Abstract
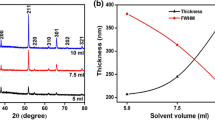
Fluorine-doped tin oxide thin films with amorphous/crystal mixed phases were deposited on silicon and quartz sheets by an ultrasonic spraying method and investigated with XPS, XRD, AFM and TEM techniques. The XRD spectra and the results of TEM analysis show that nanoscale amorphous clusters were formed within the grain boundary region. At room temperature, electron transportation is predominantly limited by amorphous defect scattering of the crystal grain boundary region. The minimum electrical resistivity 4.0×104Ωcm was obtained through decreasing the amorphous phase fraction and the preferred orientation arrangement of the crystal grains. A 0.8-eV shift exists between the tin 3d binding energy in thin films having the preferred crystallite orientation with (1 1 0) plane parallel to the substrate and that with the (2 0 0) plane parallel to the substrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. K. Fang, F. Y. Chen and J. D. Hwang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 62 (1993) 490.
A. Subrahmanyam, V. Vasu, P. Santanaraghavan and J. Kumar, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 14 (1992) 365.
H. Cachet, A. Messad, M. Froment and J. Bruneaux, Proc. SPIE 1729 (1992) 114.
M. D. Giulio, D. Manno and G. Micocci, Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 31 (1993) 235.
A. Messad, J. Bruneaux and H. Cachet, J. Mater. Sci. 29 (1994) 5095.
Y. Kobayashi, M. Okamoto and A. Tomita, ibid. 31 (1996) 6125.
H. Nedo, M. Sakai and Y. Watanabe, Appl. Phys. Lett. 62 (1993) 559.
K. Itoyama, J. Electrochem. Soc. 126 (1979) 691.
R. Pommier, C. Gril and J. Marucchi, Thin Solid Films 77 (1981) 91.
D. V. Morgan, Y. H. Aliyu and R. W. Bunce, ibid. 312 (1998) 268.
E. Shanthi, A. Banerjee and K. L. Chopra, ibid. 88 (1982) 93.
E. Shanthi, A. Banerjee and V. Dutta, J. Appl. Phys. 53 (1982) 1615.
D. H. Zhang and H. L. Ma, Appl. Phys. A 62 (1996) 487.
G. Sanon, R. Rup and A. Mansingh, Thin Solid Films 190 (1990) 287.
S. P. Singh and R. Thangaraj, ibid. 117 (1984) 95.
R. C. Weast (ed.) “Handbook of Physical Chemistry”, 63rd edn (CRC Press, Boca Roton, USA, 1982).
Seon-Soon Kim, Se-Young Choi and Chan-Gyung Park, Thin Solid Films 347 (1999) 155.
T. J. Ghuang, C. R. Brundle and D. W. Rice, Surf. Sci. 59 (1979) 413.
H. Feng, S. J. Laverty and P. Maguire, J. Electrochem. Soc. 143 (1996) 2048.
H. L. Ma and D. H. Zhang, Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 40 (1996) 371.
P. G. Lecomber and W. E. Spear, Phys. Rev. Lett. 25 (1970) 509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z.B., Cui, R.Q., Hadi, G.M. et al. Mixed phase F-doped SnO2 film and related properties deposited by ultrasonic spraying. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 12, 417–421 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011247017682
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011247017682