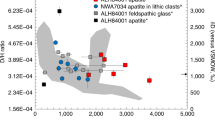
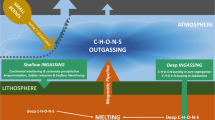
Abstract
The early development of Mars is of enormous interest, not just in its own right, but also because it provides unique insights into the earliest history of the Earth, a planet whose origins have been all but obliterated. Mars is not as depleted in moderately volatile elements as are other terrestrial planets. Judging by the data for Martian meteorites it has Rb/Sr ≈ 0.07 and K/U ≈ 19,000, both of which are roughly twice as high as the values for the Earth. The mantle of Mars is also twice as rich in Fe as the mantle of the Earth, the Martian core being small (∼20% by mass). This is thought to be because conditions were more oxidizing during core formation. For the same reason a number of elements that are moderately siderophile on Earth such as P, Mn, Cr and W, are more lithophile on Mars. The very different apparent behavior of high field strength (HFS) elements in Martian magmas compared to terrestrial basalts and eucrites may be related to this higher phosphorus content. The highly siderophile element abundance patterns have been interpreted as reflecting strong partitioning during core formation in a magma ocean environment with little if any late veneer. Oxygen isotope data provide evidence for the relative proportions of chondritic components that were accreted to form Mars. However, the amount of volatile element depletion predicted from these models does not match that observed — Mars would be expected to be more depleted in volatiles than the Earth. The easiest way to reconcile these data is for the Earth to have lost a fraction of its moderately volatile elements during late accretionary events, such as giant impacts. This might also explain the non-chondritic Si/Mg ratio of the silicate portion of the Earth. The lower density of Mars is consistent with this interpretation, as are isotopic data. 87Rb-87Sr, 129I-129Xe, 146Sm-142Nd, 182Hf-182W, 187Re-187Os, 235U-207Pb and 238U-206Pb isotopic data for Martian meteorites all provide evidence that Mars accreted rapidly and at an early stage differentiated into atmosphere, mantle and core. Variations in heavy xenon isotopes have proved complicated to interpret in terms of 244Pu decay and timing because of fractionation thought to be caused by hydrodynamic escape. There are, as yet, no resolvable isotopic heterogeneities identified in Martian meteorites resulting from 92Nb decay to 92Zr, consistent with the paucity of perovskite in the martian interior and its probable absence from any Martian magma ocean. Similarly the longer-lived 176Lu-176Hf system also preserves little record of early differentiation. In contrast W isotope data, Ba/W and time-integrated Re/Os ratios of Martian meteorites provide powerful evidence that the mantle retains remarkably early heterogeneities that are vestiges of core metal segregation processes that occurred within the first 20 Myr of the Solar System. Despite this evidence for rapid accretion and differentiation, there is no evidence that Mars grew more quickly than the Earth at an equivalent size. Mars appears to have just stopped growing earlier because it did not undergo late stage (>20 Myr), impacts on the scale of the Moon-forming Giant Impact that affected the Earth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens, T.J.:1990, 'Earth Accretion', in H.E. Newsom and J.H. Jones (eds.), Origin of the Earth, Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, pp. 211-227.
Allègre, C.J., Poirier, J.-P., Humler, E., and Hofmann, A.W.:1995, 'The Chemical Composition of the Earth', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 134, 515-526.
Benz, W.:2000, 'Low Velocity Collisions and the Growth of Planetesimals', in W. Benz, R. Kallenbach, and G.W. Lugmair (eds.), From Dust to Terrestrial Planets, Space Sci. Rev. 92, 279-294.
Benz, W., and Cameron, A.G.W.:1990, 'Terrestrial Effects of the Giant Impact', in H.E. Newsom and J.H. Jones (eds.), Origin of the Earth, Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 61-67.
Benz, W., Cameron, A.G.W., and Slattery, W.L.:1987, 'Collisional Stripping of Mercury's Mantle', Icarus 74, 516-528.
Bertka, C.M., and Fei, Y.J.:1997, 'Mineralogy of the Martian Interior up to Core-mantle Boundary Pressures', J. Geophys. Res. 102, 5251-5264.
Birck, J.-L., and Allègre, C.J.:1988, 'Manganese-chromium Isotope Systematics and the Developement of the Early Solar System', Nature 331, 579-584.
