Abstract
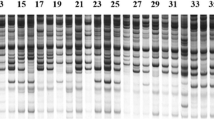
The elite and popular cultivars of Cymbopogon martinii were examined for genomic and expressed molecular diversity through RAPD, enzyme and SDS-PAGE protein polymorphisms. The allelic score at each locus of the enzymes as well as presence and absence profiling in RAPDs, overall occurrence of band types etc. were subjected to computation of gene diversity, expected heterozygosity, allele number per locus, and similarity matrix. These, in turn, provide inputs to derive primary account of allelic variability, genetic bases of the cultivated germplasm, putative need for gene/trait introgression from the wild or geographically diverse habitat etc. in elite selections. ‘PRC1’ possessed highest number of unique bands based on RAPD polymorphism. In variety ‘IW31245E’, diaphorase and glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase isozymes generated two unique bands as dia-III 2 and got-II 4. ‘RRL(B)77’ exhibited three unique bands; one produced by esterase as allele est-II 1 and two by malic enzyme (me-III 1,3). Only one unique band was generated by malic enzyme in variety ‘Trishna’. But sofia had three unique bands, two contributed by diaphorase (dia-II 3 and dia-II 4 and one by glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (got-II 2). SDS-PAGE analysis revealed presence of unique polypeptide fragments (97.7 kDa to 31.6 kDa) in varieties ‘IW31245E’, ‘RRL(B)77’, ‘Tripta’, ‘Trishna’, ‘PRC1’ and var. sofia, generated as a diagnostic marker. In general, molecular distinctions associated with var. motia and var. sofia have been clearly noticed in C. martinii.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R.P. & M.R. Dafforn, 1997-98. DNA sampling of the Pan tropical vetiver grass uncovers genetic uniformity in erosion-control germplasm. Diversity 13: 27-28.
Anderson, W.R. & D.J. Fairbanks, 1990. Molecular markers: important tools for plant genetic resource characterization. Diversity 6: 51-53.
Anonymous, 1992. Evaluation of geraniol rich variant in lemongrass. CIMAP Annual Report.
Boelens, M.H., 1994. Sensory and chemical evaluation of tropical grass oils. Perfumer Flav 19: 29-45.
Botstein, D., R.L. White, M. Skolnick & R.W. Davis, 1980. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphism. Am J Hum Genet 32: 314-331.
Britton-Davidian, J., 1993. Starch gel electrophoresis in vertebrates. In: A.Z. Elizabeth et al. (Eds.), Molecular Evolution: Producing and Biochemical data. Vol 224: pp. 98-112.
Bult, C.J. & Yun-Tzu Kiand, 1993. One-Dimensional electrophoretic comparisions of plant proteins. In: A.Z. Elizabeth et al. (Eds.), Molecular Evolution: Producing and Biochemical data. Vol 224: pp. 81-97.
Chalmers, K.J., R. Waugh, J.I. Sprent, A.J. Simons & W. Powell, 1992. Detection of genetic variations between and within populations of Gliricidia sepium and G. maculata using RAPD markers. Heredity 69: 465-472.
Cheliak, W.M. & J.A. Pitel, 1984a. Genetic control of allozyme variants in mature tissues of white spruce trees. J Hered 75: 34-40.
Excoffer, L., P.E. Smouse & J.M. Quattro, 1992. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplophytes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131: 479-491.
Ferreira, J.J., E. Alvarez, M.A. Fueyo, A. Roca & R. Giraaldej, 2000. Determination of out crossing rate Phaseolus vulgaris L. using seed protein marker. Euphytica 113: 259-263.
Husain, A., J.R. Sharma, H.S. Puri & B.R. Tyagi, 1984. Genetic Resources of Important Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in South Asia. Status report, IBPGR, Rome, Italy.
Jagdishchandra, K.S., 1975. Recent studies on Cymbopogon Spreng. (Aromatic grasses) with special reference to Indian taxa: Taxonomy, cytogenetics, chemistry and scope. J Planta Crops 3: 43-57.
