Abstract
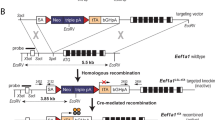
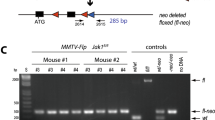
Using the phage P1-derived Cre/loxP recombination system, we have developed a strategy for efficient mammary tissue specific inactivation of floxed genes. Transgenic mice were generated which express Cre DNA-recombinase under the control of the mammary gland specific promoter of the ovine beta- lactoglobulin (BLG) gene. To test the specificity of Cre mediated recombination, we crossed these mice to animals harbouring a floxed DNA ligase I allele. We show that the BLG-Cre construct specifies mammary specific gene deletion, and furthermore that it is temporally regulated, predominantly occurring during lactation. We fully characterised the extent of gene deletion in one line (line 74). In this strain the virgin gland is characterised by low levels (7%) of Cre mediated deletion, whereas 70–80% of cells within the lactating mammary gland have undergone recombination. Immunohisto-chemistry and indirect in situ PCR were used respectively to demonstrate that both Cre protein and Cre activity were evenly distributed throughout the population of secretory epithelial cells. The level of background recombination in non-mammary tissues was found to be ≤1.1%, irrespective of mammary gland developmental status. Crossing the transgenic BLG-Cre strain described here to mice harbouring other floxed alleles will facilitate the functional analysis of those genes during differentiation and development of the mammary gland.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, S. and Clark, J. (1988) Characterisation of the gene encoding ovine β-lactoglobulin: similarity to the genes for retinol binding protein and other secretory proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 199, 415–26.
Archibald, A.L., McClenaghan, M., Hornsey, V., Simons, J.P. and Clark, A.J. (1990) High-level expression of biologically active human α1–antitrypsin in the milk of transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 5178–82.
Barlow, C., Schroeder, M., Lekstrom-Himes, J., Kylefjord, H., Deng, C.-X., Wynshaw-Boris, A., Spiegelman, B.M. and Xanthopoulos, K.G. (1997) Targeted expression of Cre recombinase to adipose tissue of transgenic mice directs adipose-specific excision of loxP-flanked gene segments. Nucl. Acid. Res. 25, 2543–5.
Bentley, D.J., Selfridge, J., Millar, J.K., Samuel, K., Hole, N., Ansell, J.D. and Melton, D.W. (1996) DNA ligase I is required for fetal liver erythropoiesis but is not essential for mammalian cell viability. Nature Gen. 13, 489–91.
Chambers, C.A. (1994) TKO'ed Lox, stock and barrel. BioEssays 16, 865–68.
Clark, A.J., Cowper, A., Wallace, R., Wright, G. and Simons, J.P. (1992) Rescuing transgene expression by co-integration. Bio/Technology 10, 1450–4.
Dale, E.C. and Ow, D.W. (1990) Intra-and intermolecular site-specific recombination in plant cells mediated by bacteriophage P1 recombinase. Gene 91, 79–85.
Dobie, K.W., Lee, M., Fantes, J.A., Graham, E., Clark, A.J., Springbett, A., Lathe, R. and McClenaghan, M. (1996) Variegated transgene expression in mouse mammary gland is determined by the transgene integration locus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93, 6659–64.
Farini, E. and Whitelaw, C.B.A. (1995) Ectopic expression of β-lactoglobulin transgenes. Mol. Gen. Genet. 246, 734–8.
Gu, H., Marth, J.D., Orban, P.C., Mossmann, H. and Rajewsky, K (1994) Deletion of a DNA polymerase β gene segment in T cells using cell type-specific gene targeting. Science 265, 103–6.
Günzburg, W.H., Salmons, B., Zimmermann, B., Müller, M., Erfle, V. and Brem, G. (1991) A Mammary-Specific Promotor Directs Expression of Growth Hormone not only to the Mammary Gland, but also to Bergman Glia Cells in Transgenic Mice. Mol. Endo. 5, 123–33.
Harris, S., McClenaghan, M., Simons, J.P., Ali, S. and Clark, A.J. (1991) Developmental Regulation of the Sheep β-Lactoglobulin Gene in the Mammary Gland of Transgenic Mice. Dev. Gen. 12, 299–307.
Kilby, N.J., Snaith, M.R. and Murray, J.A. (1993) Site-specific recombinases: tools for genome engineering. Trends Genet. 9, 413–21.
Kitamoto, T., Nakamura, K., Nakao, K., Shibuya, S., Shin, R.W., Gondo, Y., Katsuki, M. and Tateishi, J. (1996) Humanized prion protein knock-in by Cre-induced site-specific recombination in the mouse. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 222, 742–7.
