Abstract
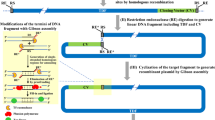
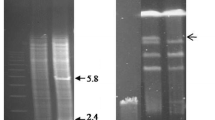
Streptomyces species have a linear chromosome of approximately 8 Mb in size. Many strains also carry linear plasmids. Most of these linear elements contain terminal proteins covalently bound to the 5′ ends of the DNA. Using a method for the visualisation of terminal DNA fragments in agarose gels, it was possible to see three fragments in S. rimosus and five fragments in S. avermitilis. The method was also used to clone the 298 bp BamHI fragment carrying the left end of plasmid SLP2. Analysis of the sequence showed that the end resembled other Streptomyces chromosome and plasmid ends, but there were eight palindromes (instead of seven) and a tandem duplication of a 14 bp sequence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burg RW, Miller BM, Baker EE, Birnbaum J, Currie SA, Hartmann R, Kong YL, Monaghan RL, Olson G, Putter I, Tunac JB, Wallick H, Stapley EO, Õiwa R & Õmura S (1979) Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: producing organism and fermentation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 15: 361–367
Chen CW, Yu TW, Lin YS, Kieser HM & Hopwood DA (1993) The conjugative plasmid SLP2 of Streptomyces lividans is a 50 kb linear molecule. Mol. Microbiol. 7: 925–932
Coombs DH & Pearson GD (1978) Filter-binding assay for covalent DNA-protein complexes: adenovirus DNA-terminal protein complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75: 5291–5295
Greener A (1990) E.coli Sure: clone 'unclonable' DNA. Strategies 3: 5–6
Hopwood DA, Kieser T, Wright HM & Bibb MJ (1983) Plasmids, recombination and chromosome mapping in Streptomyces lividans 66. J. Gen. Microbiol. 129: 2257–2269
Hopwood DA, Bibb MJ, Chater KF, Kieser T, Bruton CJ, Kieser HM, Lydiate DJ, Smith CP, Ward JM & Schrempf H (1985) Genetic manipulation of Streptomyces. A Laboratory Manual. John Innes Foundation, UK.
Hopwood DA, Chater KF & Bibb MJ (1994) Genetics of antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2), a model streptomycete in genetics and biochemistry of antibiotic production. Vining LC, Stuttard C (Eds) (pp 65–102). Butterworth-Hinemann, Philadephia
Huang CH, Yang YL, Lin YS & Chen CW (1998) The telomeres of the Streptomyces chromosomes contain conserved palindromic sequences with potential to form complex secondary structures. Mol. Microbiol. 28: 905–916
Irnich S & Cullum J (1993) Random insertion of Tn4560 in Streptomyces lividans and Streptomyces avermitilis. Biotechnol. Lett. 15: 895–900
Kieser HM, Kieser T & Hopwood DA (1992) A combined genetic and physical map of the Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) chromosome. J. Bacteriol. 174: 5496–5507
Kinashi H, Shimaji-Murayama M & Sakai A (1987) Giant linear plasmids in Streptomyces which code for antibiotic biosynthesis genes. Nature 328: 454–456
Kinashi H, Shimaji-Murayama M & Hanafusa T (1991) Nucleotide sequence analysis of the unusually long terminal inverted repeats of a giant linear plasmid, SCP1. Plasmid 26: 123–130
Leblond P, Fischer G, Francou FX, Berger M, Guerineau M & Decaris B (1996) The unstable region of Streptomyces ambofaciens includes 210 kb terminal inverted repeats flanking the extremities of the linear chromosomal DNA. Mol. Microbiol. 19: 261–271
Lezhava A, Mizukami T, Kajitani T, Kameoka D, Redenbach M, Shinkawa H, Nimi O & Kinashi H (1995) Physical map of the linear chromosome of Streptomyces griseus. J. Bacteriol. 177: 6492–6498
Lin YS, Kieser HM, Hopwood DA & Chen CW (1993) The chromosomal DNA of Streptomyces lividans 66 is linear. Mol. Microbiol. 10: 923–933
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF & Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Pandza K, Pfalzer G, Cullum J & Hranueli D (1997) Physical mapping shows that the unstable oxytetracycline gene cluster of Streptomyces rimosus lies close to one end of the linear chromosome. Microbiol. 143: 1493–1501
Pandza S, Biukovit G, Paravit A, Dadbin A, Cullum J & Hranueli D (1998) Recombination between the linear plasmid pPZG101 and the linear chromosome of Streptomyces rimosus can lead to exchange of ends. Mol. Microbiol. 28: 1165–1176
Peñalva MA & Salas M (1982) Initiation of phage φ29 DNA replication in vitro: Formation of a covalent complex between the terminal, p3, and 5′-dAMP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79: 5522–5526
Pigac J & AlaLcevit M (1979) Mapping of oxytetracycline genes in Streptomyces rimosus. Period. Biol. 81: 575–582
Reeves AR, Post DA & Vanden Boom TJ (1998) Physical-genetic map of the erythromycin-producing organism Saccharopolyspora erythraea.Microbiol. 144: 2151–2159
Stoll A & Cullum J (2000) An improved method for the isolation and visualisation of terminal protein-bound DNA fragments in actinomycetes. Biotechniques (in press).
Thomas CA, Saigo K, McLeod E & Ito J (1979) The separation of DNA segments attached to protein. Anal. Biochem. 93: 158–166
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J & Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequence of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33: 103–119
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoll, A., Horvat, LI., Lopes-Shikida, S.A. et al. Isolation and cloning of Streptomyces terminal fragments. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 78, 223–226 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010228110822
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010228110822