Birck, J.-L., and Allègre, C.J.:1994, 'Contrasting Re/Os Fractionation in Planetary Basalts', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 124, 139-148.
Birck, J.L., Rotaru, M., and Allègre, C.J.:1999, 53Mn-53Cr Evolution of the Early Solar System', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 63, 4111-4117.
Blichert-Toft, J., Gleason, J.D., Télouk, P., and Albarède, F.:1999, 'The Lu-Hf Isotope Geochemistry of Shergottites and the Evolution of the Martian Mantle-crust System', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 173, 25-39.
Blum, J.:2000, 'Laboratory Experiments on Preplanetary Dust Aggregation', in W. Benz et al. (eds.), From Dust to Terrestrial Planets, Space Sci. Rev. 92, 265-278.
Bogard, D.D., and Garrison, D.H.:1998, 'Relative Abundances of Argon, Krypton, and Xenon in the Martian Atmosphere as Measured in Martian Meteorites', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 62, 1829-1835.
Borg, L.E., Nyquist, L.E., Taylor, L.A., Wiesmann, H., and Shih, C.-Y.:1997, 'Constraints on Martian Differentiation Processes from Rb-Sr and Sm-Nd Isotopic Analyses of the Basaltic Shergottite QUE94201', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61, 4915-4931.
Boss, A.P.:1990, '3D Solar Nebula Models: Implications for Earth Origin', in H.E. Newsom and J.H. Jones (eds.), Origin of the Earth, Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, pp. 3-15.
Brandon, A.D., Walker, R.J, Morgan, J.W., and Goles, G.G.:2000, 'Re-Os Isotopic Evidence for Early Differentiation of the Martian Mantle', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 64, 4083-4095.
Breuer, D., Spohn, T., and Wüllner, U.:1993, 'Mantle Differentiation and the Crustal Dichotomy of Mars', Planet. Space Sci. 41, 269-283.
Breuer, D., Yuen, D.A., and Spohn, T.:1997, 'Phase Transitions in the Martian Mantle: Implications for Partially Layered Convection', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 148, 457-469.
Cameron, A.G.W., and Ward:1976, 'The Origin of the Moon', Lunar Science 7, Lunar Science Institute, Houston.
Cameron, A.G.W., and Benz, W.:1991, 'Origin of the Moon and the Single Impact Hypothesis IV.', Icarus 92, 204-216.
Canup, R.M., and Agnor, C.:1998, 'Accretion of Terrestrial Planets and the Earth-moon System', Origin of the Earth and Moon, LPI Contribution 597, LPI, Houston, pp. 4-7.
Carr, M.H.:1973, 'Volcanism on Mars', J. Geophys. Res. 78, 4049-4062.
Carr, M.H.:1999, 'Retention of an Atmosphere on Early Mars', J. Geophys. Res. 104, 21,897-21,909.
Carr, M.H., and Wänke, H.:1992, 'Earth and Mars: Water Inventories as Clues to Accretional Histories', Icarus 98, 61-71.
Cassen, P., and Woolum, D.S.:1997, 'Nebular Fractionations and Mn-Cr Systematics', Proc. 28 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 211-212.
Chen, J.H., and Wasserburg, G.J.:1986, 'Formation Ages and Evolution of Shergotty and its Parent Planet from U-Th-Pb Systematics', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 955-968.
Christie, D.M., Carmichael, I.S.E., and Langmuir, C.H.:1986, 'Oxidation States of Mid-ocean Ridge Basalt Glasses', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 79, 397-417.
Clark, S.P., Jr., Turekian, K.K., and Grossman, L.:1972, 'Model for the Early History of the Earth', in E.C. Robertson (ed.), The Nature of the Solid Earth, McGraw Hill, pp. 3-18.
Clayton, R.N.:1986, 'High Temperature Isotope Effects in the Early Solar System', in J.W. Valley, H.P. Taylor, and J.R. O'Neil (eds.), Stable Isotopes in High Temperature Geological Processes, Mineral. Soc. Am., Washington D.C., pp. 129-140.
Clayton, R.N.:1993, 'Oxygen Isotopes in Meteorites', Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 21, 115-149.
Clayton, R.N., and Mayeda, T.K.:1996, 'Oxygen Isotope Studies of Achondrites', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60, 1999-2017.
Delano, J.W., and Arculus, R.J.:1980, 'Nakhla: Oxidation State and Other Constraints', Proc. 11 th Lunar Planet. Sci., 219-221.
