Abstract
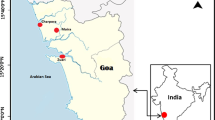
Cd, Cu and Zn content in sediments and bivalves (Limnoperna fortunei and Corbicula fluminea) were studied in the lower 500 km stretch of the Paraná River and in the right margin of the Río de la Plata Estuary. Both bivalves species showed higher metal contents at the Paraná River, possibly related to water chemistry. The Paraná water is circumneutral and soft, while the Río de la Plata coastal water is alkaline, hard, with a higher organic content. Bivalves sampled at the thermal effluent of the Atucha Nuclear Power Plant, at the Paraná River, showed the highest metal content, either from increased absorption at the higher water temperatures (12 °C higher than the river water) or from metal corrosion of the power plant cooling system. L. fortunei and C. fluminea appeared to be successful biomonitor organisms for Cd pollution in the basin, while Cu and Zn content in bivalve tissues was apparently not related to metal load.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abaychi, J. K. & Y. Z. Mustafa, 1988. The Asiatic clam, Corbicula fluminea: an indicator of trace metal pollution in the Shatt al-Arab River, Iraq. Envir. Pollut. 54: 109-122.
Abbe, G. R. & J. G. Sanders, 1986. Condenser replacement in a coastal power plant: copper uptake and incorporation in the American oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Mar. environ. Res. 19: 93-113.
AGOSBA-OSN-SIHN, 1992. Río de la Plata. Calidad de aguas. Franja costera sur (San Isidro-Magdalena). Buenos Aires.
APHA, 1985. Standard Methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington: 1268 pp.
Belanger, S. E., L. J. Farris, D. S. Cherry & J. Cairns, 1990. Validation of Corbicula fluminea growth reductions induced by copper in artificial streams and river systems. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 47: 904-914.
Belanger, S. E., 1991. The effect of dissolved oxygen, sediment and sewage treatment plant discharges upon growth, survival and density of Asiatic clams. Hydrobiologia 218: 113-126.
Bettinelli, M., U. Baroni & N. Pastorelli, 1989. Determinazione diretta di elementi in traccia in matrici ambientali mediante imprego dell+ ETA-AAS Zeeman e midificazione di matrice. InMinoia, C. & S. Caroli (eds), Applicazioni dell+ETA-AAS Zeeman nel laboratorio chimico e tossicologico. Eddizioni Libreria Cortina, Padova (Vol. 1): 49-81.
Bilos, C., J. C. Colombo & M. J. Rodriguez Presa, 1998. Trace metals in suspended particles, sediments and Asiatic clams (Corbicula fluminea) of the Río de la Plata Estuary, Argentina. Envir. Pollut. 99: 1-11.
Bodek, I., J. W. Lyman, W. F. Rechl & D. Rosenblat, 1988. Environmental Inorganic Chemistry. Pergamon Press, New York.
Boltovskoy, D., N. Correa, D. Cataldo, J. Stripeikis & M. Tudino, 1997. Environmental stress on Corbicula fluminea (Bivalvia) in the Paraná River delta (Argentina): complex pollution-related disruption of population structures. Arch. Hydrobiol. 168: 483-507.
Broman, D., L. Lindqvist & Y. Lundbergh, 1991. Cadmium and Zinc in Mytilus edulis L. from the Bothnian sea and the Northern Baltic Proper. Envir. Pollut. 74: 227-244.
Colombo, J. C., C. Bilos, M. Campanaro, M. J. Rodriguez Presa & J. A. Catoggio, 1995. Bioaccumulation of Polychlorinated Biphenils and Chlorinated Pesticides by the Asiatic clam Corbicula fluminea: its use as a sentinel organism in the Río de la Plata Estuary, Argentina. Envir. Sci. Technol. 29: 914-927.
Darrigran, G. A. & A. Coppola, 1994. Los bivalvos invasores del Río de la Plata. Su potencial uso como bioindicadores ambientales. Tankay 1: 150-152.
Darrigran, G. A., 1992. Variación temporal y espacial de la distribución de las especies de Corbicula (Megerle, 1811) (Bivalvia, Corbiculidae) en el estuario del Río de la Plata, Rep. Arg. Neotropica 38: 59-63.
Darrigran, G. A., 1994. Composición de la malacofauna del litoral del estuario del Río de la Plata. RepÚblica Argentina. Tankay 1: 147-149.
Dean, W. E., 1974. Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: comparison with other methods. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 44: 242-248.
Doherty, F. G. & D. S. Cherry, 1988. Tolerance of the Asiatic Clam Corbicula spp. to lethal levels of toxic stressors. A review. Envir. Pollut. 51: 69-313.
Eisler, R., 1985. Cadmium hazards to fish, wildlife and invertebrates: a synoptic review. - Fish and wildlife service. U.S. Dep. Interior. Contaminant Hazard Reviews. Rep. 85 (1.2).
Eisler, R., 1993. Zinc hazards to fish, wildlife and invertebrates: a synoptic review. Fish and wildlife service. U.S. Dep. Interior. Contaminant Hazard Reviews. Rep. 10: 106 pp.
Farris, J. L., S. E. Belanger, D. S. Cherry & J. Cairns, 1989. Cellulolytic activity as a novel approach to assess long-term zinc stress to Corbicula. Wat. Res. 23: 1275-1283.
