Abstract
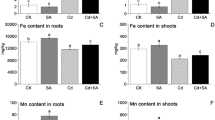
Rational utilization of exogenous additives is the key to enhance phytoremediation efficiency for removal of heavy metal contamination in soil. However, the physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms of organic acids promoting the removal of Cd from soil by hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum are still not well understood. EDTA and five organic acids, oxalic acid (OA), citric acid (CA), malic acid (MA), tartaric acid (TA), and succinic acid (SA), were added as exogenous additives to S. nigrum seedlings treated with Cd. The effect of EDTA and organic acids on physiological processes, Cd accumulation, and the expression of Cd stress related-genes in S. nigrum under Cd stress were analyzed. The growth of S. nigrum seedlings was significantly inhibited by Cd, but the addition of CA resulted in a 3.01-fold increase in seedling biomass compared to those treated with Cd alone. The content of the photosynthetic pigments in seedlings decreased significantly due to Cd toxicity, while CA could effectively restore the photosynthetic pigments to the level of CK. The levels of MDA, proline, and H2O2 induced by Cd toxicity decreased after CA application, which revealed that CA effectively alleviated Cd toxicity to S. nigrum. CA alleviates the Cd toxicity in the following aspects: it maintains the non-enzymatic antioxidant content, mediates the expression of enzymatic antioxidant genes such as SnCAT1, and alters the chemical form of Cd from high toxicity to low toxicity. Notably, CA effectively stimulates the expression of Cd transport and compartment-related genes, such as SnNRAMP3 and SnPCS1, thus facilitating Cd transport from the roots to the shoots. Through comprehensive evaluation, CA is considered to be the most effective chelating agent to enhance the efficiency of S. nigrum in removing Cd contamination. CA effectively alleviates photosynthetic pigment degradation and ROS homeostasis imbalance caused by Cd toxicity by regulating gene expression, thereby maintaining the growth of S. nigrum under Cd stress. Additionally, CA facilitates the accumulation of Cd in the shoots of S. nigrum. These findings suggest that CA can replace EDTA as a chelating agent for enhancing the ability of S. nigrum to remove Cd contamination.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Afshan S, Ali S, Bharwana SA et al (2015) Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:11679–11689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4396-8
Azeez L, Adejumo AL, Lateef A et al (2019) Zero-valent silver nanoparticles attenuate Cd and Pb toxicities on Moringa oleifera via immobilization and induction of phytochemicals. Plant Physiol Biochem 139:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.03.030
Bleicher A (2016) Technological change in revitalization-Phytoremediation and the role of nonknowledge. J Environ Manage 184:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.046
Cai W, Chen T, Lei M (2021) Effective strategy to recycle arsenic-accumulated biomass of Pteris vittata with high benefits. Sci Total Environ 756:143890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143890
Chen S, Wang Q, Lu H et al (2019) Phenolic metabolism and related heavy metal tolerance mechanism in Kandelia obovata under Cd and Zn stress. Environ Pollut 169:134–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.11.004
Chen Y, Huang L, Liang X et al (2020) Enhancement of polyphenolic metabolism as an adaptive response of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) roots to aluminum stress. Environ Pollut 261:114230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114230
Chen Y, Jiang H, Liu Y et al (2022) A critical review on EDTA washing in soil remediation for potentially toxic elements (PTEs) pollutants. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 21:399–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-022-09613-4
Debela AS, Dawit M, Tekere M et al (2022) Phytoremediation of soils contaminated by lead and cadmium in Ethiopia, using Endod (Phytolacca dodecandra L.). Int J Phytorem 24:1339–1349. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2021.2025336
Fattahi B, Arzani K, Souri MK et al (2021) Morphophysiological and phytochemical responses to cadmium and lead stress in coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.). Ind Crops. Prod 171:113979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113979
Gavrilescu M (2022) Enhancing phytoremediation of soils polluted with heavy metals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 74:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2021.10.024
Guan H, Dong L, Zhang Y et al (2022) GLDA and EDTA assisted phytoremediation potential of Sedum hybridum ‘Immergrunchen’ for Cd and Pb contaminated soil. Int J Phytorem 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2022.2031865
Habiba U, Ali S, Farid M et al (2015) EDTA enhanced plant growth, antioxidant defense system, and phytoextraction of copper by Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1534–1544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3431-5
Huo C, He L, Yu T et al (2022) The superoxide dismutase gene family in nicotiana tabacum: genome-wide identification, characterization, expression profiling and functional analysis in response to heavy metal stress. Front Plant Sci 13:904105. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.904105
Ibrahim MH, Chee Kong Y, Mohd Zain NA (2017) Effect of cadmium and copper exposure on growth, secondary metabolites and antioxidant activity in the medicinal plant sambung nyawa (gynura procumbens (lour.) merr). Molecules 22:1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101623
Kim SH, Lee IS (2010) Comparison of the Ability of Organic Acids and EDTA to Enhance the Phytoextraction of Metals from a Multi-Metal Contaminated Soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84:255–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9888-0
Li R, Yang Y, Cao H et al (2023) Heterologous expression of the tobacco metallothionein gene NtMT2F confers enhanced tolerance to Cd stress in Escherichia coli and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 195:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.01.027
Li Y, Wang Y, Khan MA et al (2021) Effect of plant extracts and citric acid on phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 211:111902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.090
Li Z, Ma Z, van der Kuijp TJ et al (2014) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 468:843–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111902
Liao Y, Li Z, Yang Z et al (2023) Response of Cd, Zn translocation and distribution to organic acids heterogeneity in brassica juncea L. Plants 12:479. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12030479
Liu W, Huo C, He L et al (2022) The NtNRAMP1 transporter is involved in cadmium and iron transport in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Plant Physiol Biochem 173:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.01.024
