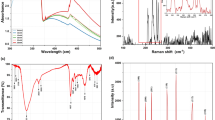
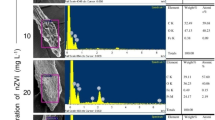
Abstract
Nanoparticles (NPs) have the potential to influence the growth and development of plants. NPs mediated seed priming is an efficient strategy for crop improvement and agricultural sustainability. However, the effect of NPs on plant growth and development is still not fully understood. Therefore in the present study, the impact of MgO-NPs (10, 50, 100, and 150 μg/ml) on the lentils (Lens culinaris) via nanopriming was determined. The morphological parameters, accumulation of enzymatic, non-enzymatic antioxidants and protein, and carbohydrate content were estimated in response to MgO-NPs priming. The lentils showed 39 and 43% reduction in the shoot and root length, respectively on exposure to 150 μg/ml MgO-NPs as compared to the untreated plants. MgO-NPs induced chlorophyll degradation and a 2–11% reduction in the carbohydrate level. A significant reduction in the flavonoid (27%) and total phenol (80%) accumulation led to a considerable decrease in the antioxidant potential (63%) of nanoprimed lentils than the untreated control. The accumulation and bioavailability of protein was also decreased in MgO-NPs treated lentils. MgO-NPs priming reduced the protein content by 27% and the digestibility by 31% than control lentils. The observed increase in protein precipitable tannins because of reduced carbohydrates was responsible for the evident reduction in protein digestibility and solubility. Overall, the study suggested the potential toxicity of MgO-NPs to lentils in a concentration-dependent manner. However, the observed results cannot be generalized for other crops including legumes. Hence, there is urgent need to investigate the plant responses to MgO-NPs exposure.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas Q, Liu G, Yousaf B, Ali MU, Ullah H, Ahmed R (2019) Effects of biochar on uptake, acquisition and translocation of silver nanoparticles in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in relation to growth, photosynthetic traits and nutrients displacement. Environ Pollut 250:728–736
Acharya P, Jayaprakasha GK, Crosby KM, Jifon JL, Patil BS (2020) Nanoparticle-mediated seed priming improves germination, growth, yield, and quality of watermelons (Citrullus lanatus) at multi-locations in Texas. Sci Rep 10:1–16
Agathokleous E, Belz RG, Kitao M, Koike T, Calabrese EJ (2019) Does the root to shoot ratio show a hormetic response to stress? An ecological and environmental perspective. J For Res 30(5):1569–1580
AlQuraidi AO, Mosa KA, Ramamoorthy K (2019) Phytotoxic and genotoxic effects of copper nanoparticles in coriander (Coriandrum sativum—Apiaceae). Plants 8:19
Anand KV, Anugraga AR, Kannan M, Singaravelu G, Govindaraju K (2020) Bio-engineered magnesium oxide nanoparticles as nano-priming agent for enhancing seed germination and seedling vigour of green gram (Vigna radiata L). Mater Lett 271:127792
Arakawa T, Kita Y, Carpenter JF (1991) Protein–solvent interactions in pharmaceutical formulations. Pharm Res 8:285–291
Avellan A, Schwab F, Masion A, Chaurand P, Borschneck D, Vidal V, Rose J, Santaella C, Levard C (2017) Nanoparticle uptake in plants: gold nanomaterial localized in roots of Arabidopsis thaliana by X-ray computed nanotomography and hyperspectral imaging. Environ Sci Technol 51:8682–8691
Bera MB, Mukherjee RK (1989) Solubility, emulsifying, and foaming properties of rice bran protein concentrates. J Food Sci 54:142–145
Cai L, Chen J, Liu Z, Wang H, Yang H, Ding W (2018a) Magnesium oxide nanoparticles: effective agricultural antibacterial agent against Ralstonia solanacearum. Front Microbiol 9:790
Cai L, Liu M, Liu Z, Yang H, Sun X, Chen J, Ding W (2018b) MgO NPs can boost plant growth: evidence from increased seedling growth, morpho-physiological activities, and Mg uptake in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L). Molecules 23:3375
Cakmak I, Kirkby EA (2008) Role of magnesium in carbon partitioning and alleviating photooxidative damage. Physiol Plant 133:692–704
Chahardoli A, Karimi N, Ma X, Qalekhani F (2020) Effects of engineered aluminum and nickel oxide nanoparticles on the growth and antioxidant defense systems of Nigella arvensis L. Sci Rep 10:1–11
