J., Du Sichen, and Seetharaman, S., Thermodynamic Activities of FeO in CaO-FeO-SiO2 Slags, Steel Res., 1994, vol. 10, pp. 421-428.
Björkvall, J., Du Sichen, and Seetharaman, S., Thermodynamic Description of CaO-FeO-SiO2 and CaO-MnO-SiO2 Melts, High Temp. Mater. Proc., 1999, vol. 18, pp. 253-268.
Björkvall, J., Thermodynamic Study of Silicate and Aluminate Melts-A Model Approach, Lic. Thesis, Dept. Metall., Royal Inst. Technol., Stockholm, 1998.
Björkvall, J. and Stolyarova, V.L., A Knudsen Cell Mass Spectrometric Study of Al2O3-SiO2 Melts, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 2000 (in press).
Seetharaman, S. and Du Sichen, A Model for Estimation of Viscosities of Complex Metallic and Ionic Melts, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1994, vol. 25, pp. 589-595.
Sawamura, K., Activity of Lime in Blast-Furnace Type Slags, Tetsu to Hagane, 1962, vol. 2, pp. 219-225.
Sanbongi, K. and Omori, Y., Activities of Silica and Alumina in Molten CaO-SiO2-Al2O3 Slags, Physical Chemistry: Metallic Solutions and Intermetallic Compounds, II, London, 1959, pp. 1-10.
Omori, Y. and Sanbongi, K., Activity of CaO in Slag CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 System, J. Met. Inst. Jpn., 1961, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 139-143.
Stolyarova, V.L., Shornikov, S.I., Ivanov, G.G., and Shultz, M.M., High Temperature Mass Spectrometric Study of Thermodynamic Properties of the CaO-SiO2 System, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1991, vol. 138, pp. 3710-3714.
Rein, H.R. and Chipman, J., Activities in the Liquid Solution SiO2-CaO-MgO-Al2O3 at 1600°C, Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME, 1965, vol. 233, pp. 415-425.
Carter, P.T. and Macfarlane, T., Thermodynamics of Slag Systems, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1957, vol. 185, pp. 54-66.
Sharma, R.A. and Richardson, F.D., The Solubility of Calcium Sulphide and Activities in Lime-Silica Melts, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1962, vol. 200, pp. 373-379.
Kay, D.A.R. and Taylor, C.R., Activities of Silica in the Lime-Alumina-Silica System, J. Trans. Faraday Soc., 1960, vol. 56, pp. 1372-1386.
Fulton, J.C. and Chipman, J., Slag-Metal-Graphite Reactions and the Activity of Silica in Lime-Alumina-Silica Slags, Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME, 1954, vol. 200, pp. 1136-1146.
Slag Atlas, Edited by the Verein Deutscher Eisenhüttenleute, Düsseldorf: Stahleisen, 1995, 2nd ed.
Schumann, R. and Ensio, P.J., Thermodynamics of Iron-Silicate Slags: Slags Saturated with Gamma Iron, Trans. AIME, 1951, vol. 191, pp. 401-411.
Bodsworth, C., The Activity of Ferrous Oxide in Silicate Melts, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1959, vol. 193, pp. 13-24.
Ban-Ya, S., Chiba, A., and Hilkosaka, A., Thermodynamics of FetO-MxOy (MxOy = CaO, SiO2, TiO2, Al2O3) Binary Melts in Equilibrium with Solid Iron, Tetsu to Hagane, 1980, vol. 66, no. 10, pp. 1484-1493.
Van Wijngaarden, M. and Dippenaar, R., The Use of Zirconia-Based Solid Electrolytes for the Rapid Determination of Iron Oxide Activities in Iron-and Steel-Making Slags, J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall., 1989, vol. 86, no. 11, pp. 443-453.
Wanibe, Y., Yamauchi, Y., Kawai, K., and Sakao, H., Electrochemical Measurement of the Activity of Iron Oxide in FeO-SiO2 Liquid Slags, Arch. Eisenhutten., 1973, vol. 44, no. 9, pp. 711-717.
Fujita, H. and Maruhashi, S., Activities in the Iron-Oxide Silica Slags, Tetsu to Hagane, 1969, vol. 55, pp. 249-260.
Distin, P.A., Whiteway, S.G., and Masson, C.R., Thermodynamics and Constitution of Ferrous Silicate Melts, Can. Metall. Quart., 1971, vol. 10, pp. 73-78.
Takeda, Y. and Yazawa, A., Nippon Kogyokaishi, 1980, vol. 96, pp. 901-906.
Iwase, M., Yamada, N., Nishida, K., and Ichise., E., Rapid Determinations of the Activities in CaO-FexO Liquid Slags by Disposable Electrochemical Oxygen Probes, Trans. Iron Steel Soc. AIME, 1984, vol. 4, pp. 69-75.
Fujita, H., Iritani, Y., and Maruhashi, S., Activities in the Iron-Oxide Lime Slags, Tetsu to Hagane, 1968, vol. 54, pp. 359-370.
Kambayashi, S. and Kato, E., A Thermodynamic Study of (Magnesium Oxide + Silicon Dioxide) by Mass-Spectrometry, J. Chem. Thermodyn., 1983, vol. 15, pp. 701-707.
Von Schenck, H., Frohberg, M.G., and El Gammal, T., Bestimmung der Aktivität des Manganoxyduls in flussigen Manganoxydul-Kieselsäure-Schlacken bei 1550°C, Arch. Eisenhutten., 1961, vol. 32, pp. 509-511.
Abraham, K.P., Davies, M.W., and Richardson, F.D., Activities of Manganese Oxide in Silicate Melts, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1960, vol. 196, pp. 82-89.
