Abstract
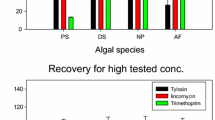
The effect of irradiance over the range 5 to 70 μmol photon m-2 s-1 on production of antibiotically active metabolites was assessed for male and female gametophytes and tetrasporophytes of the red alga Sphyridia filamentosa (Wulfen) Harvey in Hooker in culture. Whole-algal extracts and ten recognizable TLC-separable zones were assayed against five human microorganisms pathogenic to humans. For all experimental irradiance conditions, the ten TLC zones displayed activity against four of the microorganisms. The maximum number of TLC zones with activity under any of the culture conditions was six each for male and female Spyridia at 70 μmol photon m-2 s-1. Small changes in irradiance resulted both in different activities against specific microorganisms and degree of activity. The fact that every TLC zone showed differing activities at different light conditions or when extracted from different life history stages strongly suggests the presence of multiple antibiotic principals in individual TLC zones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballantine DL, Gerwick WH, Velez SM, Alexander E, Guevara P (1987) Antibiotic activity of lipid-soluble extracts from Caribbean marine algae. Hydrobiologia 151/152: 463-469.
Burkholder PR, Burkholder LM, Almodóvar LR (1960) Antibiotic activity of some marine algae of Puerto Rico. Bot. mar. 2: 149-156.
Gerwick WH, Fenical W, Norris JN (1985) Chemical variation in the tropical seaweed Stypopodium zonale(Dictyotaceae). Phytochemistry 24: 1279-1283.
Lewin J (1966) Silicon metabolism in diatoms V. Germanium dioxide, a specific inhibitor of diatom growth. Phycologia 6: 1-12.
Masuda M, Abe T, Sato S, Suzuki T, Suzuki M (1997) Diversity of halogenated secondary metabolites in the red alga Laurencia nipponica(Rhodomelaceae: Ceramiales). J. Phycol. 33: 196-208.
Meyer KD, Paul VJ (1992) Intraplant variation in secondary metabolite concentration in three species of Caulerpa(Chlorophyta: Caulerpales) and its effects on herbivirous fishes. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 82: 2149-257.
Olesen PE, Maretzki A, Almodóvar LR (1964) An investigation of antimicrobial substances from marine algae. Bot. mar. 6: 224-232.
Pratt R, Daniels TC, Eiler JJ, Gunnison JB, Kumler WD, Oneto JF, Strait LA (1944) Chlorellin, an antibacterial substance from Chlorella. Science 99: 351-352.
Provasoli L (1963) Growin marine seaweeds. In: DeVirville D, Feldmann J (eds), Proc. Int. Seaweed Symp. Vol. 4. Pergamon Press, Oxford: 9-17.
Robles Centeno PO, Ballantine DL, Gerwick WH (1996) Dynamics of antibacterial activity in three species of Caribbean marine algae as a function of habitat and life history. Hydrobiologia 326/327: 457-462.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robles Centeno, P.O., Ballantine, D.L. Effects of culture conditions on production of antibiotically active metabolites by the marine alga Spyridia filamentosa (Ceramiaceae, Rhodophyta). I. Light. Journal of Applied Phycology 10, 453–460 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008038418777
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008038418777