Abstract
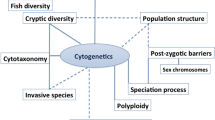
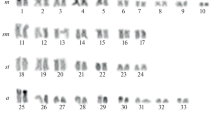
The aim of this review is to introduce current knowledge in the field of sturgeon genetics. The first section deals with sturgeon cytogenetics, reviewing karyotype organization and polyploidization events during evolution of Acipenseriformes. The second section concerns the results of applications of molecular biology to studies of phylogenetic relationships between extant species, intraspecific analysis of wild populations and stocks for conservation purposes, together with characterization of molecular markers for species identification, relevant to forensic and conservation issues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarcón, J.A. & M.C. Alvarez, 1999. Genetic identification of sparid species by isozyme markers: application to interspecific hybrids. Aquaculture 173: 95–103.
Arefjev, V.A., 1983. Polykaryogram analysis of ship, Acipenser nudiventris Lovetsky (Acipenseridae, Chondrostei). Voprosy Ichthyol. 23: 209–216.
Arefjev, V.A., 1993. NOR-banding studies of Acipenser baeri karyotype, pp. 30–31 in Int. Symp. Sturgeons. VNIRO Publishing, Moscow.
Arnason, U., S. Gretarsdottir & B. Widegren, 1992. Mysticete (baleen whale) relationships based upon the sequence of the common cetacean DNA satellite. Mol. Biol. Evol. 9: 1018–1028.
Artyukhin, E.N., 1995. On biogeography and relationships within the genus Acipenser. Sturg. Quart. 3(2): 6–8.
Avise, J.C., J. Arnold, R.M. Ball, E. Bermingham, T. Lamb, J.E. Neigel, C.A. Reeb & N.C. Saunders, 1987. Intraspecific phylogeography: the mitochondrial DNA bridge between population genetics and systematics. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 18: 489–522.
Bachmann, K., O.B. Goin & C.J. Goin, 1972. The nuclear DNA of Polypterus palmas. Copeia 1972: 363–365.
Bemis, W.E., E.K. Findeis & L. Grande, 1997. An overview of Acipenseriformes. Environ. Biol. Fish. 48: 25–72.
Bemis, W.E. & B. Kynard, 1997. Sturgeon rivers: an introduction to acipenseriform biogeography and life history. Environ. Biol. Fish. 48: 167–184.
Bennett, M.D., 1995. The development and use of genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) as a new tool in plant biosystematics, pp. 167–183 in Kew Chromosome Conference IV, edited by P.E. Brandham & M.D. Bennet. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, UK.
Berg, L.S., 1962. Freshwater Fishes of the USSR and Adjacent Countries, pp. 52–111, Vol. 1. (Translated by Israel Program for Scientific Translation, Jerusalem) Oldbourne Press, London.
Birstein, V.J. & V.P. Vasil'ev, 1987. Tetraploid-octoploid relationships and karyological evolution in the order Acipenseriformes (Pishes): karyotypes, nucleoli, and nucleolus-organizer regions in four acipenserid species. Genetica 73: 3–12.
Birstein, V.J., A.I. Poletaev & B.F. Goncharov, 1993. The DNA content in Eurasian sturgeon species determined by flow cytometry. Cytometry 14(4): 337–383.
Birstein, V.J., R. Hanner & R. DeSalle, 1997.Phylogeny of the Acipenseriformes: cytogenetic and molecular approaches. Environ. Biol. Fish. 48: 127–155.
Birstein, V.J. & R. DeSalle, 1998. Molecular phylogeny of Acipenserinae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 9: 141–155.
Blacklidge, K.H. & C.A. Bidwell, 1993.Three ploidy levels indicated by genome quantification in Acipenseriformes of North America. J. Hered. 84: 27–430.
Bowen, B.W. & J.C. Avise, 1990. Genetic structure of Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico populations of sea bass, menhaden, and sturgeon: influence of zoogeographic factors and life-history patterns. Mar. Biol. 107: 371–381.
Brown, J.R., A.T. Beckenbach & M.J. Smith, 1992a. Mitochondrial DNA length variation and heteroplasmy in populations of white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus). Genetics 132: 221–228.