Dreibus, G, and Wänke, H.:1984, 'Accretion of the Earth and the Inner Planets', Proc. 27 th Int. Geol. Conf. 11, VNU Science Press, Utrecht, pp. 1-20.
Dreibus, G., and Wänke, H.:1985, 'Mars: A Volatile Rich Planet', Meteoritics 20, 367-382.
Dreibus, G., and Wänke, H.:1987, 'Volatiles on Earth and Mars: A Comparison', Icarus 71, 225-240.
Franchi, I.A., Wright, I.P., Sexton, A.S., and Pillinger, C.T.:1999, 'The Oxygen Isotopic Composition of Earth and Mars', Met. Planet. Sci. 34, 657-661.
Gaetani, G.A., and Grove, T.L.:1997, 'Partitioning of Moderately Siderophile Elements Among Olivine, Silicate Melt and Sulfide Melt:Constraints on Core Formation in the Earth and Mars', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61, 1829-1846.
Galy, A., Young, E.D., Ash, R.D., and O'Nions, R.K.:2000, 'High Precision Magnesium Isotopic Composition of Allende Material:A Multiple Collector Inductively Coupled Mass Spectrometry Study', Lunar Planet. Sci. 31, 1193-1194.
Gilmour, J.D., Whitby, J.A., and Turner, G.:1998, 'Xenon Isotopes in Irradiated ALH84001: Evidence for Shock-induced Trapping of Ancient Martian Atmosphere', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 62, 2555-2571.
Grossman, L.:1972, 'Condensation in the Primitive Solar Nebula', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 36, 597-619.
Grossman, L., and Larrimer, J.W.:1974, 'Early Chemical History of the Solar System', Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 12, 71-101.
Haggerty, S.R.:1981, 'Opaque Mineral Oxides in Terrestrial Igneous Rocks', Oxide Minerals, Miner. Soc. Am., pp. Hg101-Hg278.
Halliday, A.N.:2000a, 'Terrestrial Accretion Rates and the Origin of the Moon', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 176, 17-30.
Halliday, A.N.:2000b, 'Hf-W Chronometry and Inner Solar System Accretion Rates', in W. Benz et al. (eds.), From Dust to Terrestrial Planets, Space Sci. Rev. 92, 355-370.
Halliday, A.N., and Lee, D.-C.:1999, 'Tungsten Isotopes and the Early Development of the Earth and Moon', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, (C.J. Allègre 60th Birthday Volume) 63, 4157-4179.
Halliday, A.N., and Porcelli, D.:2001, 'In Search of Lost Planets-the Paleocosmochemistry of the Inner Solar System', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., in submission.
Halliday, A.N., Rehkämper, M., Lee, D.-C., and Yi, W.:1996, 'Early Evolution of the Earth and Moon: New Constraints from Hf-W Isotope Geochemistry', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 142, 75-90.
Harder, H., and Christensen, U.R.:1996, 'A One-plume Model of Martian Mantle Convection', Nature 380, 507-509.
Harper, C.L., and Jacobsen, S.B.:1996, 'Evidence for 182Hf in the Early Solar System and Constraints on the Timescale of Terrestrial Core Formation', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60, 1131-1153.
Harper, C.L., Völkening, J., Heumann, K.G., Shih, C.-Y., and Wiesmann, H.:1991, 182Hf-182W: New Cosmochronometric Constraints on Terrestrial Accretion, Core Formation, the Astrophysical Site of the r-Process, and the Origin of the Solar System', Proc. 22 nd Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 515-516.
Harper, C.L., Nyquist L.E., Bansal, B., Wiesmann, H., and Shih, C.-Y.:1995, 'Rapid Accretion and Early Differentiation of Mars Indicated by 142Nd/144Nd in SNC Meteorites', Science 267, 213-217.
Hartmann, W.K., and Davis, D.R.:1975, 'Satellite-sized Planetesimals and Lunar Origin', Icarus 24, 504.
Hewins, R.H., and Ulmer, G.C.:1983, 'Intrinsic Oxygen Fugacity Measurements for Clasts in Diogenites and Mesosiderites', Proc. 14 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 311-312.
Higuchi, H., and Morgan, J.W.:1975, 'Ancient Meteoritic Component in Apollo 17 Boulder', Proc. 6 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 1625-1651.