Mehta, S.R. and Richardson, F.D., Activities of Manganese Oxide and Mixing Relationships in Silicate and Aluminate Melts, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1965, vol. 203, pp. 524-528.
Rao, B.K.D.P. and Gaskell, D.R., The Thermodynamic Properties of Melts in the System MnO-SiO2, Metall. Trans. B, 1981, vol. 12, pp. 311-317.
Glasser, F.P., The system MnO-SiO2, Am. J. Sci., 1958, vol. 256, no. 6, pp. 398-412.
Sharma, R.A. and Richardson, F.D., Activities in Lime-Alumina Melts, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1961, vol. 198, pp. 386-390.
Cameron, J., Gibbons, T.B., and Taylor, J., Calcium Sulphide Solubilities and Lime Activities in the Lime-Alumina-Silica System, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1966, vol. 204, pp. 1223-1228.
Kor, G.J.W. and Richardson, F.D., Sulfur in Lime-Alumina Mixtures, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1968, vol. 206, pp. 700-704.
Edmunds, D.M. and Taylor, J., Reaction CaO + 3C = CaC2 + CO and Activity of Lime in CaO-Al2O3-CaF2 System, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1972, vol. 210, pp. 280-283.
Allibert, M., Chatillon, C., Jacob, K.T., and Lourtau, R., Mass-Spectrometric and Electrochemical Studies of Thermodynamic Properties of Liquid and Solid Phases in the System CaO-Al2O3, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1981, vol. 64, pp. 307-314.
Hino, M., Thermodynamics of Phosphorus in Carbon-Saturated Manganese-Based Alloys, CAMP-ISIJ, 1994, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 40-41.
Sharma, R.A. and Richardson, F.D., Activities of Manganese Oxide, Sulfide Capacities, and Activity Coeffi-cients in Aluminate and Silicate Melts, Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME, 1965, vol. 233, pp. 1587-1592.
Jacob, K.T., Revision of Thermodynamic Data on MnO-Al2O3 Melts, Can. Metall. Quart., 1981, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 89-92.
Shornikov, S.I., Stolyarova, V.L., and Shultz, M.M., High Temperature Mass Spectrometric Study of 3Al2O3 · 2SiO2, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 1994, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 478-480.
Zaitzev, A.I., Litvina, A.D., and Mogutnov, B.M., Thermodynamic Properties of Mullite 3Al2O3 · 2SiO2, Neorg. Mater., 1995, vol. 31, no. 6, pp. 768-772.
Dhima, A., Stafa, B., and Allibert, M., Activity Measurements in Steel-Making-Related Oxide Melts by Differential Mass-Spectrometry, High Temp. Sci., 1986, vol. 21, pp. 143-159.
Hillert, M., Sundman, B., and Xizhen Wang, A Thermodynamic Evaluation of the Al2O3-SiO2 System, TRITA-MAC-0402 Materials Research Center, Stockholm: Royal Inst. Technol., 1989.
Klug, F.J., Prochazka, S., and Doremus, R.H., Alumina-Silica Phase Diagram in the Mullite Region, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1987, vol. 70, no. 10, pp. 750-759.
Ogura, T., Fujiwara, R., Mochizuki, R., Kawamoto, Y., Oishi, T., and Iwase, M., Activity Determinator for the Automatic Measurements of Chemical Potentials of FeO in Metallurgical Slags, Metall. Trans. B, 1992, vol. 23, pp. 459-466.
Ban-Ya, S. and Shim., J.-D., Application of the Regular Solution Model for the Equilibrium of Distribution of Oxygen between Liquid Iron and Steelmaking Slags, Can. Metall. Quart., 1982, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 319-328.
Fujita, H. and Maruhashi, S., Equilibrium between FeO-MnO-SiO2 Slags and Molten Iron, Tetsu to Hagane, 1970, vol. 56, no. 7, pp. 830-854.
Sommerville, D., Ivanchev, I., and Bell, H.B., Activity in Melts Containing FeO, MnO, Al2O3, and SiO2, Proc. Int. Symp. Metall. Chem. Application in Ferrous Metallurgy, Sheffield: Iron and Steel Inst., 1971, pp. 23-25.
Ban-Ya, S., Hino, M., and Yuge, N., Activity of the Constituents in FeO-SiO2-MnO Slags in Equilibrium with Solid Iron, Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1985, vol. 71, pp. 853-860.
Fischer, W.A. and Bardenheuer, P.W., Die Gleichgewichte zwischen mangan-, aluminium-und sauerstoff-haltigen Eisenschmelzen und ihren Schlacken im Mangan(II)-Oxydtiegel bei 1530 bis 1700°C, Arch. Eisenhutten., 1968, vol. 39, pp. 637-643.
Maruhashi, S., Equilibrium between FeO-MnO-Al2O3 Slags and Molten Iron, Tetsu to Hagane, 1971, vol. 57, pp. 891-902.
Wasastjema, J.A., On the Theory of the Heat of Formation of Solid Solutions, Soc. Sci. Fenn. Commun. Phys. Math., 1949, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 1-13.
Ji, F., Studies on Viscosities of Some Multicomponent Slags, Ph. D. Thesis, Dept. Metall., Royal Inst. Technol., Stockholm, 1999.
Licko, T. and Danek, V., Viscosity and Structure of Melts in the System CaO-MgO-SiO2, Phys. Chem. Glasses, 1986, vol. 27, pp. 22-26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Björkvall, J., Sichen, D., Stolyarova, V. et al. A Model Description of the Thermochemical Properties of Multicomponent Slags and Its Application to Slag Viscosities. Glass Physics and Chemistry 27, 132–147 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011332410674
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011332410674