Abstract
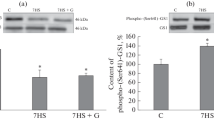
The effects of spontaneous circling motor activity on the in vitro phosphorylation of the protein kinase C substrate GAP-43/B-50 was studied on striatal membranes of developing rats (30 days of age). At this time of postnatal development, permanent plastic changes in cholinergic and dopaminergic systems are produced by physiological motor activity. Exercised animals showed a significant reduction of 31% in the level of GAP-43/B-50 endogenous phosphorylation in the contralateral striatum respect to the ipsilateral side (P < 0.01), while control animals did not show asymmetric differences. Compared to controls, the contralateral striatum of exercised animals showed a 33% reduction in the incorporation of 32P-phosphate into GAP-43/B-50 30 minutes post-exercise (P < 0.01). This change in GAP-43/B-50 phosphorylation was correlated with the running speed developed by the animals (r:0.8986, P = 0.015). GAP-43/B-50 immunoblots revealed no changes in the amount of this protein in any group. Moreover, a significant variation of 25% (P < 0.05) in the PKC activity was seen between both exercised striata. Interhemispheric differences were not found in control animals. We conclude that endogenous phosphorylation of this protein is also altered by motor activity in the same period that permanent changes in striatal neuroreceptors are triggered after motor training.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Gerfen, C. R. 1992. The neostriatal mosaic: Multiple levels of compartmental organization. Trends Neurosci. 15:133-139.
Gerfen, C. R. 1992. The neostriatal mosaic: Multiple levels of compartmental organization in the basal ganglia. T Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 15:285-320.
Worley, P. F., Baraban, J. M., De Souza, E. B., and Snyder S. H. 1986. Mapping second messenger in the brain: Differential localizations of adenylate cyclase and protein kinase C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 83:4053-4057.
Fordyce, D. E., and Farrar, R. P. 1991. Physical activity effects on hippocampal and parietal cortical cholinergic functions and spatial learning in F344 rats. Behav Brain Res. 43:115-123.
Mc Rae, P. G., Spidurso, W. W., Walters, T. J., Farrar, R. P., and Wilcox, R. E. 1987. Endurance training effects on striatal D2 dopamine receptor binding and striatal dopamine metabolites in presenescent older rats. Psychopharmacol. 92:236-240.
Gilliam, P. E., Spirduso, W. W., Martin, T. P., Walters, T. J., Wilcox, R. E., and Farrar, R. P. 1984. The effects of exercise training on 3H-Spiperone binding in rat striatum. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 20:863-867.
Neeper, S. A., Gómez Pinilla, F., Choi, J., and Cotman, C. 1995. Exercise and brain neurotrophins. Nature 373:109.
Neeper, S. A., Gómez Pinilla, F., Choi, J., and Cotman, C. 1996. Physical activity increases mRNA for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor in rat brain. Brain Res. 726:49-56.
Ibarra, G. R., Rodríguez, J. A., Paratcha, G. Ch., and Azcurra, J. M. 1995. Permanent alteration of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor binding in rat striatum after circling training during development. Brain Res. 705:39-44.
Ibarra, G. R., Paratcha, G. Ch., Wolansky, M. J., and Azcurra, J. M. 1996. Co-alteration of dopamine D2 receptor and muscarinic acetylcholine receptor binding in rat striatum after circling training. Neuroreport. 7:2491-2494.
Alexander, K. A., Wakim, B. T., Doyle, G. S., Walsh, K. A., and Storm, D. R. 1988. Identification and characterization of the calmodulin-binding domain of neuromodulin, a neurospecific calmodulin binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 263:7544-7549.
Aloyo, J., Zwiers, H., and Gispen, W. H. 1983. Phosphorylation of B-50 protein by calcium activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase and B-50 protein kinase. J. Neurochem. 41:649-653.
Oestreicher, A. B., and Gispen, W. H. 1986. Comparison of the immunocytochemical distribution of the phosphoprotein B-50 in the cerebellum and hippocampus of immature and adult rat brain. Brain Res 375:267-279.
