Abstract
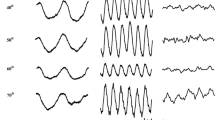
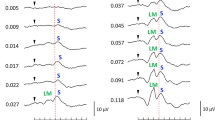
There is evidence that recording the photopic ON- and OFF-responses with long-duration stimuli is useful for determining the contribution of the cone ON- and OFF-pathways to the primate photopic electroretinogram (ERG). In this study, the optimal conditions for recording multifocal ON-OFF responses are described, and the technique is applied to normal subjects and two patients with unusual retinal diseases. The results from the normal subjects demonstrated that there were topographical variations of the photopic ERG waveform: when responses were normalized to the ON-response (b-wave) amplitude, the OFF-response (d-wave) amplitude increased with increasing eccentricity. The changes in the waveform in two patients suggested relatively greater defects of the hyperpolarizing or depolarizing bipolar cells. We conclude that the multifocal ERG technique with long-duration stimuli can be a useful tool to assess the function of local cone ON- and OFF-pathways in normal and diseased retinas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sutter EE, Tran D. The field topography of ERG components in man. 1. The photopic luminance response. Vis Res 1992; 32: 433–46.
Wu S, Sutter EE. A topographic study of oscillatorry potentials in man. Vis Neurosci 1995; 12: 1013–1025.
Bearse MA, Sutter EE. Imaging localized retinal dysfunction with the multifocal electroretinogram. J Opt Soc Am A 1996; 13: 634–40.
Palmowski AM, Sutter EE. Bearse MA Jr. Fung W. Mapping of retinal function in diabetic retinopathy using the multifocal electroretinogram. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1997; 382586–96.
Sutter EE, Bearse MA Jr. The optic nerve head component of the human ERG. Vis Res 1999; 39: 419–36.
Hood DC, Seiple W, Holopigian K, Greenstein V. A. comparison of the components of the multi-focal and full-field ERGs. Vis Neurosci 1997; 14: 533–44.
Kondo M, Miyake Y, Horiguchi M, Suzuki S, Tanikawa A. Clinical evaluation of multifocal electroretinogram. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1995; 36: 2146–150.
Hood DC, Holopigian K, Greenstein V, Seiple W, Li J, Sutter EE, Carr RE. Assessment of local retinal function in patients with retinitis pigmentosa using the multi-focal ERG technique. Vis Res 1997; 38: 163–79.
Kretschmann U, Seeliger MW, Ruether K, Usui T, Apfelstedt-Sylla E, Zrenner E. Multifocal electroretinography in patients with Stargardt's macular dystrophy. Br J Ophthalmol 1998; 82: 267–75.
Seeliger M, Kretschmann U, Apfrlstedt-Sylla E, Ruther K, Zrenner E. Multifocal electroretinography in retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Ophthalmol 1998; 125: 214–26.
Seeliger MW, Biesalski HK, Wissinger B, Gollnick H, Gielen S, Frank J, Beck S, Zrenner E. Phenotype in retinol deficiency due to a hereditary defect in retinol binding protein synthesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1999; 40: 3–1.
Marmor MF, Tan F, Sutter EE, Bearse MA Jr. Topography of cone electrophysiology in the enhanced S cone syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1999; 40: 1866–73.
Fortune B, Schneck ME, Adams AJ. Multifocal electroretinogram delays reveal local retinal dysfunction in early diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1999; 40: 2638–51.
Piao CH, Kondo M, Tanikawa A, Terasaki H, Miyake Y. Multifocal electroretinogram in occult macular dystrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2000; 41: 3–517.
Horiguchi M, Suzuki S, Kondo M, Tanikawa A, Miyake Y. Effect of glutamate analogues and inhibitory neurotransmitters on the electroretinograms elicited by random sequence stimuli in rabbits. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1998; 39: 2171–6.
Heck J. The flicker electroretinogram of the human eye. Acta Physiol Scand 1957; 39: 158–66.
Howarth CI. On-off interaction in the human electroretinogram. J Opt Soc Am 1961; 51: 345–52.
