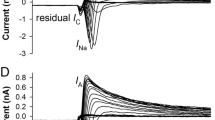
Abstract
Serotonin (5-HT) applied to the exposed but otherwise intact nervous system results in enhanced excitability of Hermissenda type-B photoreceptors. Several ion currents in the type-B photoreceptors are modulated by 5-HT, including the A-type K+ current (IK,A), sustained Ca2+ current (ICa,S), Ca-dependent K+ current (IK,Ca), and a hyperpolarization-activated inward rectifier current (Ih). In this study, we developed a computational model that reproduces physiological characteristics of type B photoreceptors, e.g. resting membrane potential, dark-adapted spike activity, spike width, and the amplitude difference between somatic and axonal spikes. We then used the model to investigate the contribution of different ion currents modulated by 5-HT to the magnitudes of enhanced excitability produced by 5-HT. Ion currents were systematically varied within limits observed experimentally, both individually and in combinations. A reduction of IK,A or IK,Ca, or an increase in Ih enhanced excitability by 20–50%. Decreasing ICa,S produced a dramatic decrease in excitability. Reductions of IK,V produced only minimal increases in excitability, suggesting that IK,V probably plays a minor role in 5-HT induced enhanced excitability. Combinations of changes in IK,A, IK,Ca, Ih and ICa,S produced increases in excitability comparable to experimental observations. After 5-HT application, the cell's depolarization force is shifted from the Ih–ICa,S combination to predominantly Ih.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Urquidi J, Crow T (1993) Differential modulation of voltagedependent currents in Hermissenda typeBphotoreceptors by serotonin. J. Neurophysiol. 70: 541-548.
Acosta-Urquidi J, Crow T (1995) Characterization of voltagedependent currents in Hermissenda type B photoreceptors. J. Neurosci. 15: 319-332.
Alkon DL, Fuortes MGF (1972) Responses of photoreceptors in Hermissenda. J. Gen. Physiol. 60: 631-649.
Baxter DA, Cai Y, Brembs B, Byrne JH (2000) Simulating physiological and morphological properties of neurons with SNNAP (Simulator for Neural Networks and Action Potentials). Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 26: 45.
Blackwell KT (1999) Dynamics of light-induced current in Hermissenda. Neurocomputing 26/27: 61-67.
Blackwell KT (2000) Evidence for a distinct light-induced calciumdependent potassium current in Hermissenda Crassicornis. J. Comput. Neurosci. 9: 149-170.
Cai Y, Baxter DA, Crow T (2000) Computational model of Hermissenda type-B photoreceptors. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 26: 2032.
Cai Y, Baxter DA, Crow T (2001) Computational model of Hermissenda type-B photoreceptors. I: Ionic currents underlying changes in excitability produced by one-trial conditioning. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 27: 2532.
Connor JA, Stevens CF (1971) Prediction of repetitive firing behaviour from voltage clamp data on an isolated neurone soma. J. Physiol. 213: 31-53.
Crow T (1985) Conditioned modification of phototactic behavior in Hermissenda. II. Differential adaptation of B-photoreceptors. J. Neurosci. 5: 215-223.
Crow T, Bridge MS (1985) Serotonin modulates photoresponses in Hermissenda type-B photoreceptors. Neurosci. Lett. 60: 83-88.
Crow T, Forrester J (1986) Light paired with serotonin mimics the effect of conditioning on phototactic behavior of Hermissenda. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA 83: 7975-7978.
Crow T, Forrester J (1991) Light paied with serotonin in vivo produces both short-and long-term enhancement of generator potentials of identified B-photoreceptors in Hermissenda. J. Neurosci. 11: 608-617.
Crow T, Heldman E, Hacopian V, Enos R, Alkon DL (1979) Ultrastructure of photoreceptors in the eye of Hermissenda labelled with intracellular injections of horseradish peroxidase. J. Neurocytol. 8: 181-195.
Crow T, Siddiqi V (1997) Time-dependent changes in excitability after one-trial conditioning of Hermissenda. J. Neurophysiol. 78: 3460-3464.
Crow T, Xue-Bian J-J, Siddiqi V (1999) Protein synthesis-dependent and mRNA synthesis-independent intermediate phase of memory in Hermissenda. J. Neurophysiol. 82: 495-500.
Eakin RM, Westfall JA, Dennis MJ (1967) Fine structure of the eye of a Nudibranch Mollusc, Hermissenda crassicornis. J. Cell Sci. 2: 349-358.