Chang CC, Yang MH, Wen HM, Chern JC (2002) Estimation of total flavonoid content in propolis by two complementary colorimetric methods. J Food Drug Anal 10
Chory J (1992) A genetic model for light-regulated seedling development in Arabidopsis. Development 115:337–354
Doganlar ZB, Demir K, Basak H, Gul I (2010) Effects of salt stress on pigment and total soluble protein contents of three different tomato cultivars. Afr J Agric Res 5:2056–2065
Eckardt NA (2009) A new chlorophyll degradation pathway. Plant Cell 21:700
Fang Z, Bouwkamp J, Solomos T (1998) Chlorophyllase activities and chlorophyll degradation during leaf senescence in nonyellowing mutant and wild type of Phaseolus vulgaris L. J Exp Bot 49:503–510
Faris MEAIE, Takruri HR, Issa AY (2013) Role of lentils (Lens culinaris L.) in human health and nutrition: a review. Mediterr J Nutr Metab 6:3–16
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases: II. Purification and quantitative relationship with water-soluble protein in seedlings. Plant Physiol 59:315–318
Guleria P, Kumar V (2018) Impact of recombinant DNA technology and nanotechnology on agriculture. In: Lichtfouse E (EDS) Sustainable agriculture reviews 32. Sustainable agriculture reviews, vol 32. Springer, Cham.
Guleria P, Yadav SK (2014) Overexpression of a glycosyltransferase gene SrUGT74G1 from Stevia improved growth and yield of transgenic Arabidopsis by catechin accumulation. Mol Biol Rep 41:1741–1752
Guleria P, Masand S, Yadav SK (2014) Overexpression of SrUGT85C2 from Stevia reduced growth and yield of transgenic Arabidopsis by influencing plastidial MEP pathway. Gene 539:250–257
Guo W, Nazim H, Liang Z, Yang D (2016) Magnesium deficiency in plants: an urgent problem. Crop J 4:83–91
Harbertson JF, Yuan C, Mireles MS, Hanlin RL, Downey MO (2013) Glucose, fructose and sucrose increase the solubility of protein–tannin complexes and at high concentration, glucose and sucrose interfere with bisulphite bleaching of wine pigments. Food Chem 138:556–563
Hauer-Jákli M, Tränkner M (2019) Critical leaf magnesium thresholds and the impact of magnesium on plant growth and photo-oxidative defense: a systematic review and meta-analysis from 70 years of research. Front Plant Sci 10:766
Hermans C, Conn SJ, Chen J, Xiao Q, Verbruggen N (2013) An update on magnesium homeostasis mechanisms in plants. Metallomics 5:1170–1183
Hossain Z, Mustafa G, Sakata K, Komatsu S (2016) Insights into the proteomic response of soybean towards Al2O3, ZnO, and Ag nanoparticles stress. J Hazard Mater 304:291–305
Imada K, Sakai S, Kajihara H, Tanaka S, Ito S (2016) Magnesium oxide nanoparticles induce systemic resistance in tomato against bacterial wilt disease. Plant Pathol 65:551–560
Jahani M, Khavari-Nejad RA, Mahmoodzadeh H, Saadatmand S (2020) Effects of cobalt oxide nanoparticles (Co3O4 NPs) on ion leakage, total phenol, antioxidant enzymes activities and cobalt accumulation in Brassica napus. L Not Bot Hort Agrobot Cluj Napoca 48
Jhansi K, Jayarambabu N, Reddy KP, Reddy NM, Suvarna RP, Rao KV, Rajendar V (2017) Biosynthesis of MgO nanoparticles using mushroom extract: effect on peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) seed germination. 3 Biotech 7:1–11
Johnson N, Johnson CR, Thavarajah P, Kumar S, Thavarajah D (2020) The roles and potential of lentil prebiotic carbohydrates in human and plant health. Plants People Planet 2:310–319
Kah M, Tufenkji N, White JC (2019) Nano-enabled strategies to enhance crop nutrition and protection. Nat Nanotechnol 14:532–540
Kumar V, Guleria P (2020) Application of DNA-nanosensor for environmental monitoring: recent advances and perspectives. Curr Pollut Rep: 1–21
Kumar V, Guleria P, Kumar V, Yadav SK (2013) Gold nanoparticle exposure induces growth and yield enhancement in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci Total Environ 461:462–468
Kumar K, Solanki S, Singh SN, Khan MA (2016) Abioticconstraints of pulse production in India. In: Biswas SK, Kumar S, Chand G (eds) Disease of pulse crops and their sustainable management, BiotechBooks, New Delhi
Kumar V, Jain A, Wadhawan S, Mehta SK (2018) Synthesis of biosurfactant-coated magnesium oxide nanoparticles for methylene blue removal and selective Pb2+ sensing. IET Nanobiotechnol 12:241–253
