Abstract
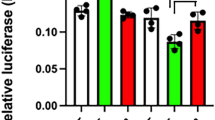
The proopiomelanocortin (POMC) gene expressed in corticotrophs of the anterior pituitary encodes several biologically active peptides and is primarily under the positive control of hypophysiotropic factors (e.g. corticotropin releasing hormone). Using AtT20 cells as a model, we show that these factors increase levels of POMC primary RNA transcripts representative of a transcriptional activation of the gene. This effect is mimicked by several activators of the cAMP signaling pathway. Inhibition of protein synthesis with cycloheximide did not modify the CRH-induced increase in POMC hnRNA suggesting that these early effects are mediated by preexisting transcription factors. Using a reporter gene containing 706 bp of the POMC promoter region, we observe transcriptional activation with the same compounds, their effects being abolished when protein kinase A (PKA) is inactivated by a dominant inhibitory mutant. Promoter deletion analyses mapped an essential cAMP inducible element within the first exon of the POMC gene. This element (PTRE: TGACTAA) located at nucleotides +41/+47 was shown to bind the cAMP responsive element binding protein (CREB) by gel shift analyses and confers strong transcriptional activation by an expression vector coding a CREB-VP16 activator domain fusion protein. Further, expression of a dominant inhibitory mutant of CREB reduced cAMP stimulated transcription of the full length POMC promoter and the PTRE. Taken together, these results show that the major hypophysiotropic factors stimulate POMC transcription through a signaling cascade that involves PKA and CREB.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Therrien M, Drouin J. Pituitary pro-opiomelanocortin gene expression requires synergistic interactions of several regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol 1991;11:3492–3503.
Riegel AT, Yang L, Remenick J, Wolford RG, Berard DS, Hager GL. Prooopiomelanocortin gene promoter elements required for constitutive and glucocorticoid-repressed transcription. Mol Endocrinol 1991;5:1973–1982.
Liu B, Hammer GD, Rubinstein M, Mortrud M, Low MJ. Identification of DNA elements cooperatively activating proopiomelanocortin gene expression in the pituitary glands of transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol 1992;12:3978–3990.
Drouin J, Sun YL, Nemer M. Glucocorticoid repression of pro-opiomelanocortin gene transcription. J Steroid Biochem 1989;34:63–69.
Levin N, Roberts JL. Positive regulation of proopiomelanocortin gene expression in corticotropes and melanotropes. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology 1991;12:1–22.
Loeffler JP, Kley N, Pittius CW, Hollt V. Corticotropin-releasing factor and forskolin increase proopiomelanocortin messenger RNA levels in rat anterior and intermediate cells in vitro. Neurosci Lett 1985;62:383–388.
Loeffler JP, Kley N, Pittius CW, Hollt V. Calcium ion and cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate regulate proopiomelanocortin messenger ribonucleic acid levels in rat intermediate and anterior pituitary lobes. Endocrinology 1986;119: 2840–2847.
Eberwine JH, Jonassen JA, Evinger MJQ, Roberts JL.Complex transcriptional regulation by glucocorticoids and corticotropin-releasing hormone of proopiomelanocortin gene expression in rat pituitary cultures.DNA 1987;6: 483–492.
Reisine T D, Rougon G, Barbet J, Affolter HU. Corticotropin-releasing factor-induced adrenocorticotropin hormone release and synthesis is blocked by incorporation of the inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase into anterior pituitary tumor cells by liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1985;82:8261.
Luini A, Lewis D, Guild S, Corda D, Axelrod J. Hormone secretagogues increase cytosolic calcium by increasing cAMP in corticotropin-secreting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1985;82:8034–8038.
Von Dreden G, Loeffler JP, Grimm C, Höllt V. Influence of calcium ions on proopiomelanocortin mRNA levels in clonal anterior pituitary cells. Neuroendocrinology 1988;47: 32–37.
Dave JR, Eiden LE, Lozovsky D, Waschek JA, Eskay RL. Calcium-independent and calcium-dependent mechanisms regulate corticotropin-releasing factor-stimulated proopiomelanocortin peptide secretion and messenger ribonucleic acid production. Endocrinology 1987;120, 305–311.
