Abstract
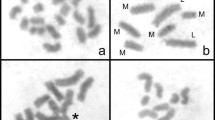
Telomeres, besides their main role in the protection and maintenance of chromosome ends, have several other vital functions in the cell cycle. We studied their role in the achiasmatic meiosis of female Lepidoptera, insects with holokinetic chromosomes. By fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) with the insect telomeric probe, (TTAGG) n , we mapped the distribution of telomeric and interstitial telomeric sequences (ITS) in female meiotic chromosomes of two species, Orgyia antiqua with a reduced chromosome number (2n=28) and Ephestia kuehniella mutants, possessing a radiation-induced chromosome fusion in the genome (2n=59). In addition to the strong typical telomeric signals, O. antiqua displayed weaker hybridization signals in interstitial sites of pachytene bivalents. The observed ITS most probably reflect remnants of chromosomal rearrangements and support the hypothesis that the Orgyia karyotype had arisen by multiple fusions of ancestral chromosomes. On the other hand, the absence of ITS in the chromosome fusion of Ephestia indicated the loss of telomeres before the two original chromosomes fused. When the telomeric probe was amplified by enzymatic reaction with tyramid, the number of ITS observed increased in Orgyia, and a few ITS were also observed in several chromosomes of Ephestia but not in the fused chromosome. This suggests that the genomes of both species also contain ITS other than those originating from chromosome fusions. The analysis of female meiotic prophase I revealed non-homologous associations of postpachytene bivalents mediated by telomeric DNA, which were not observed in the pachytene stage. Surprisingly, in early postpachytene nuclei the telomeric associations also involved ITS, whereas later postpachytene nuclei displayed chains of bivalents interconnected only by true telomeres. This finding favours a hypothesis that telomeric associations between bivalents play a role in chromosome segregation in the achiasmatic meiosis of female Lepidoptera.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azzalin CM, Nergadze SG, Giulotto E (2001) Human intrachromosomal telomeric-like repeats: sequence organisation and mechanisms of origin. Chromosoma 110: 75–82.
Bizzaro D, Mandrioli M, Zanotti M, Giusti M, Manicardi GC (2000) Chromosome analysis and molecular characterization of highlyre peated DNAs in the aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum (Aphididae, Hemiptera). Genetica 108: 197–202.
Blackburn EH (1991) Structure and function of telomeres. Nature 350: 569–573.
BoufLer SD (1998) Involvement of telomeric sequences in chromosomal aberrations. Mutat Res 404: 199–204.
Canapa A, Cerioni PN, Barucca M, Olmo E, Caputo V (2002) A centromeric satellite DNA maybe involved in heterochromatin compactness in gobiid fishes. Chromosome Res 10: 297–304.
Carpenter ATC (1994) Chiasma function. Cell 77: 959–962.
Castiglia R, Gornung E, Corti M (2002) Cytogenetic analyses of chromosomal rearrangements in Mus minutoides/musculoides from North-West Zambia through mapping of the telomeric sequence (TTAGGG)n and banding techniques. Chromosome Res 10: 399–406.
Chew JSK, Oliveira C, Wright JM, Dobson MJ (2002) Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of the telomeric (TTAGGG)n repetitive sequences in the Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Teleostei: Cichlidae). Chromosoma 111: 45–52.
Chikashige Y, Ding D, Imai Y, Yamamoto M, Haraguchi T, Hiraoka Y (1997) Meiotic nuclear reorganization: switching the position of centromeres and telomeres in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J 16: 193–200.
Danjinou AT, Dionne I, Gravel S, LeBel C, Parenteau J, Wellinger RJ (1999) Cytological and functional aspects of telomere maintenance. Histol Histopathol 14: 517–524.
Desmaze C, Alberti C, Martins L et al. (1999) The influence of interstitial telomeric sequences on chromosome instability in human cells. Cytogenet Cell Genet 86: 288–295.
de Lange T (1992) Human telomeres are attached to the nuclear matrix. EMBO J 11: 717–724.
de Lange T (2001) Telomere capping— one strand fits all. Science 292: 1075–1076.