Brown, J.R., A.T. Beckenbach & M. Smith, 1992b. Influence of Pleistocene glaciations and human intervention upon mitochondrial DNA diversity in white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus) populations. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 49: 358–367.
Brown, J.R., K. Beckenbach, A.T. Beckenbach & M.J. Smith, 1996. Length variation, heteroplasmy and sequence divergence in the mitochondrial DNA of four species of sturgeon (Acipenser). Genetics 142: 525–535.
Buroker, N.E., J.R. Brown, T.A. Gilbert, P.J. O'Hara, A.T. Beckenbach, W.K. Thomas & M.J. Smith, 1990. Length heteroplasmy of sturgeon mitochondrial DNA: an illegitimate elongation model. Genetics 124: 157–163.
Burtzev, J.A., J. Nikoljukin & E.V. Serebryakova, 1976. Karyology of the Acipenseridae family in relation to the hybridization and taxonomy problems. Acta Biol. Jugosl. Ser. Ichthyol. 8: 27–34.
Campton, D.E., A.L. Bass, F.A. Chapman & B.W. Bowen, 2000. Genetic distinction of pallid, shovelnose, and Alabama sturgeon: emerging species and the US endangered species act.Conserv. Genet. 1: 17–32.
Carlson, D.M., M.K. Kettler, S.E. Fisher & G.S. Whitt, 1982. Low genetic variability in paddlefish populations. Copeia 1982: 721–725.
Carvalho, G.R. & L. Hauser, 1995. Molecular genetics and the stock concept in fisheries, pp. 55–79 in Molecular Genetics of Fishes, edited by G.R. Carvalho & T.J. Pitcher. Chapman & Hall, London, UK.
Comincini, S., M. Lanfredi, R. Rossi & F. Fontana, 1998. Use of RAPD markers to determine the genetic relationships among sturgeons (Acipenseridae, Pisces). Fish. Sci. 64: 35–38.
De La Herrán, R., F. Fontana, M. Lanfredi, L. Congiu, M. Leis, R. Rossi, C. Ruiz Rejón, M. Ruiz Rejón & M.A Garrido-Ramos, 2001. Slow rates of evolution and sequence homogenization in an ancient satellite DNA family of sturgeons. Mol. Biol. Evol. 18: 432–436.
DeSalle, R. & V.J. Birstein, 1996. PCR identification of black caviar. Nature 381: 197–198.
Dingerkus, G. & W.M. Howell, 1976. Karyotypic analysis and evidence of tetraploidy in the North American paddlefish, Polyodon spathula. Science 194: 842–844.
Doukakis, P., V.J. Birstein, G.I. Ruban & R. DeSalle, 1999. Molecular genetic analysis among subspecies of two Eurasian sturgeon species, Acipenser baerii and A. stellatus. Mol. Ecol. 8: 117–127.
Ferguson, M.M., L. Bernatchez, M. Gatt, B.R. Konkle, S. Lee, M.L. Malott & R.S. McKinley, 1993. Distribution of mitochondrial DNA variation in lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens) from the Moose river basin, Ontario Canada. J. Fish. Biol. 43: 91–101.
Findeis, E.K., 1997. Osteology and phylogenetic relationships of recent sturgeons. Environ. Biol. Fish. 48: 73–126.
Flajšhans, M. & V. Vajcová, 2000. Odd ploidy levels in sturgeon suggest a backcross of interspecific hexaploid sturgeon hybrids to evolutionary tetraploid and/or octaploid parental species. Folia Zool. 49(2): 133–138.
Fontana, F., 1976. Nuclear DNA content and cytometric of erythrocytes of Huso huso L., Acipenser sturio L. and Acipenser naccarii Bonaparte. Caryologia 29: 127–138.
Fontana, F., 1994. Chromosomal nucleolar organizer regions in four sturgeon species as markers of karyotype evolution in Acipenseriformes (Pisces). Genome 37: 888–892.
Fontana, F. & G. Colombo, 1974. The chromosomes of Italian sturgeons. Experientia 30: 739–742.
