Abstract
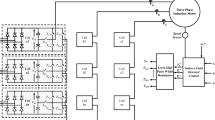
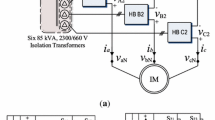
Medium- and high-voltage motors are characterized by high power and large inertia, and are widely used in industrial frequency conversion. The cascaded H-bridge multilevel (CHB-ML) inverter adopts a modular design concept to realize high-voltage and high-power functions by cascading multiple identical low-voltage conversion units. Moreover, the harmonic content of the output current of the inverter is small. For this purpose, a multilevel inverter consisting of eight H-bridge inverter units cascaded in each phase is introduced to drive medium- and high-voltage asynchronous motors for starting and frequency regulation. The carrier phase-shifted sinusoidal pulse-width modulation technique, DC voltage equalization control of power unit, and speed sensorless vector control strategy based on a voltage–current hybrid chain observer are mainly introduced. The simulation and experimental results of the real-time digital simulation system (RTDS) of the asynchronous motor dragged by the inverter verify that the CHB-ML inverter with the proposed control strategy has good starting and frequency regulation performance. These findings provide a technical guarantee for the field of medium- and high-voltage high-power drives.























Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Kumar, R., Kant, P., Singh, B.: An 18-pulse converter and 4-level cascaded inverter based induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 58(3), 4122–4133 (2022)
Singh, B., Kumar, R., Kant, P.: Adjustable speed induction motor drive fed by 13-level cascaded inverter and 54-pulse converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 58(1), 890–900 (2022)
Ogawa, R., Takiguchi, M., Tadano, Y.: Multilevel fixed pulse pattern control for medium-voltage high-frequency inverter. IEEJ J. Industry Appl. 10(6), 652–662 (2021)
Saito, K., Akagi, H.: A real-time real-power emulator for a medium-voltage high-speed electrical drive: discussion on mechanical vibrations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 57(2), 1482–1494 (2021)
Titus, J., Harikrishnan, P., Hatua, K.: An SCR-based CSI-fed induction motor drive for high power medium voltage applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(6), 4657–4666 (2021)
Wei, Q., Xing, L., Xu, D.W., Wu, B., Zargari, N.R.: Modulation schemes for medium-voltage pwm current source converter-based drives: an overview. IEEE J. Emerg. Selected Top. Power Electr. 7(2), 1152–1161 (2019)
Zhu, N., Xu, D., Wu, B., Zargari, N.R., Kazerani, M., Liu, F.R.: Common mode voltage reduction methods for current-source converters in medium voltage drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 28(2), 995–1006 (2013)
Ebrahimi, J., Karshenas, H., Bakhshai, A.: A five-level nested diode-clamped converter for medium-voltage applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 69(7), 6471–6483 (2022)
Attique, Q.M., Wang, K., Zheng, Z.D., Zhu, H., Li, Y.D., Rodriguez, J.: A generalized simplified virtual vector pwm to balance the capacitor voltages of multilevel diode-clamped converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 37(8), 9377–9391 (2022)
Jacobo-Palmer A., Garrido J., Escobedo-Trujillo B., Revuelta-Acosta JD.: Design and simulation of reduced diode clamped multilevel inverter. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Engineering Veracruz. 1–5 (2021)
Choi S., Meliopoulos A. P.: Space Vector Modulation (SVM)-exploited Binary Capacitor Voltage Control (BCVC)-based Flying-Capacitor-Clamped Multilevel Converter (FCCMC) for Low Nominal DC Voltage Applications. 2021 22nd IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology. 488–493 (2021)
Ebrahimi, J., Karshenas, H., Eren, S., Bakhshai, A.: A fast-decoupled space vector modulation scheme for flying capacitor-based multilevel converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 36(12), 14539–14549 (2021)
Liu, J., Zhang, D., Dong, D.: Modeling and control method for a three-level hybrid modular multilevel converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 37(3), 2870–2884 (2022)
Le, D.D., Lee, D.C.: A modular multilevel converter topology with novel middle submodules to reduce capacitor voltage fluctuations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 37(1), 70–75 (2022)
Fan, B.R., Wang, J., Yu, J.H., et al.: Cell capacitor voltage switching-cycle balancing control for modular multilevel converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 37(3), 2525–2530 (2022)
Lewicki, A., Odeh, C., Morawiec, M.: Space vector pulse width modulation strategy for multilevel cascaded h-bridge inverter with DC-link voltage balancing ability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 70(2), 1161–1170 (2023)
Cheerangal, M.J., Jain, A.K., Das, A.: Dynamic addition of common mode voltage in post fault operation of cascaded h-bridge converter fed induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 70(2), 1261–1269 (2023)
Kang, D., Badawi, S., Ni, Z., Abuelnaga, A.H., Narimani, M., Zargari, N.R.: Review of reduced switch-count power cells for regenerative cascaded H-bridge motor drives. IEEE Access. 10, 82944–82963 (2022)
Fang, W., Yang, Z., Sun, X., et al.: Speed sensorless control of bearingless induction motors based on adaptive flux observer. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 17, 1803–1813 (2022)
Jo, G.J., Choi, J.W.: Rotor flux estimator design with offset extractor for sensorless driven induction motors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 37(4), 4497–4510 (2022)
Yang, Z.B., Lu, C.L., Sun, X.D., Ji, J.L., Ding, Q.F.: Study on active disturbance rejection control of a bearingless induction motor based on an improved particle swarm optimization-genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans Transport Electr. 7(2), 694–705 (2021)
Yildiz, R., Barut, M., Sun, X.D., Demir, R.: Extended Kalman filter based estimations for improving speed-sensored contro lperformance of induction motors. IET Electric Power Appl. 14(12), 2471–2479 (2020)
Mansouri SA., Ahmarinejad A., Javadi MS., Heidari R., Catalao JPS.: Improved double-surface sliding mode observer for flux and speed estimation of induction motors. IET Electric Power Appl. 14(6), 1002–1010 (2020)
Devanshu, A., Singh, M., Kumar, N.: An improved nonlinear flux observer based sensorless FOC IM drive with adaptive predictive current control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35(1), 652–666 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52067008), the Science and Technology Research Project of the Education Department of Jiangxi Province of China (GJJ210823), and the Graduate Innovation Project of the Education Department of Jiangxi Province of China (YC2023-B219).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WW was involved in the technical research, simulation modeling, experimental platform building and testing, software, and paper writing. XL carried out technical proposal guidance, experiment guidance, paper review, and funding acquistion. JL, ZL and CH conducted the technical proposal guidance, and paper review.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, W., Liu, X., Liang, J. et al. Application of cascaded H-bridge multilevel inverter in the speed regulation of medium- and high-voltage asynchronous motor. J. Power Electron. 24, 391–413 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-023-00759-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-023-00759-0