Abstract
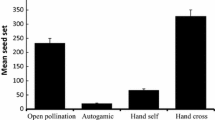
In this paper, we study the sources of variability in seed provisioning in Rhamnus alpinus, a dioecious shrub producing three-seeded fleshy fruits (range 1–4). Discarding position effects in access to resources as a source of variation, since pyrenes are radially oriented inside the fruit, we conducted a pollination experiment, in which different pollen donors were used to make single and mixed pollinations on different female plants. We found strong maternal effects on brood size and seed mass. Although we found no effects of pollen load or pollen source on fruit set, brood size or seed mass, all variables showed enhanced values after multiple pollination treatments. Furthermore, we found an increase of intra-brood variance in seed mass after multiple pollination, suggesting that multiple siring really occurs when multiple donors were involved in pollination, and that sibling rivalry could be a mechanism implicated in seed provisioning, discarding maternal choice as the alternative scenario. Our results on resource provisioning fits with a hierarchical model, since disparities in shares increased down the dominance rank, being the middle sized seed the least sensitive to resource partitioning, and the disparities were reduced when more resources were available in terms of fruit mass. Maternal effects, number of pollen donors, and sibling competition are therefore accounting for seed mass variability in R. alpinus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bañuelos, M.J. (2001) Ecología del crecimiento y de la reproducción en el arbusto dioico Rhamnus alpinus L. PhD Dissertation. Departamento de Biología de Organismos y Sistemas, Universidad de Oviedo. Oviedo, Asturias, Spain.
Bawa, K.S. and Webb, C.J. (1984) Flower, fruit and seed abortion in tropical forest trees: implications for the evolution of paternal and maternal reproductive patterns. Am. J. Bot. 71, 736-751.
Bertin, R.I. (1990) Paternal success following mixed pollinations of Campsis radicans. Am. Midl. Nat. 124, 153-163.
Charnov, E.L. (1979) Simultaneous hermaphroditism and sexual selection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 2480-2484.
Endler, J.A. (1986) Natural selection in the wild. In R.M. May (ed.) Monographs in Population Biology, Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey.
Forbes, L.S. (1993) Avian brood reduction and parent-offspring ''conflict''. Am. Nat. 142, 82-117.
Ganeshaiah, K.N. and Uma Shaanker, R. (1988) Seed abortion in wind-dispersed pods of Dalbergia sissoo: maternal regulation or sibling rivalry? Oecologia 77, 135-139.
Haig and Westoby, M. (1988) Inclusive fitness, seed resources, and maternal care In J. Lovett-Doust and L. Lovett-Doust (eds) Plant Reproductive Ecology, Patterns and Strategies, Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 60-79.
Hamilton, W.D. (1964) The genetical evolution of social behavior. J. Theor. Biol. 7, 1-52.
Johnston, M.O. (1993) Tests of two hypotheses concerning pollen competition in a self-compatible, long-styled species (Lobelia cardinalis: Lobeliaceae). Am. J. Bot. 80, 1400-1406.
Karron, J.D. and Marshall, D.L. (1993) Effects of environmental variation on fitness of singly and multiply sired progenies of Raphanus sativus (Brassicaceae). Am. J. Bot. 80, 1407-1412.
Marcelis, L.F.M. and Baan Hofman-eijer, L.R. (1997) Effects of seed number on competition and dominance among fruits in Capsicum annuum L. Ann. Bot. 79, 687-693.
Marshall, D.L. (1991) Nonrandomm ating in wild radish: variation in pollen donor success and effects of multiple paternity among one-to six-donor pollinations. Am. J. Bot. 78, 1404-1418.
Marshall, D.L. and Folsom, M.W. (1991) Mate choice in plants: an anatomical to population perspective. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 22, 37-63.
Marshall, D.L. and Whittaker, K.L. (1989) Effects of pollen donor identity on offspring quality in wild radish, Raphanus sativus. Am. J. Bot. 76, 1081-1088.
Marshall, D.L., Avritt, J.J., Shaner, M. and Leigh Saunders, R. (2000) Effects of pollen load size and composition on pollen donor performance in wild radish, Raphanus sativus (Brassicaceae). Am. J. Bot. 87, 1619-1627.