King, L.M. & B.A. Schaal, 1989. Ribosomal DNA variation and distribution in Rudbeckia missouriensis. Evolution 43: 1117-1119.
Kresovich, S., W.F. Lamboy, R. Li, J. Ren, A.K. Szewc-Mcfadden & S.M. Blick, 1994. Application of molecular methods and statistical analysis for discrimination of accessions and clones of vetiver grass. Crop Sci 34: 805-809.
Laemmli, U.K., 1970. Cleavage of structural protein during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680-685.
Mishra, L.N., M.S. Siddiqui, A.K. Singh & Y.N. Shukla, 2000. Essential oils of Cymbopogons: uses and biological activities. In: S. Kumar et al. (Eds.), Cymbopogon The aromatic grasses, pp. 315-367. CIMAP, Lucknow.
Nei, M. & W.H. Li, 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 5269-5273.
Nei, M., 1987. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. Columbia University Press, New York.
Pdi, 1996. Diversity Database TM: software tools for all types of fragment analysis and data basing.
Pdi, 405 Oakwood Road, Huntington Station, New York 11746.
Rajora, O.P. & L. Zsuffa, 1989. Multilocus genetic structure, characterization and relationships of Populus × canadensis cultivars. Genome 32: 99-108.
Sahoo, S., S.P. Kanungo, M. Bapuji & P.K. Dutta, 1986. Herb, oil yield and geraniol content of improved palmarosa selection at RRL-Bhuaneshwar. Indian Perfumer 30: 240-244.
Sangwan, R.S., A.H.A. Farooqi, R.P. Bansal & N.S. Sangwan, 1993. Interspecific variation in physiological and metabolic responses of five species of Cymbopogon to water stress. J Plant Physiol 142: 618-622.
Sangwan, N.S., A.H.A. Farooqi & R.S. Sangwan, 1994. Effect of drought stress on growth and essential oil metabolism in Lemongrasses. New Phytol 128: 173-179.
Sangwan, N.S., R.S. Sangwan & S. Kumar, 1998. Isolation of genomic DNA from antimalarial plant Artemisia annua L. Plant Mol Biol Rep 16: 365.
Sangwan, R.S., N.S. Sangwan, D.C. Jain, S. Kumar & S.A. Ranade, 1999. RAPD profile based genetic characterization of chemotypic variants of Artemisia annua L. Biochem Mol Biol Int 46: 935-944.
Sangwan, R.S., A.H.A. Farooqi, S. Fatima & N.S. Sangwan, 2001a. Regulation of essential oil production in higher plants. Plant Growth Reg 34: 3-21.
Sangwan, R.S. & N.S. Sangwan, 2000. Metabolic analysis of oil-chemotypic diversity in Cymbopogons. In: S. Kumar et al. (Eds.), Cymbopogon The aromatic grasses, pp. 223-247. CIMAP, Lucknow.
Sangwan, N.S., U. Yadav & R.S. Sangwan, 2001b. Molecular analysis of genetic diversity in major elite aromatic Cymbopogon species. Plant Cell Report 20: 437-444.
Sharma, J.R., H.O. Misra & R.K. Lal, 1987b. A genetically superior synthetic variety Trishna of palmarosa developed. Pafai J 9: 21-26.
Sharma, J.R., R.K. Lal & H.O. Misra, 1997. Tripta: A superior variety of palmarosa. Pafai J 19: 37-44.
Shukla, N., N.S. Sangwan, H.O. Misra & R.S. Sangwan. Genetic diversity in Boerhavia diffusa L. of different geographic locations in India using RAPD marker Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution (in press).
Soenarko, S., 1977. The genus Cymbopogon. Reinwardta 9: 225-226.
Sokal, R.R. & A. Michener, 1958. A statistical method for evaluating systematic relationships, Univ Kan Sci Bull 38: 1409-1438.
Welsh, J.M. & McClelland, 1990. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucl Acid Res 18: 7213-7218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sangwan, N.S., Yadav, U. & Sangwan, R.S. Genetic diversity among elite varieties of the aromatic grasses, Cymbopogon martinii . Euphytica 130, 117–130 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022385126720
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022385126720