Fontana, F., D. Jankovic & S. Zivkovic, 1975. Somatic chromosome of Acipenser ruthenus L. Arch. Biol. nauka, Beograd 27: 33–35.
Fontana, F., M. Lanfredi, R. Rossi, P. Bronzi & G. Arlati, 1996. Karyotypic characterization of Acipenser gueldenstaedtii with C-, AgNO3, and fluorescence banding techniques. Ital. J. Zool. 63: 113–118.
Fontana, F., R. Rossi, M. Lanfredi, G. Arlati & P. Bronzi, 1997. Cytogenetic characterization of cell lines from three sturgeon species. Caryologia 50: 91–95.
Fontana, F., J. Tagliavini, L. Congiu, M. Lanfredi, M. Chicca, C. Laurenti & R. Rossi, 1998a. Karyotypic characterization of the great sturgeon, Huso huso, by multiple staining techniques and fluorescent in situ hybridization. Mar. Biol. 132: 495–501.
Fontana, F., M. Lanfredi, M. Chicca, V. Aiello & R. Rossi, 1998b. Localization of the repetitive telomeric sequence (TTAGGG)n in four sturgeon species. Chrom. Res. 6: 303–306.
Fontana, F., M. Lanfredi, M. Chicca, L. Congiu, J, Tagliavini & R. Rossi, 1999. Fluorescent in situ hybridization with rDNA probes on chromosomes of Acipenser ruthenus and Acipenser naccarii (Osteichthyes, Acipenseriformes). Genome 42: 1008–1012.
Garrido-Ramos, M.A.,M.C. Soriguer, R. de la Herran, M. Jamilena, C. Ruiz Rejón, A. Domezain, J.A. Hernando & M. Ruiz Rejón, 1997. Morphometric and genetic analysis as proof of the existence of two sturgeon species in the Guadalquivir river. Mar. Biol. 129: 33–39.
Grande, L. & W.E. Bemis, 1991. Osteology and phylogenetic relationships of fossil and recentpaddlefishes (Polyodontidae) with comments on the interrelationships of Acipenseriformes. J. Vert. Paleo. 11 (suppl. No 1): 121 pp.
Guenette, S., E. Rassart & R. Fortin, 1992. Morphological differentiation of lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens) from the St. Lawrence river and Lac des Deux Montagnes (Quebec, Canada). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 49: 1959–1965.
Holcik, J. & L. Jedlicka, 1994. Geographical variation of some taxonomically important characters in fishes: the case of the bitterling Rhodeus sericeus. Environ. Biol. Fish. 41: 147–170.
Howell, M.W., 1977. Visualization of ribosomal gene activity: silver stains proteins associated with rRNA transcribed from oocyte chromosomes. Chromosoma 62: 361–367.
Jenneckens, I., J.N. Meyer, L. Debus, C. Pitra & A. Ludwig, 2000. Evidence of mitochondrial DNA clones of Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baeri, within Russian sturgeon, Acipenser gueldenstaedtii, caught in the River Volga. Ecol. Lett. 3(6): 503–508.
Kocher, T.D., W.K. Thomas, A. Meyer, S.V. Edwards, S.F. Paabo, F.X. Villablanca & A.C. Wilson, 1989. Dynamics of mtDNA evolution in animals: amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 6196–6200.
Krieger J., P.A. Fuerst & T.M. Cavender, 2000. Phylogenetic relationships of the north american sturgeon (order Acipenseriformes) based on mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1: 64–72.
Lanfredi, M., L. Congiu, M.A. Garrido-Ramos, R. De La Herrán, M. Leis, M. Chicca, R. Rossi, J. Tagliavini, C. Ruiz Rejón, M. Ruiz Rejón & F. Fontana, 2001. Chromosomal location and evolution of a satellite DNA family in seven sturgeon species. Chrom. Res. 9: 47–52.
Li, M.F., V. Marrayatt, C. Annand & P. Odense, 1985. Fish cell culture: two newly developed cell lines from Atlantic sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus) and guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Can. J. Zool. 63: 2867–2874.
Ludwig, A. & F. Kirschbaum, 1998. Comparison of mitochondrial DNA sequences between the European and the Adriatic sturgeon. J. Fish. Biol. 52: 1289–1291.