Mazer, S.J. (1987) Maternal investment and male reproductive success in angiosperms: parent-offspring conflict or sexual selection? Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 30, 115-133.
McCall, C., Mitchell-Olds, T. and Waller, D. (1989) Fitness consequences of outcrossing in Impatiens capensis: Tests of the frequency-dependent and sib-competition models. Evolution 43, 1075-1084.
Méndez, M. (1997) Sources of variation in seed mass in Arum italicum. Int. J. Plant Sci. 158, 298-305.
Mock, D.W. and Parker, G.A. (1997) The evolution of sibling rivalry. In R.M. May and P.H. Harvey (eds) Oxford Series in Ecology and Evolution, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Mock, D.W. and Parker, G.A. (1998) Siblicide, family conflict and the evolutionary limits of selfishness. Anim. Behav. 56, 1-10.
Mohan Raju, B., Shaanker, U. and Ganeshaiah, K.N. (1996) Intra-fruit seed abortion in a wind dispersed tree, Dalbergia sissoo Roxb: proximate mechanisms. Sex. Plant Reprod. 9, 273-278.
Niesenbaum, R.A. (1999) The effect of pollen load size and donor diversity on pollen performance, selective abortion, and progeny vigor in Mirabilis jalapa (Nyctaginaceae). Am. J. Bot. 86, 261-268.
Obeso, J.R. (1993) Seed mass variation in the perennial herb Asphodelus albus: sources of variation and position effect. Oecologia 93, 571-575.
Parker, G.A., Mock, D.W. and Lamey, T.C. (1989) How selfish should stronger sibs be? Am. Nat. 133, 846-868.
Pasonen, H.L., Pulkkinen, P. and Käpylä, M. (2001) Do pollen donors with fastest-growing pollen tubes sire the best offspring in an anemophilous tree, Betula pendula (Betulaceae)? Am. J. Bot. 88, 854-860.
Queller, D.C. (1984) Models of kin selection on seed provisioning. Heredity 53, 151-165.
Queller, D.C. (1994) Male-female conflict and parent-offspring conflict. Am. Nat. 144, s84-s99.
Rigney, L.P., Thomson, J.D., Cruzan, M.B. and Brunet, J. (1993) Differential success of pollen donors in a self-compatible lily. Evolution 47, 915-924.
Roach, D.A. and Wulff, R.D. (1987) Maternal effects in plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 18, 209-235.
Schemske, D.W. and Paulter, L. (1984) The effects of pollen composition on fitness components in a neotropical herb. Oecologia 62, 31-36.
Simons, A.M. and Johnston, M.O. (2000) Variation in seed traits of Lobelia inflata (Campanulaceae): sources and fitness consequences. Am. J. Bot. 87, 124-132.
Susko, D.J. and Lovett-Doust, L. (2000) Patterns of seed mass variation and their effects on seedling traits in Alliaria petiolata (Brassicaceae). Am. J. Bot. 87, 56-66.
Temme, D.H. (1986) Seed size variability: a consequence of variable genetic quality among off-spring? Evolution 40, 414-417.
Trivers, R.L. (1974) Parent-offspring conflict. Am. Zool. 14, 249-264.
Tutin, T.G., Heywood, V.H., Burges, N.A., Moore, D.M., Valentine, D.H., Walters, S.M. and Webb, D.A. (1968) Flora Europaea, vol 2. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Uma Shaanker, R., Ganeshaiah, K.N. and Bawa, K.S. (1988) Parent-offspring conflict, sibling rivalry, and brood size patterns in plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 19, 177-205.
Waser, N.M., Price, M.V., Montalvo, A.M. and Gray, R.N. (1987) Female mate choice in a perennial herbaceous wildflower, Delphinium nelsoni. Trends Plant Sci. 1, 29-33.
Zhang, D.Y. and Jiang, X.H. (2000) Costly solicitation, timing of offspring conflict, and resource allocation in plants. Ann. Bot. 86, 123-131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bañuelos, M., Obeso, J. Maternal provisioning, sibling rivalry and seed mass variability in the dioecious shrub Rhamnus alpinus . Evolutionary Ecology 17, 19–31 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022430302689
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022430302689