Abstract
Objectives: Despite being in use for nearly two decades, the utility of [18F]2-fluoro-2deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography (FDG PET) in the evaluation and treatment of brain tumors remains controversial. We retrospectively analyzed all patients with histologically proven gliomas, between the years 1990 and 2000, who underwent FDG PET studies at various stages of their treatment and who were followed till either death or for a minimum period of 1 year in an attempt to bring resolution to this controversy.
Methods: All PET scans prior to 1997 were acquired on an ECAT 951/31 scanner in 2D. Scans since 1997 were obtained on a Siemens HR+ scanner in 3D mode. The majority of FDG PET scans were co-registered with the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans to aid in diagnosis and therapy. Based on independent visual inspection, two board certified nuclear medicine physicians graded the highest activity level of the tumor using the metabolic grading: 0 = no uptake; 1 = uptake less or equal to normal white matter; 2 = uptake greater than normal white matter and less than gray matter; 3 = uptake equal to or greater than gray mater. The measure of association of lambda λ was used to measure the strength of predictive ability of FDG PET for pathological grading of the gliomas. The Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to assess the significance of grade of uptake on survival.
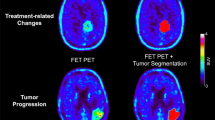
Results: A total of 331 patients were analyzed of which 137 had a PET scan prior to histological diagnosis and therapeutic intervention (mean age = 46.5years; M:F = 1.7:1). Eighty six percent (143/166) of the patients with low uptake (metabolic scores 0,1) had low-grade gliomas (grade I,II) and 14% (23/166) high-grade gliomas (grade III,IV) on histologic examination. Ninety four percent (154/165) of the patients with high uptake (metabolic scores 2,3) on PET had high-grade gliomas and 7% (11/165) had low-grade gliomas on histologic examination. The grade of uptake had increasing significance on survival as the level increased from 'low' to 'high' (P = 0.0009). Ninety four percent (156/166) of the patients with low uptake survived for >1 year (median survival of 28 months) and 19% survived for >5 years. Only 29% (48/165) of patients with high uptake survived for >1 year, (median survival of 11 months) and none survived for >5 years. Irrespective of when the scan showed a high uptake of FDG, before or after intervention, the prognosis following that scan was poor.
Conclusions: Our observations confirm the utility of FDG PET as a prognostic tool for the histological grading and survival in patients with gliomas and appears to more than complement pathological grading.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Chiro G, DeLaPaz RL, Brooks RA: Glucose utilization of cerebral gliomas measured by [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography. Neurology 32: 1323–1329, 1982
Di Chiro G: Positron emission tomography using [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose in brain tumors: a powerful diagnostic and prognostic tool. Invest Radiol 22: 360–371, 1986
Di Chiro G: Positron emission tomography using [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose in brain tumors. A powerful diagnostic and prognostic tool. Invest Radiol 22: 360–371, 1987
Kubota R, Yamada S, Kubota K, Ishiwata K, Tamahashi N, Ido T: Intratumoral distribution of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose in vivo: high accumulation in macrophages and granulation tissues studied by microautoradiography. J Nucl Med 33: 1972–1980, 1992
Janus TJ, Kim EE, Tilbury R, Bruner JM, Yung WK: Use of [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in patients with primary malignant brain tumors. Ann Neurol 33: 540–548, 1993
Alavi JB, Alavi A, Chawluk J, Kushner M, Powe J, Hickey W, Reivich M: Positron emission tomography in patients with glioma. A predictor of prognosis. Cancer 62: 1074–1078, 1988