Ludwig, A., B. May, L. Debus & I. Jenneckens, 2000. Heteroplasmy in the mtDNA control region of sturgeon (Acipenser, Huso and Scaphirhynchus). Genetics 156: 1933–1947.
May, B., C. C. Krueger & H. L. Kincaid, 1997.Genetic variation at microsatellite loci in sturgeon: primer sequence homology in Acipenser and Scaphyrhynchus. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 54: 1542–1547.
Mayden, R.L. & B.R. Kuhajda, 1996. Systematics, taxonomy, and conservation status of the endangered Alabama sturgeon Scaphirhynchus suttkusi William and Clemmer (Actinopterygii, Acipenseridae). Copeia 1996: 241–275.
Medrano, L., G. Bernardi, J. Couturier, B. Dutrillaux & G. Bernardi, 1988. Chromosome banding and genome compartmentalization in fishes. Chromosoma 96: 178–183.
Meyer, A., T.D. Kocher, P. Basasibwaki & A.C. Wilson, 1990. Monophyletic origin of Lake Victoria cichlid fishes suggested by mitochondrial DNA sequences. Nature 347: 550–553.
Miracle, A.L. & D.E. Campton, 1995. Tandem repeat sequence variation and length heteroplasmy in the mitochondrial DNA D-loop of the threatened Gulf of Mexico sturgeon, A. oxyrinchus desotoi. J. Hered. 86: 22–27.
Mirsky, A.E. & H. Ris, 1951. The DNA content of animal cells and its evolutionary significance. J. Gen. Physiol. 34: 451–462.
Nowruzfashkhami, M.R., M. Pourkazemi & S. Baradarannoveiri, 2000. Chromosome study of persian sturgeon Acipenser persicus B. Cytologia 65: 197–202.
Ohno, S., J. Muramoto, C. Stenius, L. Christian & W.A. Kitterell, 1969. Microchromosomes in holocephalian, chondrostean and holostean fishes. Chromosoma 226: 35–40.
Ohno, S., 1970. Evolution by Gene Duplication. Springer-Verlag, Heildelberg, New York.
Ong, T.L., J. Stabile, I. Wirgin & J.R. Waldman, 1996. Genetic divergence between Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus and A. o. desotoi as assessed by mitochondrial DNA sequencing analysis. Copeia 1996: 464–469.
Patterson, C., 1982. Morphology and interrelationships of primitive actinopterygian fishes. Am. Zool. 22: 241–259.
Pendás, A.M., P. Morán, J.L. Martinez & E. Garcia-Vazquez, 1995. Application of 5S in Atlantic salmon, brown trout, and in Atlantic salmon X brown trout hybrid identification. Mol. Ecol. 4: 275–276.
Phelps, S.R. & F.W. Allendorf, 1983. Genetic identity of pallid and shovelnose sturgeon (Scaphirhynchus albus and S. platorynchus). Copeia 1983: 696–700.
Pourkazemi, M., D.O.F. Skibinski & J.A. Beardmore, 1999. Application of mtDNA d-loop region for the study of Russian sturgeon population structure from Iranian coastline of the Caspian Sea. J. Appl. Ichtyol. 15: 23–28.
Ráb, P., V.A. Arefjev & M. Rábova, 1996. C-banded karyotype of the sterlet, Acipenser ruthenus, from the Danub river. Sturg. Quart. 4(4): 10–12.
Rehbein, H., C. Gonzales-Sotelo, R. Perez-Martin, J. Quinteiro, M. Rey-Mendez, S. Pryde, I.M. Mackie & T. Santos, 1999. Differentiation of sturgeon caviar by single strand conformation polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) analysis. Archiv für Lebensmittelhygiene 50: 13–17.
Rochard, E., P. Williot, G. Castelnaud & M. Lepage, 1991. Elements de systematique et de biologie des populations sauvages d'esturgeons, pp. 475–507, in Acipenser, edited by P. Williot. Cemagref Publication.
Schmid, M. & M. Guttenbach, 1988. Evolutionary diversity of reverse fluorescent chromosome bands in vertebrates. Chromosoma 97: 101–114.
