Abstract
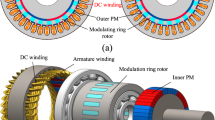
This paper is a comparative analysis study on topologies of magnetic geared motors for the application of railway vehicle traction systems. The magnetic geared motor (MGM) is a system in which a magnetic gear and a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) are mechanically combined, and it consists of a dual rotor that rotates at different speeds. Due to these characteristics, it has the advantages of high-power density and lightweight compared to the existing traction system. However, since the input/output relationship and electromagnetic field characteristics of this motor are completely different depending on topology, it is important to select an appropriate topology according to the application. Recently, some studies have been conducted to reflect this in industry or electric vehicles, but there is no study as a traction motor for urban railway vehicles. Therefore, in this paper, the FEM model was presented by selecting the MGM topology suitable for railway vehicles. Also, it was verified through a miniature model experiment for the corresponding topology.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atallah K, Howe D (2001) A novel high-performance magnetic gear. IEEE Trans Magn 37(4):2844–2846
C-B Park, G Jeong (2017) Design and analysis of magnetic-geared permanent magnet synchronous motor for driving electric vehicles. In: 2017 20th international conference on electrical machines and systems (ICEMS) pp. 1–5.
Jo I-H, Lee H-W, Jeong G, Ji W-Y, Park C-B (2019) A study on the reduction of cogging torque for the skew of a magnetic geared synchronous motor. IEEE Trans Magn 55(2):1–5
Sun L, Cheng M, Jia H (2015) Analysis of a novel magnetic-geared dual-rotor motor with complementary structure. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 62(11):6737–6747
Wang Y, Ho SL, Fu WN, Shen JX (2013) A novel rotor position detection method for sensorless control of magnetic-geared permanent-magnet brushless motor. IEEE Trans Magn 49(7):3961–3964
Sun L, Cheng M, Zhang J, Song L (2016) Analysis and control of complementary magnetic-geared dual-rotor motor. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(11):6715–6725
Shin K, Cho H, Kim K, Hong K, Choi J (2018) Analytical investigation of the on-load electromagnetic performance of magnetic-geared permanent-magnet machines. IEEE Trans Magn 54(11):1–5
Ito K, Nakamura K (2021) Investigation of magnetic interaction of IPM-type magnetic-geared motor. IEEE Trans Magn 57(2):1–5
Zhang X, Liu X, Chen Z (2016) Investigation of unbalanced magnetic force in magnetic geared machine using analytical methods. IEEE Trans Magn 52(7):1–4
Jo IH, Lee J, Lee HW, Lee JB, Lim JH, Kim SH, Park CB (2022) A study on MG-PMSM for high torque density of 45 kW–class tram driving system. Energies 15(5):1749
Zhu ZQ, Liu Y (2018) Analysis of air-gap field modulation and magnetic gearing effect in fractional-slot concentrated-winding permanent-magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(5):3688–3698
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Korea Agency for Infrastructure Technology Advancement (KAIA) grant funded by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (22RSCD-A163330-03) and by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MIST). (No.2021R1F1A1064291)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, IH., Lee, J., Lee, HW. et al. A Topology Study for the Application of Magnetic Geared Motor as Traction for Urban Railway Vehicle. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 18, 4473–4479 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-023-01397-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-023-01397-z