Abstract
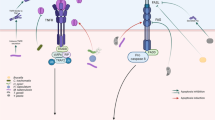
Interaction of mammalian cells with pathogenic bacteria results in a whole variety of responses in the infected cells including internalization or phagocytosis of the bacterium, release of cytokines, secretion of defensins or production of oxygen radicals. However, recent studies pointed out that many bacteria are able to trigger apoptosis in the host cell. The induction of apoptosis upon infection results from a complex interaction of bacterial proteins with cellular proteins finally mediating apoptosis. Thus, bacteria are able to activate several pro-apoptotic proteins, e.g. caspases, to inactivate anti-apoptotic proteins, e.g. NFκB or MAP-kinases, or to upregulate endogenous receptor/ligand systems, that induce apoptosis, on the surface of the infected cell. Host cell apoptosis very often serves the bacteria to attack the host and to gain access to the tissue. However, in some infections, apoptosis of mammalian cells significantly contributes to the host defense against the bacteria further indicating the role of apoptosis in host-pathogen interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weinrauch Y, Zychlinski A. The induction of apoptosis by bacterial pathogens. Annu Rev Microbiol 1999; 53: 155-187.
Savill J, Fadok V. Corpse clearance defines the meaning of cell death. Nature 2000; 407: 784-788.
Schmitz I, Kirchhoff S, Krammer PH. Regulation of death receptor-mediated apoptosis pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2000; 32: 1123-1136.
Kroemer G, Dallaporta B, Resche-Rigon M. The mitochondrial death/life regulator in apoptosis and necrosis. Annu Rev Physiol 1998; 60: 619-642.
Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang X. Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: Requirment for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell 1996; 86: 147-157.
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, et al. Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 1999; 397: 441-446.
Zou H, Henzel WJ, Liu X, et al. Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. Elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase 3. Cell 1997; 90: 405-413.
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, et al. Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death. Nature 2001; 410: 549-554.
Yang YL, Li XM. The IAP family: Endogenous caspase inhibitors with multiple biological activities. Cell Res 2000; 10: 169-177.
Newton K, Strasser A. Cell death control in lymphocytes. Adv Immunol 2000; 76: 179-226.
O'Connor L, Strasser A. The Bcl-2 protein family. Results Probl Cell Differ 1999; 23: 173-207.
Reed JC. Bcl-2 family proteins. Oncogene 1998; 17: 3225-3236.
Kubori T, Sukhan A, Aizawa SI, Galan JE. Molecular characterization and assembly of the needle complex of the Salmonella typhimurium type III protein secretion system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 10225-10230.
Kubori T, Matsushima Y, Nakamura D, et al. Supramolecular structure of the Salmonella typhimurium type III protein secretion system. Science 1998; 280: 602-605.
Zychlinsky A, Prevost MC, Sansonetti PJ. Shigella flexneri induces apoptosis in infected macrophages. Nature 1992; 358: 167-169.
Zychlinsky A, Kenny B, Menard R, et al. IpaB mediates macrophage apoptosis induced by Shigella flexneri. Mol Microbiol 1994; 11: 619-627.
Hilbi H, Moss JE, Hersh D, et al. Shigella-induced apoptosis is dependent on caspase-1 which binds to IpaB. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 32895-32900.
Chen Y, Smith MR, Thirumalai K, Zychlinski A. A bacterial invasin induces macrophage apoptosis by binding directly to ICE. EMBO J 1996; 15: 3853-3860.
Hersh D, Monack DM, Smith MR, et al. The Salmonella invasin SipB induces macrophage apoptosis by binding to caspase-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 2396-2401.
Chen LM, Kaniga K, Galan JE. Salmonella spp. are cytotoxic for cultured macrophages. Mol Microbiol 1996; 21: 1101-1115.
Menzies BE, Kourteva I. Internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by endothelial cells induces apoptosis. Infect Immun 1998; 66: 5994-5998.
Esen M, Schreiner B, Jendrossek V, et al. Mechanisms of Staphylococcus aureus induced apoptosis of human endothelial cells. Apoptosis 2001; 6: 431-439.
Bleves S, Cornelis GR. How to survive in the host: The Yersinia lesson. Microbes Infect 2000; 2: 1451-1460.
Monack DM, Mecsas J, Bouley D, Falkow S. Yersinia-induced apoptosis in vivo aids in the establishment of a systemic infection of mice. J Exp Med 1998; 188: 2127-2137.
Orth K, Xu Z, Mudgett MB, et al. Disruption of signaling by Yersinia effector YopJ, a ubiquitin-like protein protease. Science 2000; 290: 1594-1597.
Orth K, Palmer LE, Bao ZQ, et al. Inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase superfamily by a Yersinia effector. Science 1999; 285: 1920-1923.
Denecker G, Declercq W, Geuijen CAW, et al. Yersinia enterocolitica YopP-induced apoptosis of macrophages involves the apoptotic signaling cascade upstream of Bid. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 19706-19714.
Grassmé H, Kirschnek S, Riethmueller J, et al. Host defense to Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires CD95/CD95 ligand interaction on epithelial cells. Science 2000; 290: 527-530.
Valente E, Assis MC, Alvim IMP, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces apoptosis in human endothelial cells. Microbial Pathogenesis 2000; 29: 345-356.
Aballay A, Ausubel FM. Programmed cell death mediated by ced-3 and ced-4 protects Caenorhabditis elegans from Salmonella typhimurium-mediated killing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001, 98: 2735-2739.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grassmé, H., Jendrossek, V. & Gulbins, E. Molecular mechanisms of bacteria induced apoptosis. Apoptosis 6, 441–445 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012485506972
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012485506972