Patronas NJ, De Chiro G, Kufta C, Bairamian D, Kornblith PL, Simon R, Larson SM: Prediction of survival in glioma patients by means of positron emission tomography. J Neurosurg 62: 816–822, 1985
Hamacher K, Coenen HH, Stoklin G: Efficient stereospecific synthesis of no-carrier-added-2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose using aminopolyether supported nucleophilic substitution. J Nucl Med 27: 235–238, 1986
Ding L, Goshtasby A, Satter M: Volume image registration by template matching. Image Vision Comput 19: 821–832, 2001
Evans AC, Marrett S, Collins L, Peters TM: Anatomicalfunctional correlative analysis of the human brain using three dimensional imaging systems. Proc. SPIE-MI III 1092: 264–274, 1989
Delbeke D, Meyerowitz C, Lapidus RL, Maciunas RJ, Jennings MT, Moots PL, Kessler RM: Optimal cutoff levels of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the differentiation of low-grade from high-grade brain tumors with PET. Radiology 195: 47–52, 1995
Roelcke U: PET: brain tumor biochemistry. J Neuro-Oncol 22: 275–279, 1994
Valk PE, Budinger TF, Levin VA, Silver P, Gutin PH, Doyle WK: PET of malignant cerebral tumors after interstitial brachytherapy. Demonstration of metabolic activity and correlation with clinical outcome. J Neurosurg 69: 830–838, 1988
Herholz K, Piertrzyk U, Voges J, Schroder R, Halber M, Treuer H, Sturm V, Heiss WD: Correlation of glucose comsumption and tumor cell density in astrocytomas. J Neurosurg 79: 853–858, 1993
Fischman AJ, Alpert NM: FDG PET in oncology: there's more to it than looking at pictures. J Nucl Med 34: 6–11, 1993
Herholz K, Rudolf J, Heiss WD: FDG transport and phosphorylation in human gliomas measured with dynamic PET. J Neuro-Oncology 12: 159–165, 1992
De Witte O, Lefranc F, Levivier M, Salmon I, Brotchi J, Goldman S: FDG-PET as a prognostic factor in high-grade astrocytoma. J Neuro-Oncol 49: 157–163, 2001
Goldman S, Levivier M, Pirotte B, Brucher JM, Wikler D, Damhaut P, Dethy S, Brotchi J, Hilderbrand J: Regional glucose metabolism and histopathology of gliomas. A study based on positron emission tomography-guided stereotactic biopsy. Cancer 78: 1098–1106, 1996
Goldman S, Wikler D, Damhaut P, Monclus M, Levivier M, Pirotte B, De Witte O, Brotchi J, Hilderbrand J: Positron emission tomography and brain tumors. Acta Neurol Belg 97: 183–186, 1997
Meyer PT, Schreckenberger M, Petzger U, Meyer GF, Sabri O, Setani KS, Zeggel T, Buell U: Comparison of visual and ROI-based brain tumor grading using 18F-FDG PET: ROC analyses. Eur J Nucl Med 28: 165–174, 2001
Kim CK, Alavi JB, Alavi A, Reivich M: New grading system of cerebral gliomas using positron emission tomography with F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose. J Neuro-Oncol 10: 85–91, 1991
De Witte O, Levivier M, Violon P, Salmon I, Damhaut P, Wickler D, Hilderbrand J, Brotchi J, Goldman S: Prognostic value of positron emission tomography with FDG in lowgrade glioma. Neurosurgery 39: 470–477, 1996
Muller W, Afra D, Schroder R: Supratentorial recurrences of gliomas: Morphological studies in relation to time intervals with astrocytomas. Acta Neurochir (Wein) 37: 75–91, 1977
Mineura K, Sasajima T, Kowada H, Ogawa T, Hatazawa J, Shishido F, Uemura K: Perfusion and metabolism in predicting the survival of patients with cerebral gliomas. Cancer 73: 2386–2394, 1994
Barker FG, Chang SM, Valk PE, Pounds TR, Prados MD: 18-Fluorodeoxyglucose uptake and survival of patients with suspected recurrent malignant glioma. Cancer 79: 115–126, 1997
Tyler JL, Diksic M, Villemure JG, Evans AC, Yamamoto YL, Feindel W: Metabolic and hemodynamic evaluation of gliomas using positron emission tomography. J Nucl Med 28: 1123–1133, 1987
Rozenthal JM, Cohen JD, Mehta MP, Levine RL, Hanson JM, Nickles RJ: Acute changes in glucose uptake after treatment: the effects of carmustine (BCNU) on human glioblastoma multiforme. J Neuro-Oncol 15: 57–66, 1993
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padma, M., Said, S., Jacobs, M. et al. Prediction of Pathology and Survival by FDG PET in Gliomas. J Neurooncol 64, 227–237 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025665820001
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025665820001