López-Hidalgo C, Meijón M, Lamelas L et al (2021) The rainbow protocol: a sequential method for quantifying pigments, sugars, free amino acids, phenolics, flavonoids and MDA from a small amount of sample. Plant Cell Environ 44:1977–1986. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.14007
Ma LQ, Komar KM, Tu C et al (2001) A fern that hyperaccumulates arsenic. Nature 409:579–579. https://doi.org/10.1038/35078151
Mahmud JA, Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K et al (2018) Insights into citric acid-induced cadmium tolerance and phytoremediation in Brassica juncea L.: coordinated functions of metal chelation, antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:990–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.045
McCormac AC, Fischer A, Kumar AM et al (2001) Regulation of HEMA1 expression by phytochrome and a plastid signal during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 25:549–561. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00986.x
Meers E, Hopgood M, Lesage E et al (2004) Enhanced phytoextraction: in search of EDTA alternatives. Int J Phytorem 6:95–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/16226510490454777
Muradoglu F, Gundogdu M, Ercisli S et al (2015) Cadmium toxicity affects chlorophyll a and b content, antioxidant enzyme activities and mineral nutrient accumulation in strawberry. Biol Res 48:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-015-0001-3
Najeeb U, Xu L, Ali S et al (2009) Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of manganese and plant growth by alleviating the ultrastructural damages in Juncus effusus L. J Hazard Mater 170:1156–1163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.084
Nouri J, Khorasani N, Lorestani B et al (2009) Accumulation of heavy metals in soil and uptake by plant species with phytoremediation potential. Environ Earth Sci 59:315–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0028-2
Panchal P, Miller AJ, Giri J (2021) Organic acids: versatile stress-response roles in plants. J Exp Bot 72:4038–4052. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erab019
Panwar BS, Ahmed KS, Sihag D et al (2005) Distribution of cadmium and nickel among various forms in natural and contaminated soils amended with EDTA. Environ Dev Sustain 7:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-003-6374-4
Pedro GC, Luigi DF, Alvina G et al (2021) Oxidative stress and antioxidant metabolism under adverse environmental conditions: a review. Bot Rev 87:421–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12229-020-09231-1
Qureshi FF, Ashraf MA, Rasheed R et al (2020) Organic chelates decrease phytotoxic effects and enhance chromium uptake by regulating chromium-speciation in castor bean (Ricinus communis L.). Sci Total Environ 716:137061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137061
Saifullah ME, Qadir M et al (2009) EDTA-assisted Pb phytoextraction. Chemosphere 74:1279–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.007
Sebastian A, Prasad MNV (2018) Exogenous citrate and malate alleviate cadmium stress in Oryza sativa L.: Probing role of cadmium localization and iron nutrition. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 166:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.084
Seregin IV, Kozhevnikova AD (2023) Phytochelatins: sulfur-containing metal(loid)-chelating ligands in plants. Int J Mol Sci 24:2430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032430
Shen X, Dai M, Yang J (2022) A critical review on the phytoremediation of heavy metals from environment: Performance and challenges. Chemosphere 291:132979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132979
Vega A, Delgado N, Handford M (2022) Increasing heavy metal tolerance by the exogenous application of organic acids. Int J Mol Sci 23:5438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105438
Wan X, Lei M, Chen T (2016) Cost-benefit calculation of phytoremediation technology for heavy-metal-contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 563:796–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.080
Wang X, Liu Y, Zeng G et al (2008) Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in Bechmeria nivea (L.) Gaud. Environ Exp Bot 62:389–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.10.014
Wang Z, Hong X, Hu K et al (2017) Impaired magnesium protoporphyrin IX methyltransferase (ChlM) Impedes Chlorophyll Synthesis and Plant Growth in Rice. Front Plant Sci 8:1694. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01694
Wu L, Luo Y, Xing X et al (2004) EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil with Indian mustard and associated potential leaching risk. Agric Ecosyst Environ 102:307–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2003.09.002
Xie H, Bai G, Lu P et al (2022) Exogenous citric acid enhances drought tolerance in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Plant Biol 24:333–343. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.13371
Ye X, Liu C, Yan H et al (2022) Genome-wide identification and transcriptome analysis of the heavy metal-associated (HMA) gene family in Tartary buckwheat and their regulatory roles under cadmium stress. Gene 847:146884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2022.146884
Yuan X, Xue N, Han Z (2021) A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years. J Environ Sci 101:217–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.08.01.3
Zhang P, Zhao D, Liu Y et al (2019) Cadmium phytoextraction from contaminated paddy soil as influenced by EDTA and Si fertilizer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:23638–23644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05654-5
Zhi Y, Zhou Q, Leng X et al (2020) Mechanism of remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil with low-energy plant snapdragon. Front Chem 8:222. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00222
Zou Z, Yang J (2019) Genomics analysis of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding (Lhc) superfamily in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Gene 702:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.03.071
Funding
This work was supported by Chongqing Municipal Education Commission [Grant No. KJZD-K202001504] and Chongqing Natural Science Foundation project [Grant No. CSTB2022NSCQ-MSX1587].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LW: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration. YT: Data curation, Methodology, Investigation. CH: Investigation. PX: Methodology, Resources. YY: Investigation. LR: Methodology, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Yu, T., Cao, H. et al. Effects of EDTA and Organic Acids on Physiological Processes, Gene Expression Levels, and Cadmium Accumulation in Solanum nigrum Under Cadmium Stress. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 3823–3833 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01302-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01302-7