Kumar V, Guleria P, Ranjan S (2021) Phytoresponse to nanoparticles exposure. In: Kumar V, Guleria P, Ranjan S, Dasgupta N, Lichtfouse E (eds) Nanotoxicology and nanoecotoxicology, Springer Nature, Switzerland AG
Li M, Ahammed GJ, Li C, Bao X, Yu J, Huang C, Zhou J (2016) Brassinosteroid ameliorates zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced oxidative stress by improving antioxidant potential and redox homeostasis in tomato seedling. Front Plant Sci 7:615
Liu R, Lal R (2015) Potentials of engineered nanoparticles as fertilizers for increasing agronomic productions. Sci Total Environ 514:131–139
López–Luna J, Camacho–Martínez MM, Solís–Domínguez FA, González–Chávez MC, Carrillo–González R, Martinez–Vargas S, Cuevas–Díaz MC (2018) Toxicity assessment of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles on wheat plants. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A 81:604–619
Ma Y, Kuang L, He X, Bai W, Ding Y, Zhang Z, Zhao Y, Chai Z (2010) Effects of rare earth oxide nanoparticles on root elongation of plants. Chemosphere 78:273–279
Maathuis FJ (2009) Physiological functions of mineral macronutrients. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:250–258
MacKinney G (1941) Absorption of light by chlorophyll solutions. J Biol Chem 140:315–322
Makkar HP, Blümmel M, Borowy NK, Becker K (1993) Gravimetric determination of tannins and their correlations with chemical and protein precipitation methods. J Sci Food Agri 61:161–165
Mall RK, Gupta A, Sonkar G (2017) Effect of climate change on agricultural crops. In: Dubey SK, Pandey A, Sangwan RS (eds) Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering. Elsevier
Mattson MP (2008) Hormesis defined. Ageing Res Rev 7(1):1–7
Mohammadkhani N, Heidari R (2008) Effects of drought stress on soluble proteins in two maize varieties. Turk J Biol 32:23–30
Nikolova M, Slavchov R, Nikolova G (2020) Nanotechnology in medicine. In: Hock F, Gralinski M (eds) Drug discovery and evaluation: methods in clinical pharmacology. Springer, Cham
Niu Y, Chai R, Liu L, Jin G, Liu M, Tang C, Zhang Y (2014) Magnesium availability regulates the development of root hairs in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant Cell Environ 37:2795–2813
Porgali ZB, Yurekli F (2005) Salt stress induced alterations in proline accumulation, relative water content and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in salt sensitive Lycopersicon esculentum and salt tolerant L. pennellii. Acta Bot Hun 47:173–182
Praburaj L, Design F, Nadu T (2018) Role of agriculture in the economic development of a country. Shanlax Int J Comm 6:1–5
Raigond P, Raigond B, Kaundal B, Singh B, Joshi A, Dutt S (2017) Effect of zinc nanoparticles on antioxidative system of potato plants. J Environ Biol 38:435
Rajput V, Minkina T, Mazarji M, Shende S, Sushkova S, Mandzhieva S, Jatav H (2020) Accumulation of nanoparticles in the soil-plant systems and their effects on human health. Ann Agric Sci 65:137–143
Rana DS, Dass A, Rajanna GA, Kaur R (2016) Biotic and abiotic stress management in pulses. Indian J Agron 61:S238–S248
Rani P, Kaur G, Rao KV, Singh J, Rawat M (2020) Impact of green synthesized metal oxide nanoparticles on seed germination and seedling growth of Vigna radiata (Mung Bean) and Cajanus cajan (Red Gram). J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 30:4053–4062
Rathore I, Tarafdar JC (2015) Perspectives of biosynthesized magnesium nanoparticles in foliar application of wheat plant. J Bionanosci 9:209–214
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ali B, Adrees M, Arshad M, Hussain A, Ur Rehman MZ, Waris AA (2019) Zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles improved the plant growth and reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat. Chemosphere 214:269–277
Shah V, Belozerova I (2009) Influence of metal nanoparticles on the soil microbial community and germination of lettuce seeds. Water Air Soil Pollut 197:143–148
Sharma P, Kumar V, Khosla R, Guleria P (2020) Exogenous naringenin improved digestible protein accumulation and altered morphology via VrPIN and auxin redistribution in Vigna radiata. 3 Biotech 10:1–14