Fagundes V, Yonenaga-Yassuda Y (1998) Evolutionary conservation of whole homeologous chromosome arms in the Akodont rodents Bolomys and Akodon (Muridae, Sigmodontinae): maintenance of interstitial telomeric segments (ITBs) in recent event of centric fusion. Chromosome Res 6: 643–648.
Franklin AE, Cande WZ (1999) Nuclear organisation and chromosome segregation. Plant Cell 11: 523–534.
Harrington LA, Greidler CW (1991) Telomerase primer sensitivity and chromosome healing. Nature 353: 451–454.
Hastie ND, Allshire RC (1989) Human telomeres: fusion and interstitial sites. Trends Genet 5: 326–331.
Ijdo JW, Baldini A, Ward DC, Reeders ST, Wells RA (1991a) Origin of human chromosome 2: an ancestral telomere-telomere fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 9051–9055.
Ijdo JW, Wells RA, Baldini A, Reeders ST (1991b) Improved telomere detection using a telomere repeat probe (TTAGGG)n generated by PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 19: 17.
Jönsson F, Postberg J, Schafctzel Ch, Lipps HJ (2002) Organisation of the macronuclear gene-sized pieces of stichotrichous cilliates into a higher order structure via telomere matrix interactions. Chromosome Res 10: 445–453.
Kohli J (1994) Telomeres lead chromosome movement. Curr Biol 4: 724–727.
Krutilina RI, Oei SL, Buchlow G et al. (2001) A negative regulator telomere-length protein TRF1 is associated with interstitial (TTAGGG)n block in immortal Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 280: 471–475.
Lee C, Sasi R, Lin CC (1993) Interstitial localisation of telomeric DNA sequences in the Indian muntjac chromosomes: further evidence for tandem chromosome fusions in the karyotypic evolution of the Asian muntjacs. Cytogenet Cell Genet 63: 156–159.
Maestra B, de Jong H, Shepherd K, Naranjo T (2002) Chromosome arrangement and behaviour of two rye homologous telosomes at the onset of meiosis in disomic wheat-5RL addition lines with and without the Ph1 locus. Chromosome Res 10: 655–667.
Mandrioli M (2002) Cytogenetic characterization of telomeres in the holocentric chromosomes of the lepidopteran Mamestra brassicae. Chromosome Res 10: 279–286.
Marec F (1990) Genetic control of pest Lepidoptera: Induction of sex-linked recessive lethal mutations in Ephestia kuehniella (Pyralidae). Acta Entomol Bohemoslov 87: 455–458
Marec F (1996) Synaptonemal complexes in insects. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 25: 205–233.
Meyne J, Baker RJ, Hobart HH et al. (1990) Distribution of non-telomeric sites of the (TTAGGG)n telomeric sequence in vertebrate chromosomes. Chromosoma 99: 3–10.
Mignon-Ravix C, Depetris D, Delobel B, Croquette MF, Mattei MG (2002) A human interstitial telomere associates in vivo with specicc TRF2 and TIN2 proteins. Eur J Hum Genet 10: 107–112.
Natarajan AT (1984) Origin and signiccance of chromosomal alterations. In: Obe G, ed. Mutations in Man. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, pp 156–175.
Niwa O, Shimanuki M, Miki F (2000) Telomere-led bouquet formation facilitates homologous chromosome pairing and restricts ectopic interaction in cssion yeast meiosis. EMBO J 19: 3831–3840.
Nokkala S (1987) Cytological characteristics of chromosome behaviour during female meiosis in Sphinx ligustri L. (Sphingidae, Lepidoptera). Hereditas 106: 169–179.
Okazaki S, Tsuchida K, Maekawa H, Ishikawa H, Fujiwara H (1993) Identiccation of a pentanucleotide telomeric sequence, (TTAGG)n in the silkworm Bombyx mori and in other insects. Mol Cell Biol 13: 1424–1432.
Pagnozzi, JM, Silva MJJ, Yonenaga-Yassuda Y (2000) Intraspecicc variation in the distribution of the interstitial telomeric (TTAGGG)n sequences in Micoureus demerarae (Marsupialia: Didelphidae). Chromosome Res 8: 585–591.