Nagata M. Studies on the photopic ERG of the human retina. Jpn J Ophthalmol 1963; 7: 96–124.
Biersdorf WR. Rod and cone contribution to the off-effect of the human ERG. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1968; 7: 371–7.
Kawasaki K, Tsuchida Y, Jacobson JH. Positive and negative deflection in the offresponse of the electroretinogram in man. Am J Ophthalmol 1971; 72: 367–75.
Seiple W, Holopigian K. The 'OFF' response of the human electroretinogram does not contribute to the brief flash 'b-wave'. Vis Neurosci 1994; 11: 667–73.
Evers HU, Gouras P. Three cone mechanisms in the primate electroretinogram: two with, one without off-center bipolar responses. Visi Res 1986; 26: 245–54.
Sieving PA. Photopic ON-and OFF-pathway abnormalities in retinal dystrophies. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1993; 91: 701–73.
Sieving PA. 'Unilateral cone dystrophy': ERG changes implicate abnormal signaling by hyperpolarizing bipolar and/or horizontal sells. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1994; 92; 459–71.
Sieving PA, Murayama K, Naarendorp F. Push-pull model of the primate photopic electroretinogram; a role for hyperpolarizing neurons in shaping the b-wave. Vis Neurosci 1994; 11: 519–32.
Miyake Y, Yagasaki K, Horiguchi M, Kawase Y. On-and off-responses in photopic electroretinogram in complete and incomplete types of congenital stationary night blindness. Jpn J Ophthalmol 1987; 31: 81–7.
Young RSL. Low-frequency component of the photopic ERG in patients with X-linked congenital stationary night blindness. Clin Vis Sci 1991; 6: 309–15.
Alexander KR, Fishman GA, Peachey NS, Marchese AL, Tso MOM. 'On' response defect in paraneoplastic night blindness with cutaneous malignant melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1992; 33: 477–83.
Cideciyan AV, Jacobson SG. Negative electroretinograms in retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1993; 34: 3253–63.
Müller F, Wässle H, Voigt T. Pharmacological modulation of the rod pathway in the cat retina. J Neurophysiol 1988; 59: 1657–72.
Wässle H, Yamashita M, Greferath U, Grünert U, Müller F. The rod bipolar cell of the mammalian retina. Vis Neurosci 1991; 7: 99–112.
Kolb H. The connections between horizontal cells and photoreceptors in the retina of the cat: electron microscopy of Golgi preparations. J Neurocytol 1977; 6: 131–53.
Nelson R. Cat cones have rod input: A comparison of the response properties of cones and horizontal cell bodies in the retina of the cat. J Comp Neurol 1997; 172: 109–36.
Slaughter MM, Miller RF. 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid: a new pharmacological tool for retina research. Science 1981; 211: 182–5.
Slaughter MM, Miller RF. Bipolar cells in the mudpuppy retina use an excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter. Nature 1983; 303: 537–8.
Slaughter MM, Miller RF. An excitatory amino acid antagonist blocks cone input to sign-conserving second-order retinal neurons. Sci 1983; 219: 1230–2.
Kondo M, Miyake Y, Horiguchi M, Suzuki S, Tanikawa A. Recording multifocal electroretinogram on and off responses in humans. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1998; 39: 574–80.
Saeki M, Gouras P. Cone ERGs to flash trains: The antagonism of a later flash. Vis Res 1996; 36: 3229–35.
Miyake Y, Shiroyama N, Horiguchi M, Ota I. Asymmetry of focal ERG in human macular region. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1989; 30: 1743–9.
Miyake Y, Horiguchi M, Tomita N, Kondo M, Tanikawa A, Takahashi H, Suzuki S, Terasaki H. Occult macular dystrophy. Am J Ophthalmol 1996; 122: 644–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondo, M., Miyake, Y. Assessment of local cone on- and off-pathway function using multifocal ERG technique. Doc Ophthalmol 100, 139–154 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002779619050
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002779619050