Sharma P, Gautam A, Kumar V, Guleria P (2021a) In vitro exposed magnesium oxide nanoparticles enhanced the growth of legume Macrotyloma uniflorum. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16828-5
Sharma P, Kumar V, Guleria P (2021b) In vitro exposure of magnesium oxide nanoparticles negatively regulate the growth of Vigna radiata. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03738-9
Sharma P, Gautam A, Kumar V, Guleria P (2021c) In vitro exposure of magnesium oxide nanoparticles adversely affects the vegetative growth and biochemical parameters of black gram. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 16:100483
Singh A, Singh NB, Hussain I, Singh H (2017) Effect of biologically synthesized copper oxide nanoparticles on metabolism and antioxidant activity to the crop plants Solanum lycopersicum and Brassica oleracea var. botrytis. J Biotechnol 262:11–27
Tolaymat T, Genaidy A, Abdelraheem W, Dionysiou D, Andersen C (2017) The effects of metallic engineered nanoparticles upon plant systems: an analytic examination of scientific evidence. Sci Total Environ 579:93–106
Tombuloglu H, Tombuloglu G, Slimani Y, Ercan I, Sozeri H, Baykal A (2018) Impact of manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) nanoparticles on growth and magnetic character of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environ Pollut 243:872–881
Urbano G, Porres JM, Frías J, Vidal‐Valverde C (2007) Chapter 5 nutritional value. In: Yadav SS, McNeil D, Stevenson PC (eds) Lentil: an ancient crop for modern times. Springer, Berlin
Usman M, Farooq M, Wakeel A, Nawaz A, Cheema SA, UrRehman H, Ashraf I, Sanaullah M (2020) Nanotechnology in agriculture: current status, challenges and future opportunities. Sci Total Environ 721:137778
Vishwakarma K, Upadhyay N, Singh J, Liu S, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Chauhan DK, Tripathi DK, Sharma S (2017) Differential phytotoxic impact of plant mediated silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and silver nitrate (AgNO3) on Brassica sp. Front Plant Sci 8:1501
Wang X, Yang X, Chen S, Li Q, Wang W, Hou C, Gao X, Wang L, Wang S (2016) Zinc oxide nanoparticles affect biomass accumulation and photosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 6:1243
Yang J, Cao W, Rui Y (2017) Interactions between nanoparticles and plants: phytotoxicity and defense mechanisms. J Plant Interact 12:158–169
Zafar H, Abbasi BH, Zia M (2019) Physiological and antioxidative response of Brassica nigra (L.) to ZnO nanoparticles grown in culture media and soil. Toxicol Environ Chem 101:281–299
Zhang HX, Blumwald E (2001) Transgenic salt-tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in foliage but not in fruit. Nat Biotechnol 19:765–768
Zhang Z, Ke M, Qu Q, Peijnenburg WJGM, Lu T, Zhang Q, Ye Y, Xu P, Du B, Sun L, Qian H (2018) Impact of copper nanoparticles and ionic copper exposure on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) root morphology and antioxidant response. Environ Pollut 239:689–697
Zulfiqar F, Navarro M, Ashraf M, Akram NA, Munné-Bosch S (2019) Nanofertilizer use for sustainable agriculture: advantages and limitations. Plant Sci 289:110270
Zuverza-Mena N, Medina-Velo IA, Barrios AC, Tan W, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2015) Copper nanoparticles/compounds impact agronomic and physiological parameters in cilantro (Coriandrum sativum). Environ Sci Process Impacts 17:1783–1793
Acknowledgements
PS, AG, and PG are thankful to The Chancellor and The Vice-Chancellor, DAV University, Jalandhar for their continuous support and encouragement to carry out research. VK acknowledges Lovely Professional University management for encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PS: investigation, writing-original draft. AG: investigation, writing-original draft. VK: conceptualization, methodology, writing- review and editing, supervision. PG: conceptualization, methodology, writing- review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, P., Gautam, A., Kumar, V. et al. MgO nanoparticles mediated seed priming inhibits the growth of lentil (Lens culinaris). Vegetos 35, 1128–1141 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-022-00400-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-022-00400-8