Article contents
A categorical invariant of flow equivalence of shifts
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 September 2014
Abstract
We prove that the Karoubi envelope of a shift—defined as the Karoubi envelope of the syntactic semigroup of the language of blocks of the shift—is, up to natural equivalence of categories, an invariant of flow equivalence. More precisely, we show that the action of the Karoubi envelope on the Krieger cover of the shift is a flow invariant. An analogous result concerning the Fischer cover of a synchronizing shift is also obtained. From these main results, several flow equivalence invariants—some new and some old—are obtained. We also show that the Karoubi envelope is, in a natural sense, the best possible syntactic invariant of flow equivalence of sofic shifts. Another application concerns the classification of Markov–Dyck and Markov–Motzkin shifts: it is shown that, under mild conditions, two graphs define flow equivalent shifts if and only if they are isomorphic. Shifts with property (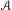 $\mathscr{A}$) and their associated semigroups, introduced by Wolfgang Krieger, are interpreted in terms of the Karoubi envelope, yielding a proof of the flow invariance of the associated semigroups in the cases usually considered (a result recently announced by Krieger), and also a proof that property (
$\mathscr{A}$) and their associated semigroups, introduced by Wolfgang Krieger, are interpreted in terms of the Karoubi envelope, yielding a proof of the flow invariance of the associated semigroups in the cases usually considered (a result recently announced by Krieger), and also a proof that property (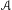 $\mathscr{A}$) is decidable for sofic shifts.
$\mathscr{A}$) is decidable for sofic shifts.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2014
References
- 10
- Cited by