Flynn M, Cai Y, Baxter DA, Crow T (2003) A computational study of the role of spike broadening in synaptic facilitation of Hermissenda. J. Comput. Neurosci. 15: 29-41.
Fost JW, Clark GA (1996) Modeling Hermissenda: I. Differential contribution of IA and IC to type-B cell plasticity. J. Comput. Neurosci. 3: 137-153.
Gandhi CC, Matzel LD (2000) Modulation of presynaptic action potential kinetics underlies synaptic facilitation of type B photoreceptors after associative conditioning in Hermissenda. J. Neurosci. 20: 2022-2035.
Hayes RD, Byrne JH, Baxter DA (2003) Neurosimulation: Tools and resources. In: Arbib MA ed. The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks. Second Edition, MIT Press, Cmbridge, pp. 776-780.
Goh Y, Alkon DL (1984) Sensory, interneuronal, and motor interactions within Hermissenda visual pathway. J. Neurophysiol. 52: 156-169.
Ito E, Oka K, Collin C, Schreurs BG, Sakakibara M, Alkon DL (1994) Intracellular calcium signals are enhanced for days after Pavlovian conditioning. J. Neurochem. 62: 1337-1344.
Jack JJB, Noble D, Tsien RW (1983) Electrical Current Flow in Excitable Cells. Oxford, Oxford.
Koch C (1999) Biophysics of Computation: Information Processing in Single Neurons. Oxford, New York.
Mainen ZF, Sejnowski TJ (1996) Influence of dendritic structure on firing pattern in model neocortical neurons. Nature 382: 363-366.
Major G, Larkman AU, Jonas P, Sakmann B, Jack JJ (1994) Detailed passive cable models of whole-cell recorded CA3 pyramidal neurons in rat hippocampal slices. J. Neurosci. 14: 4613-4638.
McEwan JR, Farnsworth PN (1987) Regional resistivity variations in lens homogenates. Exp. Eye Res. 44: 567-576.
Muzzio IA, Talk AC, Matzel LD (1998) Intracellular Ca2+ and adaptation of voltage responses to light in Hermissenda photoceceptors. Neuroreport 9: 1625-1631.
Richieri GV, Mel HC (1986) Membrane and cytoplasmic resistivity properties of normal and sivkle red blood cells. Cell Biophysics. 8: 243-258.
Rush ME, Rinzel J (1995) The potassium A-current, low firing rates and rebound excitation in Hodgkin-Huxley models. Bull. Math. Biol. 57: 899-929.
Sahley CL, Crow T (1998) Invertebrate learning: Current perspectives. In: JL Martinez Jr. and RP Kesnok, eds. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. Academic, New York, pp. 177-209.
Sakakibara M, Ikeno H, Usui S, Collin C, Alkon DL (1993) Reconstruction of ionic currents in a Molluscan photoreceptor. Biophys. J. 65: 519-527.
Senft SL, Allen RD, Crow T, Alkon DL (1982). Optical sectioning of HRP-stained molluscan neurons. J. Neurosci. Meth. 5: 153-159.
Stensaas LJ, Stensaas SS, Trujillo-Cenoz O (1969) Some morphological aspects of the visual system of Hermissenda crassicornis (Mollusca: Nudibranchia). J. Ultra. Res. 27: 510-532.
Thurbon D, Field A, Redman S (1994) Electrotonic profiles of interneurons in stratum pyramidale of the CA1 region of rat hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 71: 1948-1958.
Yamoah EN, Crow T (1994) Two components of calcium currents in the soma of photoreceptors of Hermissenda. J. Neurophysiol. 72: 1327-1336.
Yamoah EN, Crow T (1995) Evidence for a contribution of ICa to serotonergic modulation of IK, Ca in Hermissenda photoreceptors. J. Neurophysiol. 74: 1349-1354.
Yamoah EN, Crow T (1996) Protein kinase and G-protein regulation of Ca2+ currents in Hermissenda photoreceptors by 5-HT and GABA. J. Neurosci. 16: 4799-4809.
Yamoah EN, Matzel L, Crow T (1998) Expression of different types of inward rectifier currents confers specificity of light and dark responses in type A and B photoreceptors of Hermissenda. J. Neurosci. 18: 6501-6511.
Ziv I, Baxter DA, Byrne JH (1994) Simulator for neural networks and action potentials: Description and application. J. Neurophysiol. 71: 294-308.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Y., Baxter, D.A. & Crow, T. Computational Study of Enhanced Excitability in Hermissenda: Membrane Conductances Modulated by 5-HT. J Comput Neurosci 15, 105–121 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024479020420
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024479020420