Ramakers, G. M. J., De Graan, P. N. E., Urban, I. J. A., Kraay, D., Tang, T., Pasinelli, P., Oestreicher, A. B., and Gispen, W. H. 1995. Temporal differences in the phosphorylation state of pre-and post-synaptic protein kinase C substrates B-50/GAP-43 and Neurogranin during LTP. 1995. J. Biol. Chem. 270:13892-13898.
Dekker, L. V., De Graan, P. N. E., Versteeg, D. H. G., Oestreicher, A. B., and Gispen, W. H. 1989. Phosphorylation of B-50 (GAP-43) is correlated with neurotransmitter released in rat hippocampal slices. J. Neurochem. 52:24-30.
Benowitz, L. I., and Routtenberg, A. 1987. A membrane phosphoprotein associated with neural development, axonal regeneration, phospholipid metabolism and synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 10:527-531.
Gnegy, M. E., Hong, P., and Ferrell, S. T. 1993. Phosphorylation of neuromodulin in rat striatum after acute and repeated, intermittent anphetamine. Mol. Brain Res. 20:289-298.
Sheu, F. S., Mc Cabe, B. J., Horn, G., and Routtenberg, A. 1993. Learning selectively increases protein kinase C substrate phosphorylation in specific regions of the chick brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 90:2705-2709.
Azcurra, J. M., and De Robertis, E. 1967. Binding of dimethyl-14C-D-Tubocurarine-methyl-14C-hexamethonium and 3H-allopherine by isolated synaptic membranes of brain cortex. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 6:15-26.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with Follin reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265-272.
Kristjansson, G. I., Zwiers, H., Oestreicher, A. B., and Gispen, W. H. 1982. Evidence that the synaptic phosphoprotein B-50 is localized exclusively in nerve tissue. J. Neurochem. 39:371-378.
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T., and Gordon, J. 1979. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrilamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 76:4350-4354.
Oestreicher, A. B., Van Dongen, C. J., Zwiers, H., and Gispen, W. H. 1983. Affinity-purified anti B-50 protein antibody: interference with the function of the phosphoprotein B-50 in synaptic plasma membranes. J. Neurochem. 41:267-279.
Cole, G., Dobkin, K. R., Hansen, L. A., Terry, R. D., and Saitoh, T. 1988. Decreased levels of PKC in Alzheimer brain. Brain Res. 453:165-174.
Eichberg, J., De Graan, P. N. E., Schrama, L. H., and Gispen, W. H. 1986. Dioctamoyl-glycerol and phorbol-diesters enhanced phosphorylation of phosphoprotein B-50 in native synaptic plasma membranes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 136:1007-1012.
Nielander, H. B., Schrama, L. G., Van Rosen, H., Kasperaitis, M., Oestreicher, A. B., Gispen, W. H., and Schotman, P. 1990. Mutation of serine 41 in the neuron specific protein B-50 (GAP-43) prohibits phosphorylation by PKC. J. Neurochem. 55:1442-1445.
Coggins, P. J., and Gispen, W. H. 1989. Evidence for a single PKC mediated phosphorylation site in rat brain protein B-50. J. Neurochem. 53:1895-1901.
Apel, D. E., Litchfield, D. W., Clark, R. H., Krebs, E. G., and Storm, D.R. 1991. Phosphorylation of neuromodulin (GAP-43) by Casein Kinase II. J. Biol. Chem. 266:10544-10551.
Spencer, S. A., Schuh, S. M., Liu, W. S., and Willard, M. B. 1992. GAP-43, a protein associated with axon growth, is phosphorylated at three sites in cultured neurons and rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 267:9059-9064.
Han, Y., and Dokas, L. A. 1991. Okadaic acid-induced inhibition of protein phosphatases. J. Neurochem. 57:1325-1331.
Han, Y., Wang, W., Schlender, K. K., Ganjeizadeh, M., and Dokas, L. A. 1992. Protein phosphatases 1 and 2A dephosphorylate B-50 in presynaptic plasma membranes from rat brain. J. Neurochem. 59:364-374.