Hinton, R.W., and Bischoff, A.:1984, 'Ion Microprobe Magnesium Isotope Analysis of Plagioclase and Hibonite from Ordinary Chondrites', Nature 308, 169-172.
Hinton, R.W., Davis, A.M., Scatena-Wachel, D.E., Grossman, L., and Draus, R.J.:1988, 'A Chemical and Isotopic Study of Hibonite-rich Refractory Inclusions in Primitive Meteorites', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 52, 2573-2598.
Hofmann, A.W., Jochum, K.P., Seufert, M., and White, W.M.:1986, 'Nb and Pb in Oceanic Basalts: New Constraints on Mantle Evolution', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 79, 33-45.
Horan, M.F., Smoliar, M.I., and Walker, R.J.:1998, 182W and 187Re-187Os Systematics of Iron Meteorites:Chronology for Melting, Differentiation, and Crystallization in Asteroids', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 62, 545-554.
Hunten, D.M., Pepin, R.O., and Walker, J.G.C.:1987, 'Mass Fractionation in Hydrodynamic Escape', Icarus 69, 532-549.
Huss, G.R.:1988, 'The Role of Presolar Dust in the Formation of the Solar System', Earth, Moon, and Planets 40, 165-211.
Jacobsen, S.B., and Harper, Jr., C.L.:1996, 'Accretion and Early Differentiation History of the Earth Based on Extinct Radionuclides', in A. Basu and S. Hart (eds.), Earth Processes: Reading the Isotope Code, AGU, Washington D.C., pp. 47-74.
Jagoutz, E., Sorowka, A., Vogel, J.D., and Wänke, H.:1994, 'ALH84001: Alien or Progenitor of the SNC Family?', Meteoritics 28, 548-479.
Jakosky, B.M., and Jones, J.H.:1997, 'The History of Martian Volatiles', Rev. Geophys. 35, 1-16.
Kato, T., Ringwood, A.E., and Irifune, T.:1988, 'Experimental Determination of Element Partitioning Between Silicate Perovskites, Garnets and Liquids:Constraints on Early Differentiation of the Mantle', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 89, 123-145.
Kitts, K., and Lodders, K.:1998, 'Survey and Evaluation of Eucrite Bulk Compositions', Met. Planet. Sci. 33 Suppl., A197-A213.
Lee, D.-C., and Halliday, A.N.:1995, 'Hafnium-tungsten Chronometry and the Timing of Terrestrial Core Formation', Nature 378, 771-774.
Lee, D.-C., and Halliday, A.N.:1996, 'Hf-W Isotopic Evidence for Rapid Accretion and Differentiation in the Early Solar System', Science 274, 1876-1879.
Lee, D.-C., and Halliday, A.N.:1997, 'Core Formation on Mars and Differentiated Asteroids', Nature 388, 854-857.
Lee, D.-C., and Halliday, A.N.:2000a, 'Hf-W Isotopic Systematics of Ordinary Chondrites and the Initial 182Hf/180Hf of the Solar System', Chem. Geol. (G.J. Wasserburg Spec. Iss.) 169, 35-43.
Lee, D.-C., and Halliday, A.N.:2000b, 'Accretion of Primitive Planetesimals: Hf-W Isotopic Evidence from Enstatite Chondrites', Science 288, 1629-1631.
Lee, T., Papanastassiou, D.A., and Wasserburg, G.J.:1977, 'Aluminum-26 in the Early Solar System: Fossil or Fuel?', Astrophys. J. 322, L107-L110.
Lee, T., Shu, F.H., Shang, H., Glassgold, A.E., and Rehm, K.E.:1998, 'Protostellar Cosmic Rays and Extinct Radioactivities in Meteorites', Astrophys. J. 506, 898-912.
Lewis, J.S.:1972, 'Metal/silicate Fractionation in the Solar System', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 15, 286-290.
Lin, D.N.C., and Papaloizou, J.:1985, 'On the Dynamical Origin of the Solar System', in D.C. Black and M.S. Matthews (eds.), Protostars and Planets II, 981-1072, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 981-1072.
Lodders, K.:1998, 'A Survey of Shergottite, Nakhlite and Chassigny Meteorites Whole-rock Compositions', Met. Planet. Sci. 33 Suppl., A183-A190.