Schweizer, D., 1976. Reverse fluorescent chromosome banding with chromomycin and DAPI. Chromosoma 58: 307–324.
Serebryakova, E.V., 1972. Some data on the chromosome complexes in Acipenseridae, pp. 98–106 in Genetics, Selection, and Hybridization of Fish, edited by B.I. Cherfas (Translated from Russian by Israel Program for Scientific Translations). Keter Press Binding: Wiener Bindery Ltd. Jerusalem.
Sola, L., C. Cordisco, S. Bressanello & S. Cataudella, 1994. Cytogenetic characterization of the North American white sturgeon Acipenser transmontanus (Pisces, Acipenseridae). Proc. VIII Congr.SEI: 64–65.
Stabile, J., J.R. Waldman, F. Parauka & I Wirgin, 1996. Stock structure and home fidelity in Gulf of Mexico sturgeon (A. oxyrinchus desotoi) based on restriction fragment length polymorphism and sequence analyses of mitochondrial DNA. Genetics 144: 767–775.
Suciu, R. & C. Ene, 1996. Kariological study of the stellate sturgeon, Acipenser stellatus,from the Danube river. Sturg. Quart. 4: 14–15.
Tagliavini, J., P. Williot, L. Congiu, M. Chicca, M. Lanfredi, R. Rossi & F. Fontana, 1999. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of the karyotype of the European Atlantic sturgeon, Acipenser sturio. Heredity 83: 520–525.
Van Eenennaam, A.L., J.D. Murray & J.F. Medrano, 1998. Mitotic analysis of the North American white sturgeon, Acipenser transmontanus Richardson (Pisces, Acipenseridae), a fish with a very high chromosome number. Genome 41: 266–271.
Van Eenennaam, A.L., J.D. Murray & J.F. Medrano, 1999. Karyotype of the American green sturgeon. T. Am. Fish. Soc. 128: 175–177.
Vasil'ev, V.P., L.I. Sokolov & E.V. Serebryakova, 1980. Karyotype of the Siberian sturgeon Acipenser baerii Brandt from the Lena River and some questions of the acipenserid karyotypic evolution. Vopr. Ikhtiol. 23: 814–822.
Vasil'ev, V.P., 1985. Evolutionary Karyology of Fishes, edited by V.N. Orlov. Moskov, USSR: Nauka.
Vialli, M., 1957. Volume et contenu en ADN par noyau. Exptl. Cell. Res. Suppl. 4: 284–293.
Vos, P., R. Hogers, M. Bleeker, M. Reijans, T. van de Lee, M. Hornes, A. Frijters, J. Pot, J. Peleman & M. Kuiper, 1995. AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucl. Acids Res. 23: 4407–4414.
Waldman, J.R., J.T. Hart & I.I. Wirgin, 1996. Stock composition of the New York bight Atlantic sturgeon fishery based on analysis of mitochondrial DNA. T. Am. Fish. Soc. 125: 364–371.
Wichman, H.A., C.T. Payne, O.A. Ryder, M.J. Hamilton, M. Maltbie & R.J. Baker, 1991. Genomic distribution of heterochromatic sequences in equids: implications to rapid chromosomal evolution. J. Hered. 82: 369–377.
Wolf, C., P. Hubner & J. Luthy, 1999. Differentiation of sturgeon species by PCR-RFLP. Food Res. Int. 31: 699–705.
Yu, X., T. Zhou, K. Li, Y. Li & M. Zhou, 1987. On the karyosystematics of cyprinid fishes and a summary of fish chromosome studies in China. Genetica 72: 225–236.
Zhang, S., Y. Zhang, X. Zheng, Y. Chen, H. Deng, D. Wang, Q. Wie, Y. Zhang, L. Nie & Q. Wu, 2000. Molecular phylogenetic systematics of twelve species of Acipenseriformes based on mtDNA ND4L-ND4 gene sequence analysis. Sci. China(C) 43: 129–137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fontana, F., Tagliavini, J. & Congiu, L. Sturgeon genetics and cytogenetics: recent advancements and perspectives. Genetica 111, 359–373 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013711919443
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013711919443