Kühn, R., Schwenk, F., Aguet, M., and Rajewsky, K. (1995) Inducible gene targeting in mice. Science 269, 1427–9.
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature (London) 227, 722–5.
Lakso, M., Sauer, B., Mosinger Jr., B., Lee, E.J., Manning, R.W., Yu, S.H., Mulder, K.L. and Westphal, H. (1992) Targeted oncogene activation by site-specific recombination in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 6232–6.
Li, Z.-W., Stark, G., Gotz, J., Rulicke, T., Muller, U. and Weissmann, C. (1996) Generation of mice with a 200–kb amyloid precursor protein gene deletion by Cre recombinase-mediated site-specific recombination in embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93, 6158–62.
Maruyama, I.N. and Brenner, S. (1992) A selective lambda phage cloning vector with automatic excision of the insert in a plasmid. Gene 120, 135–41.
McWhir, J., Selfridge, J., Harrison, D.J., Squires, S and Melton, D.W. (1993) Mice with DNA repair gene (ERCC-1) deficiency have elevated levels of p53, liver nuclear abnormalities and die before weaning. Nature Gen. 5, 217–24.
Melton, D.W., Ketchen, A.-M., and Selfridge, J. (1997) Stability of HPRT marker gene expression at different gene-targeted loci: observing and overcoming a position effect. Nucl. Acid. Res. 25, 3937–43.
Ramírez-Solis, R., Liu, R. and Bradley, A. (1995) Chromosome engineering in mice. Nature (London) 378, 720–4.
Rickert, R.C., Roes, J. and Rajewsky, K. (1997) B lymphocyte-specific, Cre-mediated mutagenesis in mice. Nucl. Acid. Res. 26, 1317–8.
Robinson, G.W., McKnight, R.A., Smith, G.H. and Hennighausen L. (1995) Mammary epithelial cells undergo secretory differentiation in cycling virgins but require pregnancy for the establishment of terminal differentiation. Development 121, 2079–90.
Rollini, P., Billotte, J., Kolb, E. and Diggelmann, H. (1992) Expression Pattern of Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus in Transgenic Mice Carrying Exogenous Proviruses of Different Origins. J. Virol. 66, 4580–6.
Sauer, B. (1987) Functional expression of the Cre-lox site-specific recombination system in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisae. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 2087–96.
Sauer, B. and Henderson, N. (1988) Site-specific DNA recombination in mammalian cells by the Cre recombinase of bacteriophage P1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 5166–70.
Sauer, B. and Henderson, N. (1990) Targeted insertion of exogenous DNA into the eucaryotic genome by the Cre recombinase. New Biol. 2, 441–9.
Smith, A.J.H., De Sousa, M.A., Kwabi-Addo, B., Heppell-Parton, A., Impey, H. and Rabbitts, P. (1995) A site-directed chromosomal translocation induced in embryonic stem cells by Cre-loxP recombination. Nature Genet. 9, 376–85.
Thompson, S., Clarke, A.R., Pow, A.M., Hooper, M.L. and Melton, D.W. (1989) Germ line transmission and expression of a corrected HPRT gene produced by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Cell 56, 313–21.
Torres, R.M., Flaswinkel, H., Reth, M. and Rajewsky, K. (1996) Aberrant B cell development and immune response in mice with a compromised BCR complex. Science 272, 1804–8.
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T. and Gordon, J. (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 4350–4.
Tsien, J.Z., Chen, D.F., Gerber, D., Tom, C., Mercer, E.H., Anderson, D.J., Mayford, M., Kandel, E.R. and Tonegawa, S. (1996) Subregion-and Cell Type-Restricted Gene Knockout in Mouse Brain. Cell 87, 1317–26.
Wagner, K.-U., Wall, R.J., St-Onge, L., Gruss, P., Wynshaw-Boris, A., Garrett, L., Minglin, L., Furth, P.A. and Henninghausen, L. (1997) Cre-mediated gene deletion in the mammary gland. Nucl. Acid. Res. 25, 4323–30.
Whitelaw, C.B.A., Harris, S., McClenaghan, M., Simons, J.P. and Clark, A.J. (1992) Position-independent expression of the ovine β-lactoglobulin gene in transgenic mice. Biochem. J. 286, 31–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selbert, S., Bentley, D.J. Efficient BLG-Cre Mediated Gene Deletion in the Mammary Gland. Transgenic Res 7, 387–398 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008848304391
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008848304391