Lodders, K.:2000, 'An Oxygen Isotope Mixing Model for the Accretion and Composition of Rocky Planets', in W. Benz et al. (eds.), From Dust to Terrestrial Planets, Space Sci. Rev. 92, 341-354.
Lodders, K., and Fegley, B.:1997, 'An Oxygen Isotope Model for the Composition of Mars', Icarus 126, 373-394.
Longhi, J., and Pan, V.:1989, 'The Parent Magmas of the SNC Meteorites', Proc. 19 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, pp. 451-464.
Longhi, J., Knittle, E., Holloway, J.R., and Wänke, H.:1992, 'The Bulk Composition, Mineralogy and Internal Structure of Mars', in H.H. Kieffer, B.M. Jakosky, C.W. Snyder, and M.S. Matthews (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 84-208.
Lugmair, G.W., and Galer, S.J.G.:1992, 'Age and Isotopic Relationships Among the Angrites Lewis Cliff-86010 and Angra Dos Reis', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 56, 1673-1694.
Lugmair, G.W., and Shukolyukov, A.:1998, 'Early Solar System Timescales According to 53Mn-53Cr Systematics', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 62, 2863-2886.
Marti, K., Kim, J.S., Thakur, A.N., McCoy, T.J., and Keil, K.:1995, 'Signatures of the Martian Atmosphere in Glass of the Zagami Meteorite', Science 267, 1981-1984.
Matthew, K.J., and Marti, K.:2001, 'Early Evolution of Martian Volatiles: Nitrogen and Noble Gas Components in ALH84001 and Chassigny', J. Geophys. Res., in press.
McDonough, W.F., and Sun, S.-S.:1995, 'The Composition of the Earth', Chem. Geol. 120, 223-253.
Melosh, H.J.:1990, 'Giant Impacts and the Thermal State of the Early Earth, in H.E. Newsom and J.H. Jones (eds.), Origin of the Earth, Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, pp. 69-83.
Melosh, H.J., and Vickery, A.M.:1989, 'Impact Erosion of the Primordial Atmosphere of Mars', Nature 338, 487-489.
Melosh, H.J., Vickery, A.M., and Tonks, W.B.:1993, 'Impacts and the Early Environment and Evolution of the Terrestrial Planets', in E.H. Levy and J.I. Lunini (eds.), Protostars and Planets III, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, 1339-1370.
Minarik, W.G., Ryerson, F.J., and Watson, E.B.:1996, 'Textural Entrapment of Core-forming Melts', Science 272, 530-533.
Münker, C., Weyer, S., Mezger, K., Rehkämper, M., Wombacher, F., and Bischoff, A.:2000, 92Nb-92Zr and the Early Differentiation History of Planetary Bodies', Science 289, 1538-1542.
Newsom, H.E.:1990, 'Accretion and Core Formation in the Earth:Evidence from Siderophile Elements', in H.E. Newsom and J.H. Jones (eds.), Origin of the Earth, Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, pp. 273-288.
Newsom, H.E.:1995, 'Composition of the Solar System, Planets, Meteorites, and Major Terrestrial Reservoirs', Global Earth Physics, A Handbook of Physical Constants, AGU Reference Shelf 1, American Geophysical Union.
Newsom, H.E., White, W.M., Jochum, K.P., and Hofmann, A.W.:1986, 'Siderophile and Chalcophile Element Abundances in Oceanic Basalts, Pb Isotope Evolution and Growth of the Earth's core', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 80, 299-313.
Newsom, H.E., Sims, K.W.W., Noll, Jr., P.D., Jaeger, W.L., Maehr, S.A., and Bessera, T.B.:1996, 'The Depletion of W in the Bulk Silicate Earth', Geochm. Cosmochim. Acta 60, 1155-1169.
Nichols:2000, 'Short-lived Radionuclides in Meteorites:Constraints of Nebular Timescales for the Production of Solids', in W. Benz et al. (eds.), From Dust to Terrestrial Planets, Space Sci. Rev. 92, 113-122.
Nyquist, L.E., Bansal, B., Wiesmann, H., and Shih, C.-Y.:1994, 'Neodymium, Strontium and Chromium Isotopic Studies of the LEW86010 and Angra-Dos-Reis Meteorites and the Chronology of the Angrite Parent Body', Meteoritics 29, 872-885.
