Abstract
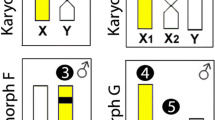
A multiple sex chromosome system of the X1X1X2X2:X1X2Y type is reported to occur in the fish species Brachyhypopomus pinnicaudatus (Gymnotiformes, Hypopomidae), being the second occurrence of this sex chromosome system in Gymnotiformes and the fifth among Neotropical freshwater fish. The possible origin of this system was hypothesized to be a centric fusion, which occurred in an ancestral form, of two medium-sized acrocentrics, giving origin to the metacentric neo-Y. Heterochromatic DAPI-positive regions were visualized in the pericentromeric region of all the chromosomes, including the Y-chromosome. In-situ hybridization with (TTAGGG) n (all-human-telomeres probe) did not detect any telomeric interstitial regions (ITS), indicating a possible loss of terminal segments of the chromosomes involved in the neo-Y formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allendorf FW, Thorgaard GH (1984) Tetraploidy and the evolution of Salmonid fishes. In: Turner BJ, ed. Evolution of Fishes. New York: Plenum, pp 1-53.
Almeida-Toledo LF, Foresti F, Toledo-Filho SA (1984) Complex sex chromosome system in Eigenmannia sp. (Pisces, Gymnotiformes). Genetica 64: 165-169.
Almeida-Toledo LF, Foresti F, Toledo-Filho SA (1985) Spontaneous triploidy and NOR activity in Eigenmannia sp. (Pisces, Sternopygidae) from the Amazon basin. Genetica 66: 85-88.
Almeida-Toledo LF, Viegas-Pequignot E, Foresti F, Toledo-Filho SA, Dutrillaux B (1988) BrdU replication patterns demonstrating chromosome homeologies in two fish species, genus Eigenmannia. Cytogenet Cell Genet 48: 117-120.
Almeida-Toledo LF, Foresti F, Daniel MFZ, Toledo-Filho SA (1999) Sex chromosome evolution in fish: the formation of the neo-Y chromosome in Eigenmannia (Gymnotiformes). Chromosoma (in press).
Bertollo LAC, Takahashi CS, Moreira-Filho O (1983) Multiple sex chromosomes in the genus Hoplias (Pisces, Erythrinidae). Cytologia 48: 1-12.
Bertollo LAC, Fontes MS, Fenocchio AS, Cano J (1997) The X1X2Y sex chromosome system in the fish Hoplias malabaricus. I. G-, C and chromosome replication banding. Chromosome Res 5: 493-499.
Dergan JÁ, Bertollo LAC (1990) Karyotypic diversification in Hoplias malabaricus (Ostheichthyes, Erythrinidae) of the São Francisco and Alto Paraná basins, Brazil. Rev Brasil Genet 13: 755-756.
Dias AL, Foresti F (1993) Cytogenetic studies on fishes of the family Pimelodidae (Siluroidei). Rev Brasil Genet 16(3): 585-600.
Feldberg E, Porto JIR, Bertollo LAC (1992) Karyotype evolution in Curimatidae (Teleostei, Characiformes) from the Amazon Region. I. Studies on the genera Curimata, Psectrogaster, Steindachnerina and Curimatella. Rev Brasil Genet 15(2): 369-383.
Howell WM Black DA (1980) Controlled silver-staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Experientia 36: 1014-1015.
Moreira-Filho O, Bertollo LAC, Galetti Jr PM (1980) Evidences for a multiple sex chromosome system with female heterogamety in Apareiodon affinis (Pisces, Parodontidae). Caryologia 33: 83-91.
Moreira-Filho O, Bertollo LAC, Galetti Jr PM (1993) Distribution of sex chromosomes mechanisms in Neotropical fish and description of a ZZ/ZW system in Parodon hilarii (Parodontidae). Caryologia 46: 115-125.
Robertson WMRB (1916) Chromosome studies I. Taxonomic relationships shown in the chromosomes of Tettegidae and Acrididiae: V-shaped chromosomes and their significance in Acrididae, Locustidae and Grillidae: chromosomes and variation. J Morphol 27: 179-331 [cited in Slijepcevic 1998].
Schmid M, Haaf T, Geile B, Sims S (1983) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. VIII. An unusual XY/XX-sex chromosome system in Gastrothecha riobambae (Anura, Hylidae). Chromosoma 88: 69-82.
Slijepcevic P (1998) Telomeres and mechanisms of Robertsonian fusion. Chromosoma 107: 136-140.
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75: 304-306.
Uyeno T, Miller RR (1971) Multiple sex chromosomes in a Mexican Cyprinodontidae fish. Nature 231: 452-453.
Uyeno T, Miller RR (1972) Second discovery of multiple sex chromosome among fishes. Experientia 15: 223-226.
White MJD (1973) Animal Cytology and Evolution. 3rd edn. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Almeida-Toledo, L.F., Daniel-Silva, M.F.Z., Lopes, C.E. et al. Sex chromosome evolution in fish. II. Second occurrence of an X1X2Y sex chromosome system in Gymnotiformes. Chromosome Res 8, 335–340 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009287630301
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009287630301