Abstract
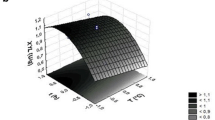
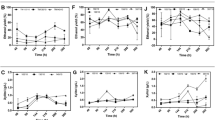
Various nitrogen and carbon sources were examined as inducers of the production of endoxylanase and β-xylosidase by Trametes trogii. T. trogii grown on xylan plus crystalline cellulose provided supernatants with the highest enzymatic activities. Organic nitrogen sources (especially asparagine and casamino acids) were the best for enzyme production. The increase in xylan concentration stimulated endoxylanase production whereas significant differences were not attained in β-xylosidase production with more than 5g xylan/l in the culture medium. pH 4.0 was optimal for endoxylanase production, while β-xylosidase production was maximum at pH 5.5. Temperatures in the range of 23–28°C stimulated enzyme production. The endoxylanase activity in the crude culture filtrate was greatest at 50°C and pH around 5.0. The optimum pH and temperature for β-xylosidase activity were 5.5 and 50°C respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchert, J., Ienkanen, M., Kantelinen, A. & Viikari, I. 1994 Application of xylanases in the pulp and paper industry. Bioresearch Technology 50, 65–72.
Copa-Patiño, J.L., Young, G.K. & Broda, P. 1993 Production and initial characterization of the xylan-degrading system of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 40, 69–76.
Coughlan, M.P. & Hazlewood, G.P. 1993 α-1, 4-D-Xylan-degrading enzyme systems: biochemistry, molecular biology and applications. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry 17, 259–289.
Eriksson, K.E. 1988 Microbial delignification-basics, potentials and applications. In Biochemistry and Genetics of Cellulose Degradation, ed Aubert, J-P., Beguin, P. & Millet, J. pp. 285–302. London: Academic Press.
Eriksson, K.E., Blanchette, R.A. & Ander, P. 1990 Microbial and Enzymatic Degradation of Wood and Wood Components. Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag.
Hrmova, M., Biely, P. & Vrsanka, M. 1986 Specificity of cellulase and α-xylanase induction in Trichoderma reesei QM 9414. Archives of Microbiology 144, 307–311.
Hrmova, M., Petrakova, E. & Biely, P. 1991 Induction of cellulose and xylan-degrading enzyme systems in Aspergillus terreus by homo and heterodisaccharides composed of glucose and xylose. Journal of General Microbiology 137, 541–547.
Khandke, K.M., Vithayathil, P.J. & Murthy, S.K. 1989 Purification of xylanase, α-glucosidase, endocellulase and exocellulase from a thermophilic fungus Thermoascus aurantiacus. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 274, 491–500.
Levin, L. & Forchiassin, F. 1995 Influencia de las fuentes carbonadas y nitrogenadas sobre la actividad celulolítica de Trametes trogii. Revista Argentina de Microbiologiá 27, 11–20.
Maijala, P., Raudaskoski, M. & Viikari, L. 1995 Hemicellulolytic enzymes in P-and S-strains of Heterobasidion annosum. Microbiology 141, 743–750.
Peltonen, S., Kayalainen, R. & Niku-Paavola, M.L. 1994 Purification and characterization of a xylanase from Bipolaris sorokiniana. Mycological Research 98, 67–73.
Planes, E., Bassi, M.H., Bensignor, J. & Burachik, M. 1985 Pulpado biológico de maderas de sauce. 21 Congreso Técnico sobre celulosa y papel. Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Royer, C. & Nakas, J.P. 1990 Interrelationship of xylanase induction and cellulase induction of Trichoderma longibrachiatum. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 56, 2535–2539.
Senior, D.J., Mayers, P.R. & Saddler, J.N. 1989 Xylanase production by Trichoderma harzianum ES8. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 32, 137–142.
Silva, H., Landa, A. & Agosin, E. 1990 Aislamiento, selección y caracterización de hongos ligninolíticos chilenos. Archivos de Biología y Medicina Experimentales 23, 41–49.
Wong, K.K.Y. 1988 Multiplicity of α-1,4-xylanase in microorganisms: functions and applications. Microbiological Reviews 52, 305–317.
Wright, J.E., Deschamps, J.R. & Rovetta, G. 1973 Basidiomycetes xilófilos de la región mesopotámica. I. Poliporos trametoides. Revista de Investigaciones Agropecuarias del INTA Serie V 10, 117–174.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levin, L., Forchiassin, F. Influence of growth conditions on the production of xylanolytic enzymes by Trametes trogii. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 14, 443–446 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008885800035
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008885800035