Nyquist, L.E., Lindstrom, D., Shih, C.-Y., Weismann, H., Mittlfelhdt, D., Wentworth, S., and Martinez, R.:1997, 'Mn-Cr Systematics of Chondrules from the Bishunpur and Chainpur Meteorites', Proc. 28 th Lunar Planet. Sci., 1033-1034.
Ott, U.:1988, 'Noble Gases in SNC Meteorites: Shergotty, Nakhla, Chassigny', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 52, 1937-1948.
Pepin, R.O.:1994, 'Evolution of the Martian Atmosphere', Icarus 111, 289-304.
Quitté, G., Birck, J.-L., and Allègre, C.J.:2000, '182Hf-182W Systematics in Eucrites:The Puzzle of Iron Segregation in the Early Solar System', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 184, 83-94.
Rammensee, W., and Wänke, H.:1977, 'On the Partition Coefficient of Tungsten Between Metal and Silicate and its Bearing on the Origin of the Moon', Proc. 8 th Lunar Sci. Conf., 399-409.
Righter, K., and Drake, M.J.:1996, 'Core Formation in Earth's Moon, Mars, and Vesta', Icarus 124, 513-529.
Ringwood, A.E.:1977, 'Composition of the Core and Implications for Origin of the Earth', Geochem. J. 11, 111-135.
Ringwood, A.E.:1979, On the Origin of Earth and Moon, Springer, New York.
Robert, F., Rejou-Michel, A., and Javoy, M.: 1992, 'Oxygen Isotope Homogeneity of the Earth:New Evidence', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 108, 1-10.
Russell, S.S., Srinivasan, G., Huss, G.R., Wasserburg, G.J., and MacPherson, G.J.:1996, 'Evidence for Widespread 26Al in the Solar Nebula and Constraints for Nebula Time Scales', Science 273, 757-762.
Safronov, V.S.:1954, 'On the Growth of Planets in the Protoplanetary Cloud', Astron. Zh. 31, 499-510.
Sanloup, C., Blichert-Toft, J., Télouk, P., Gillet, P., and Albarède, F.:2000, 'Zr Isotope Anomalies in Chondrites and the Presence of Live 92Nb in the Early Solar System', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 184, 75-81.
Sasaki, S., and Nakazawa, K.:1986, 'Metal-silicate Fractionation in the Growing Earth: Energy Source for the Terrestrial Magma Ocean', J. Geophys. Res. 91, 9231-9238.
Sato, M.:1976, 'Oxygen Fugacity and Other Thermochemical Parameters of Apollo 17 High-Ti Basalts and Their Implications on the Reduction Mechanism', Proc. 7 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 1323-1344.
Sato, M., Hickling, N.L., and McLane, J.E.:1973, 'Oxygen Fugacity Values of Apollo 12, 14 and 15 Lunar Samples and Reduced State of Lunar Magmas', Proc. 4 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 1061-1079.
Shaw, G.H.:1978, 'Effects of Core Formation', Phys. Earth Plan. Inter. 16, 361-369.
Shih, C.-Y., Nyquist, L.E., Bogard, D.D., Mckay, G.A., Wooden, J.L., Bansal, B.M., and Wiesmann, H.:1982, 'Chronology and Petrogenesis of Young Achondrites, Shergotty, Zagami and ALHA77005:Late Magmatism on a Geologically Active Planet', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 46, 2323-2344.
Shu, F.H., Adams, F.C., and Lizano, S.:1987, 'Star Formation in Molecular Clouds-Observation and Theory', Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 25, 23-81.
Shu, F.H., Shang, H., Glassgold, A.E., and Lee, T.:1997, 'X-rays and Fluctuating X-winds from Protostars', Science 277, 1475-1479.
Sleep, N.H.:1994, 'Martian Plate Tectonics', J. Geophys. Res. 99, 5639-5655.
Solomon, S.C.:1979, 'Formation, History, and Energetics of Cores in the Terrestrial Planets', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 19, 168-182.
Stevenson, D.J.:1981, 'Models of the Earth's Core', Science 214, 611-619.
Stevenson, D.J.:1990, 'Fluid Dynamics of Core Formation', in H.E. Newsom and J.H. Jones (eds.), Origin of the Earth, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 231-249.
Stolper, E.:1977, 'Experimental Petrology of Eucritic Meteorites', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 41, 587-611.
Swindle, T.D., and Jones, J.H.:1997, 'The Xenon Isotopic Composition of the Primordial Martian Atmosphere:Contrib utions from Solar and Fission components', J. Geophys. Res. 102, 1671-1678.