Foe, C. & A. Knight, 1987. Assessment of the biological impact of point source discharges employing Asiatic clams. Arch. envir. Contam. Toxicol. 16: 39-51.
Folk, R. L., 1959. Petrology of sedimentary rocks. The University of Texas. Texas.
Gómez, S. E., C. A. Villar & C. Bonetto, 1998. Zinc toxicity in the fish Cnesterodon decemmaculatus in the Paraná River and Río de la Plata Estuary. Envir. Pollut. 99(2): 159-165.
Goldberg, E. D., V. T. Bowen, J. W. Farrington, G. Harvey, J. H. Martin, P. L. Parker, R. W. Risebrough, W. Robertson, E. Schneider & E. Gamble, 1978. The Mussel Watch. Environ. Conserv. 15: 1-15.
Ituarte, C. F., 1981. Primera noticia acerca de la introducción de pelecípodos asiáticos en el area rioplatense (Mollusca, Corbiculidae). Neotrópica 27: 79-83.
MacInnes, J. R. & A. Calabrese, 1978. Response of embryos of the American oyster, Crassotrea gigas, to heavy metals at different temperatures. In McLusky, D. S. & A. J. Berry (eds), Physiology and Behavior of Marine Organisms. Pergamon Press, New York: 195-202.
Mackereth, F., J. Heron & J. Talling, 1978. Water analysis: some revised methods for limnologists. Freshwater Biological Association. Scientific Publication Nº36, Kendal: 117 pp.
Maglianesi, R. & P. Depetris, 1970. Water chemistry of the Lower Salado River (Santa Fe, Argentina). Physis 80: 19-32.
Muller, T. G. & W. C. Mackay, 1980. The effects of hardness, alkalinity and pH of test water on the toxicity of copper to rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Wat. Res. 14: 129-135.
Pastorino, G., G. Darrigran, S. Martin & L. Lunaschi, 1993. Limnoperna fortunei (Dunker, 1857) (Mytilidae), nuevo bivalvo invasor en aguas del Río de la Plata. Neotrópica 39: 34.
Riedel, F. G., G. R. Abbe & J. G. Sanders, 1995. Silver and Copper accumulation in two estuarine bivalves, the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginiana) and the hooked mussel (Ischadium recurvum) in the Patuxent River Estuary, Maryland. Estuaries 18: 455-455.
Roosemburg, W. H., 1969. Greening and copper accumulation in the American oyster, Crassostrea virginica, in the vicinity of a steam electric generating station. Chesapeake Sci. 10: 241-252.
Sanders, J. G., G. F. Riedel & G. R. Abbe, 1991. Factors controlling the spatial and temporal variability of trace metal concentrations in Crassostrea virginica (Gmelin). In M. Elliot & J. P. Ducrotoy (eds), Estuaries and Coasts: Spatial and Temporal Intercomparisons. ECSA 19 Symposium: 335-339.
Sericano, J. L., T. L. Wade, J. M. Brooks, E. L. Atlas, R. R. Fay & D. L. Wilkinson, 1993. National Status and Trends Mussel Watch Program: Chlordane-related compounds in Gulf of Mexico oysters, 1986-1990. Envir. Pollut. 82: 23-32.
Sokal, R. & F. Rohlf, 1979. Biometría. Principios y métodos estadísticos en la investigación biológica. H. Blume, Madrid: 832 pp.
Statistica, 1993. Statistica for Windows. Release 4.3. Copyright Statsoft Inc.
Strickland, J. & T. Parsons, 1972. A practical handbook for seawater analysis. Bulletin 167 J. Fish Res. Bd Can., Ottawa, Canadá.
Villar, C., L. Mercado, A. Rodriguez Capítulo & C. Bonetto, 1997. Presencia del molusco invasor Limnoperna fortunei (Dunker, 1857) (Bivalvia, Mytilidae) en el Bajo Paraná. Gayana Zool. 61: 87-96.
Villar, C., M. Tudino, C. Bonetto, L. de Cabo, J. Stripeikis, L. D'Huicque & O. Troccoli, 1998a. Heavy metal concentrations in the Lower Paraná and right margin of the Río de la Plata Estuary. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 26: 963-966.
Villar, C., L. de Cabo, P. Vaithiyanathan & C. Bonetto, 1998b. River floodplain interactions: nutrient concentrations in the Lower Paraná River. Arch. Hydrobiol. 142: 433-450.
Villar, C., M. Tudino, J. Stripeikis, L. D'Huicque, O. Troccoli & C. Bonetto, 1998c. Concentración de metales pesados en el Bajo Paraná en la zona de Atucha. In Villar, C. & C. Bonetto (eds), Estudio Limnológico del río Paraná en la Zona de Atucha. Buenos Aires: 14-20.
Villar, C., J. Stripeikis, M. Tudino, L. D'Huicque, O. Troccoli & C. Bonetto, in press. Trace metal concentrations in coastal marshes of the Lower Paraná River and the Río de la Plata Estuary. Hydrobiologia.
Wang, Y. & R. D. Evans, 1993. Influence of calcium concentrations on cadmium uptake by the freshwater mussel Elliptio complanata. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 50: 2591-2596.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villar, C., Stripeikis, J., D'Huicque, L. et al. Cd, Cu and Zn concentrations in sediments and the invasive bivalves Limnoperna fortunei and Corbicula fluminea at the Río de la Plata basin, Argentina. Hydrobiologia 416, 41–49 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003811223880
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003811223880