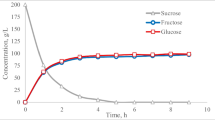
Abstract
The high phytase producing mutant of Aspergillus oryzae (KL-38) previously isolated was employed for koji making, and the produced koji rice then supplied for sake brewing. The alcohol fermentation was improved compared to that with the parent strain (A. oryzae BP-1). The effects of two phytase isozymes (Phy I and Phy II) produced by A. oryzae on yeast growth and inorganic phosphate liberation were investigated using a synthetic medium containing phytic acid as a sole phosphate source. Yeast growth and the liberation of inorganic phosphate were both enhanced by the combination of Phy I and Phy II at a ratio of 1 to 3, which was compatible with the production ratio in KL-38. Based on these results, phytase plays important role in sake brewing, and that the maximum inorganic phosphate liberation from phytic acid can be obtained by a suitable combination of Phy I and Phy II.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujita J, Budda N, Tujimoto M, Yamane Y, Fukuda H, Mikami S, Kizaki Y (2000) Isolation and characterization of phytase isozyme produced by Aspergillus oryzae. Biotechnol. Lett. 22: 1797–1802.
Fujitani T (1965) Biochemical studies on the mineral components in sake yeast. Part I. Comparative studies on the mineral composition in sake yeast and in other brewer's yeast. Agric. Biol. Chem. 29: 471–476.
Fukuda H, Park SB, Kizaki Y, Takahashi K (1999) Sake brewing characteristics and multidrug resistance of trichhothecinresistant yeast mutants. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 15: 629–630.
Greiner R, Konietzny U, Jany KD (1993) Purification and characterization of two phytases from Escherichia coli. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 303: 107–113.
Ito K (1967) Shubo moromi chu no mukiseibun no yakuwari. J. Brew. Soc. Jpn. 62: 108–113 (in Japanese).
Kim DS, Godber JS, Kim HR (1999) Culture conditions for a new phytase-producing fungus. Biotechnol. Lett. 21: 1077–1081.
Kitamoto K, Takahashi K, Totsuka A, Yoshizawa K (1985) Changes in inorganic ions during sake brewing. Study on the brewing of sake with excellent taste and flavor (Part V). J. Brew. Soc. Jpn. 30: 564–566 (in Japanese).
Lambrechts C, Boze H, Segueilha L, Moulin G, Galzy P (1993) Influence of culture conditions of Schwanniomyces castellii phytase. Biotechnol. Lett. 15: 399–404.
Maga JA (1982) Phytate: its chemistry, occurrence, food interaction, nutritional significance and methods of analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 30: 1–9.
Okabe M, Sakurada H, Shimizu H, Nakatani T, Mikami S, Iwano K (1996) Sake-koji enzymes responsible for the release of inorganic phosphate from rice. J. Brew. Soc. Jpn. 91: 203–208 (in Japanese).
Okazaki N (1993) Seisyu and gousei-seisyu. In: Nishiya T, ed. The Annotation of the Official Method of Analysis of the National Tax Administration of Agency, 4th edn. Tokyo: The Brewing Society of Japan, pp. 7–33 (in Japanese).
Olz R, Larsson K, Adler L, Gustafsson L (1993) Energy flux and osmoregulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae growth in chemostats under NaCl stress. J. Bacteriol. 175: 2205–2213.
Powar VK, Jagannathan V (1982) Purification and properties of phytate-specific phosphatase from Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 151: 1102–1108.
Ullah AHJ, Gibson DM (1987) Extracellular phytase (E.C. 3.1.3.8) from Aspergillus ficuum NRRL 3135: purification and characterization. Prep. Biochem. 17: 63–91.
Webb EC (1992) Enzyme Nomenclature 1992. California: Academic Press.
Wyss M, Brugger R, Kronenberger A, Remy R, Fimbel R, Oesterhelt G, Lehmann M, van Loon APGM (1999) Biochemical characterization of fungal phytases (myo-inositol hexakisphosphate phosphohydrolases): catalytic properties. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 367–373.
Yamane Y, Yoshii M, Mikami S, Fukuda H, Kizaki Y (2000) A solid-state culture system using a cellulose carrier containing de-fined medium as a useful tool for investigating characteristics of koji culture. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 89: 33–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, J., Fukuda, H., Yamane, Yi. et al. Critical importance of phytase for yeast growth and alcohol fermentation in Japanese sake brewing. Biotechnology Letters 23, 867–871 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010599307395
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010599307395