Abstract
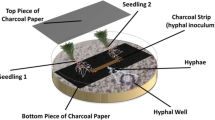
Although it is well established that ectomycorrhizas improve the mineral nutrition of forest trees, there has been little evidence that they mediate uptake of divalent cations such as Mg. We grew nonmycorrhizal seedlings and seedlings mycorrhizal with Paxillus involutus Batsch in a sand culture system with two compartments separated by a 45-μm Nylon mesh. Hyphae, but not roots, can penetrate this net. Labeling the compartment only accessible to hyphae with 25Mg showed that hyphae of the ectomycorrhizal fungus Paxillus involutus transported Mg to their host plant. No label was found in nonmycorrhizal control plants. Our data support the idea that ectomycorrhizas are important for the Mg nutrition of forest trees.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry, C R and Marx D H 1976 Sewage sludge and Pisolithus tinctorius ectomycorrhizae: their effect on growth of pine seedlings. For. Sci. 22, 351–358.
Brandes B 1999 Nährstofftransport durch das extramatrikale Myzel von Ektomykorrhizapilzen-Umfang und Einfluß auf die Ernährung der Fichte (Picea abies). PhD. Thesis, University of Göttingen, Germany.
Brandes B, Godbold D L, Kuhn A J and Jentschke G 1998 Nitrogen and phosphorus acquisition by the mycelium of the ectomycorrhizal fungus Paxillus involutus and its effect on host nutrition. New Phytol. 140, 735–743.
Jentschke G, Bonkowski M, Godbold D L and Scheu S 1995 Soil protozoa and forest tree growth: non-nutritional effects and interaction with mycorrhizae. Biol. Fertil. Soil 20, 263–269
Jongmans A, Van Breemen N, Lundström U, Van Hees P W, Finlay R, Srinivasan M, Unestam T, Giesler R, Melkerud P and Olsson M 1997 Rock-eating fungi. Nature (London) 389, 682–683.
Keltjens W 1995 Magnesium uptake by Al-stressed maize plants with special emphasis on cation interactions at root exchange sites. Plant Soil 171, 141–146.
Kuhn A J, Bauch J and Schröder W H 1995 Monitoring uptake and contents of Mg, Ca and K in Norway spruce as influence by Ph and Al, using microprobe analysis and stable isotope labelling. Plant Soil 168-169, 135–150.
Landmann G, Hunter I R and Hendershot W 1997 Temporal and spatial development of magnesium deficiency in forest stands in Europe, North America and New Zealand. In Magnesium Defi-ciency in Forest Ecosystems. Eds RF Hüttl and W Schaaf. pp 23–64. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Lamhamedi MS, Bernier P Y and Fortin J A 1992 Growth, nutrition and response to water stress of Pinus pinaster inoculated with 10 dikaryotic strains of Pisolithus sp. Tree Physiol. 10, 153–167.
Marschner H and Dell B 1994 Nutrient uptake in mycorrhizal symbiosis. Plant Soil 159, 89–102.
Melin E and Nilsson H 1955 Ca45 used as indicator of transport of cations to pine seedlings by means of mycorrhizal mycelium. Svensk Bot Tidskr. 49, 119–122.
Schlechte G 1986 Zur Mykorrhizapilzflora in geschädigten Forstbeständen. Zeitschrift für Mykologie 52, 225–232.
Smith S E and Read D J 1997 Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, California.
Ulrich B 1994 Nutrient and acid-base budget of central European forest ecosystems. In Effects of Acid Rain on Forest Processes. Eds DL Godbold and A Hüttermann. pp 1–50. Wiley-Liss, New York.
Weast R C 1989 Handbook of chemistry and physics, 70th edn. Chemical Rubber Co., Cleveland, Ohio.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jentschke, G., Brandes, B., Kuhn, A.J. et al. The mycorrhizal fungus Paxillus involutus transports magnesium to Norway spruce seedlings. Evidence from stable isotope labeling. Plant and Soil 220, 243–246 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004727331860
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004727331860