Jin WD, Boutillier AL, Glucksmann MJ, Salton SRJ, Loeffler JP, Roberts JL. Characterization of a corticotropin-releasing hormone-responsive element in the rat proopiomelanocortin gene promoter and molecular cloning of its binding protein. Mol Endocrinol 1995;8:1377–1388.
Boutillier AL, Monnier D, Lorang D, Lundblad JR, Roberts JL, Loeffler JP. Corticotropin-releasing hormone stimulates proopiomelanocortin transcription by cFos-dependent and-independent pathways: Characterization of an AP1 site in exon 1. Mol Endocrinol 1995;9:745–755.
Roberts JL, Lundblad JR, Eberwine JH, Fremeau RT, Salton SRJ, Blum M. Hormonal regulation of POMC gene expression in pituitary. Ann NY Acad Sci 1987;512:275–285.
Kraus J, Höllt V. Identification of a cAMP-response element on the human proopiomelanocortin gene upstream promoter. DNA Cell Biol 1995;14:103–110.
Autelitano DJ. Glucocorticoid regulation of c-fos, c-jun and transcription factor AP-1 in the AtT-20 corticotrope cell. J Neuroendocrinol 1994;6:627–637.
Mc Knight GS, Cadd GG, Clegg CH, Otten AD, Correll LA. Expression of wild-type and mutant subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. 1988;53:111–119.
Liu F, Green MR. A specific member of the ATF transcription factor family can mediate transcription activation by the adenovirus Ela protein. Cell 1990;61:1217–1224.
Gonzalez GA, Menzel P, Leonard J, Fischer WH, Montminy MR. Characterization of motifs which are critical for activity of the cyclic AMP-responsive transcription factor CREB. Mol Cell Biol 1991;11:1306–1312.
Levin N, Blum M, Roberts JL. Modulation of basal and corticotropin-releasing factor-stimulated proopiomelanocortin gene expression by vasopressin in rat anterior pituitary. Endocrinology 1989;125:2957–2966.
Loeffler JP, Behr JP. Gene transfer into primary and established mammalian cell lines with lipopolyamine-coated DNA. Methods in Enzymology 1993;217:599–617.
Seed B, Sheen JY. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene 1988;67: 271–277.
Dignam JD, Lebovitz RM, Roeder RG. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res 1983; 11:1475–1489.
Roberts JL, Levin N, Lorang D, Lundblad JR, Dermer S, Blum M. Regulation of pituitary proopiomelanocortin gene expression. Handbook of Exper Pharm. Opioids I, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. 1993;104: 1–39.
Jeannotte L, Trifino MA, Plante RK, Chamberland M, Drouin J. Tissue-specific activity of the pro-opiomelanocortin gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol 1987;7:4058–4064.
Labrie F, Veilleux R, Lefevre G, Coy DH, Sueiras-Diaz J, Schally AV. Corticotropin-releasing factor stimulates accumulation of adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate in rat pituitary corticotrophs. Science 1982;216:1007–1008.
Aguilera G, Harwood JP, Wilson JX, Morell J, Brown JH, Catt KJ. Mechanisms of action of corticotropin-releasing factor and other regulators of corticotropin release in rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem 1983;258:8039–8045.
Young SL, Nielsen CP, Lundblad JR, Roberts JL, Melner MH. Gonadotropin regulation of the rat proopiomelanocortin promoter: characterization by transfection of primary ovarian granulosa cells. Mol Endocrinol 1989;3:15–21.
Boutillier AL, Barthel F, Roberts JL, Loeffler JP. Beta-adrenergic stimulation of cFOS via protein kinase A is mediated by cAMP regulatory element binding protein (CREB)-dependent and tissue-specific CREB-independent mechanisms in corticotrope cells. J Biol Chem 1992;267: 23520–23526.
Boutillier AL, Sassone-Corsi P, Loeffler JP. The protooncogene c-fos is induced by corticotropin-releasing factor and stimulates proopiomelanocortin gene transcription in pituitary cells. Mol Endocrinol 1991;5:1301–1310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boutillier, AL., Gaiddon, C., Lorang, D. et al. Transcriptional Activation of the Proopiomelanocortin Gene by Cyclic AMP-responsive Element Binding Protein. Pituitary 1, 33–43 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009966808106
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009966808106