Rasmussen SW(1977) The transformation of the synaptonemal complex into the 'elimination chromatin' in Bombyx mori oocytes. Chromosoma 60: 205–221.
Robinson (1971) Lepidoptera Genetics. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Rockmill B, Roeder GS (1998) Telomere-mediated chromosome pairing during meiosis in budding yeast. Gene Dev 12: 2574–2586.
Sahara K, Marec F, Traut W (1999) TTAGG telomeric repeats in chromosomes of some insects and other arthropods. Chromosome Res 7: 449–460.
Santani A, Raudsepp T, Chowdhary BP (2002) Interstitial telomeric sites and NORs in Hartmann's zebra (Equus zebra hartmannae) chromosomes. Chromosome Res 10: 527–534.
Savage JRK (1993) Update on target theory as applied to chromosomal aberration. Environm Mol Mutagen 22: 198–207.
Scherthan H (2001) A bouquet makes ends meet. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 621–627.
Silva MJJ, Yonenaga-Yassuda Y (1998) Heterogeneityan d meiotic behaviour of B and sex chromosomes, banding patterns and localisation of (TTAGGG)n sequences by fluroscence in situ hybridisation in the neotropical water rat Nectomys (Rodentia, Cricetidae). Chromosome Res 6: 455–462.
Slijepcevic P (1998) Telomeres and mechanisms of Robertsonian fusion. Chromosoma 107: 136–140.
Suomalainen E (1969) Chromosome evolution in the Lepidoptera. Chromosomes Today 2: 132–138.
Sybenga J (1999) What makes homologous chromosomes find each other in meiosis? A review and hypothesis. Chromosoma 108: 209–219.
Traut W (1977) A study of recombination, formation of chiasmata and synaptonemal complexes in female and male meiosis of Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera). Genetica 47: 135–142.
Traut W (1986) A genetic linkage study of W-chromosome-autosome fusions, breakage, and kinetic organisation of chromosomes in Ephestia (Lepidoptera). Genetica 69: 69–79.
Traut W, Clarke CA (1997) Karyotype evolution by chromosome fusion in the moth genus Orgyia. Hereditas 126: 77–84.
Traut W, Weith A, Traut G (1986) Structural mutants of the W chromosome in Ephestia (Insecta, Lepidoptera). Genetica 70: 69–79.
Trelles-Sticken E, Loidl J, Scherthan H (1999) Bouquet formation in budding yeast: initiation of recombination is not required for meiotic telomere clustering. J Cell Sci 112: 651–658.
Vermeesch JR, De Meurichy W, Van Den Berghe H, Marynen P, Petit P (1996) Differences in the distribution and nature of the interstitial telomeric sequences in the chromosomes of the Giraffidae, okapi (Okapia johnstoni), and giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis): evidence for ancestral telomeres at the okapi polymorphic rob(4; 26) fusion site. Cytogenet Cell Genet 72: 310–315.
Walker MY, Hawley RS (2000) Hanging on to your homolog: the roles of pairing, synapsis and recombination in the maintenance of homolog adhesion. Chromosoma 109: 3–9.
Wilkie A, Lamb J, Harris P, Finney R, Higgs D (1990) A truncated human chromosome 16 associated with L. thalassemia is stabilized by addition of telomeric repeat (TTAGGG)n. Nature 346: 868–871.
Wolf KW(1994) The unique structure of lepidopteran spindles. Int Rev Cytol 152: 1–48.
Wolf KW (1996) The structure of condensed chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis of insects. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 25: 37–62.
Wolf KW, Nová k K, Marec F (1997) Kinetic organisation of metaphase I bivalents in spermatogenesis of Lepidoptera and Trichoptera species with small chromosome numbers. Heredity 79: 135–143.
Yamamoto A, Hiraoka Y (2001) How domeiotic chromosomes meet their homologous partners?: lessons from cssion yeast. BioEssays 23: 526–533.
Zakian VA (1989) Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet 23: 579–604.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rego, A., Marec, F. Telomeric and interstitial telomeric sequences in holokinetic chromosomes of Lepidoptera: Telomeric DNA mediates association between postpachytene bivalents in achiasmatic meiosis of females. Chromosome Res 11, 681–694 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025937808382
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025937808382