Taylor, S.R., and McLennan, S.M.:1985, The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution, Blackwell Sci.
Toksöz, M.N., and Hsui, A.T.:1978, 'Thermal History and Evolution of Mars', Icarus 34, 537-547.
Treiman, A.H., Drake, M.J., Janssens, M.-J., Wolf, R., and Ebihara, M.:1986, 'Core Formation in the Earth and Shergottite Parent Body (SPB):Chemical Evidence from Basalts', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 1071-1091.
Treiman, A.H., Jones, J.H., and Drake, M.J.:1987, 'Core Formation in the Shergottite Parent Body and Comparison with the Earth', J. Geophys. Res. 92, 627-632.
Turekian, K.K., and Clark, S.P., Jr.:1969, 'Inhomogeneous Accumulation of the Earth from the Primitive Solar Nebula', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 6, 346-348.
Wänke, H.:1981, 'Constitution of Terrestrial Planets', Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A303, 287-302.
Wänke, H., and Dreibus, G.:1988, 'Chemical Composition and Accretion History of Terrestrial Planets', Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A325, 545-557.
Wänke, H., and Dreibus, G.:1994, 'Chemistry and Accretion of Mars', Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond A349, 285-293.
Wänke, H., Dreibus, G., and Jagoutz, E.:1984, 'Mantle Chemistry and Accretion History of the Earth', in A. Kroner, G.N. Hanson, and A.M. Goodwin (eds.), Springer, New York, pp. 1-24.
Wallace, P., and Carmichael, I.S.E.:1992, 'Sulfur in Basaltic Magmas', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 56, 1863-1874.
Warren, P.H., and Kallemeyn, G.W.:1996, 'Siderophile Trace Elements in ALH84001, Other SNC Meteorites and Eucrites:Evidence for Heterogeneity, Possibly Time-linked, in the Mantle of Mars', Met. Planet. Sci. 31, 97-105.
Warren, P.H., and Kallemeyn, G.W.:1997, 'Yamato-793605, EET79001, and Other Presumed Martian Meteorites:Compositional Clues to Their Origin', Antarct. Meteorite Res. 10, 61-81.
Warren, P.H., Greenwood, J.P., Richardson, J.W., Rubin, A.E., and Verish, R.S.:2000, 'Geochemistry of Los Angeles, a Ferroan, La-and Th-rich Basalt from Mars', Proc. 31 st Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., LPI, Houston, abstract #2001 (CD-ROM).
Wetherill, G.W.:1986, 'Accumulation of the Terrestrial Planets and Implications Concerning Lunar Origin', in W.K. Hartmann, R.J. Phillips, and G.J. Taylor (eds.), Origin of the Moon, LPI, Houston, pp. 519-550.
Wetherill, G.W.:1994a, 'Provenance of the Terrestrial Planets', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 58, 4513-4520.
Wetherill, G.W.:1994b, 'Possible Consequences of Absences of “Jupiters” in Planetary Systems', Astrophys. Space Sci. 212, 23-32.
Wolf, R., Woodrow, A., and Anders, E.:1979, 'Lunar Basalts and Pristine Highland Rocks: Comparison of Siderophile and Volatile Elements', Proc. 10 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 2107-2130.
Yi, W., Halliday, A.N., Alt, J.C., Lee, D.-C., Rehkämper, M., Garcia, M., Langmuir, C., and Su, Y.:2000, 'Cadmium, Indium, Tin, Tellurium and Sulfur in Oceanic Basalts:Implications for Chalcophile Element Fractionation in the Earth', J. Geophys. Res. 105, 18,927-18,948.
Zahnle, K.J.:1993, 'Xenological Constraints on the Impact Erosion of the Early Martian Atmosphere', J. Geophys. Res. 98, 10,899-10,913.
Zharkov, V.N.:1996, 'The Internal Structure of Mars: A Key to Understanding the Origin of Terrestrial Planets', Sol. Syst. Res. 30, 456-465.
Zinner, E., and Göpel, C.:1992, 'Evidence for 26Al in Feldspars from the H4 Chondrite Ste Marguerite', Meteoritics 27, 311.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halliday, A., Wänke, H., Birck, JL. et al. The Accretion, Composition and Early Differentiation of Mars. Space Science Reviews 96, 197–230 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011997206080
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011997206080