Liu, Y., and Storm, D. R. 1989. Dephosphorylation of neuromodulin by calcineurin. J. Biol. Chem. 264:12800-12804.
Schrama, L. H., Heemskerk, F. M. J., and De Graan, P. N. E. 1989. Dephosphorylation of Protein Kinase C-phosphorylated B-50/GAP-43 by the calmodulin-dependent phosphatase calcineurin. Neurosci. Res. Commun. 5:141-147.
Ali, S. M., Bullock, S., and Rose, S. 1988. Phosphorylation of synaptic proteins in chick forebrain: Changes with development and passive avoidance training. J. Neurochem. 50:1579-1587.
Cammarota, M., Paratcha, G. Ch., Levi de Stein, M., Bernabeu, R., Izquierdo, I., and Medina, J. H. 1997. B-50/GAP-43 phosphorylation and PKC activity are increased in rat hippocampal synaptosomal membranes after an inhibitory avoidance training. Neurochem. Res. 22:499-505.
Giambalvo, C. T. 1988. Protein Kinase C and dopamine release. Effects of dopamine acting drugs in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 37:4009-4017.
Giambalvo, C.T., and Wagner, R. L. 1994. Activation of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors inhibits protein kinase C activity in striatal synaptoneurosomes. J. Neurochem. 63:169-176.
Nelson, R. B., Linden, D. J., and Routtenberg, A. 1989. Phosphoproteins localized to presynaptic terminal linked to persistence of long-term potentiation (LTP): quantitative analysis of two dimensional gels. Brain Res. 497:30-42.
Gianotti, C., Nunai, M. G., Gispen, W. H., and Corradetti, R. 1992. Phosphorylation of the presynaptic protein B-50 (GAP-43) is increased during electrically induced long-term potentiation. Neuron 8:843-848.
Pizzi, M., Da Prada, M., Valerio, A., Memo, A., Spano, P. F., and Haefely, W. E. 1988. Dopamine D2 receptor stimulation inhibits inositol phosphate generating system in rat striatal slices. Brain Res. 456:235-240.
Von Euler, G., and Von Euler, A. 1991. Dopamine D2 receptors attenuate phophatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in synaptosomal membranes from rat neostriatum. J. Neurochem. 56:136-140.
Kelly, E., Batty, I., and Nahorski, S. R. 1988. Dopamine receptor stimulation does not affect phosphoinositide hydrolysis in slices of rat striatum. J. Neurochem. 51:918-924.
Van Dongen, C. J., Zwiers, H., De Graan, P. N. E., and Gispen, W. H. 1985. Modulation of the activity of purified phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase by phosphorylated and dephosphorylated B-50 protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 8:1219-1227.
Van Hooff, C. O. M., De Graan, P. N. E., Oestreicher, A. B., and Gispen, W. H., 1988. B-50 phosphorylation and polyphosphoinositide metabolism in nerve growth cone membranes. J. Neurosci. 8:1789-1795.
O'Brian, C. A., Arthur, W. L., and Weinstein, I. B., 1987. The activation of PKC by the polyphosphoinositides phosphatidylinositol 4,5-diphosphate and phophatidylinositol 4-monophosphate. FEBS Lett. 214:339-342.
Van Hooff, C. O. M., De Graan, P. N. E., Oestreicher, A. B., and Gispen, W. H. 1989. Muscarinic receptor activation stimulates B-50/GAP-43 phosphorylation in isolated nerve growth cones. J. Neurosci. 9:3753-3759.
Coyle, J. T., and Campochiaro, P. J. 1976. Ontogenesis of dopaminergic-cholinergic interactions in the rat striatum: A neurochemical study. J. Neurochem. 27:673-678.
Singer, W. 1995. Development and plasticity of cortical processing architecture. Science. 270:758-764.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paratcha, G.C., Ibarra, G.R., Cabrera, R. et al. Decreased Phosphorylation of GAP-43/B-50 in Striatal Synaptic Plasma Membranes after Circling Motor Activity. Neurochem Res 23, 1241–1249 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020736014882
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020736014882