Abstract
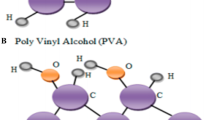
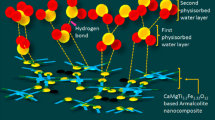
The polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and magnesium oxide (MgO) nanocomposites and (PVA–MgO) nanocomposites doped by Silicon carbide (SiC) nanoparticles have been fabricated with different concentrations of Silicon carbide and (PVA–MgO) nanocomposites. Both experimental and theoretical studies on structural and optical properties of novel (PVA–MgO–SiC) nanocomposites for humidity sensors were examined for first time with low cost, flexible and high sensitivity. The (PVA–MgO–SiC) nanocomposites were intended with various concentrations of Silicon carbide nanoparticles. The experimental results of optical properties for (PVA–MgO–SiC) nanocomposites indicated that the absorbance, absorption coefficient, extinction coefficient, refractive index, imaginary and real dielectric constants and optical conductivity of (PVA–MgO) nanocomposites increase with an increase in Silicon carbide nanoparticles concentrations. The absorbance increases from 0.432 to 2.55 a.u while the transmittance decreases from 0.779 to 0.230 a.u. The energy gap decreases from 4.4 to 2.1 eV. The energy gap theoretically decreases from 7.07 to 3.04 eV. The experimental results of novel (PVA–MgO–SiC) nanocomposites applications showed that (PVA–MgO–SiC) nanocomposites have high sensitivity for relative humidity. The results obtained were compared with theoretic results obtained by using Gaussian 09 program and Gaussian view 5.0.8 program and using density functional theory (DFT) at B3LYP level with 6-31G basis set.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Hashim, A. Hadi, Synthesis and characterization of (MgO–Y2O3–CuO) nanocomposites for novel humidity sensor application. Sens. Lett. 15(10), 858–861 (2017)
S. Ju et al., Dielectric properties of nanosilica/low-density polyethylene composites: the surface chemistry of nanoparticles and deep traps induced by nanoparticles. Exp. Polym. Lett. 8(9), 682 (2014)
I.R. Agool, K.J. Kadhim, A. Hashim, Synthesis of (PVA–PEG–PVP–ZrO2) nanocomposites for energy release and gamma shielding applications. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 21(2), 444–453 (2017)
P.H.C. Camargo, K.G. Satyanarayana, F. Wypych, Nanocomposites: synthesis, structure, properties and new application opportunities. Mater. Res. 12(1), 1–39 (2009)
D. Ham, J. Lee, Transition metal carbides and nitrides as electrode materials for low temperature fuel cells. Energies 2(4), 873–899 (2009)
J.S. Lee, T.H. Hyun, Metal carbides, in Encyclopedia of Catalysis, 1st edn., ed. by I.T. Horvath (Wiley, New York, 2003)
S. Gandhi, P. Abiramipriya, N. Pooja, J.J.L. Jeyakumari, A.Y. Arasi, V. Dhanalakshmi, R. Anbarasan, Synthesis and characterizations of nano sized MgO and its nano composite with poly(vinyl alcohol). J. Non-Cryst. Solids 357(1), 181–185 (2011)
K. Karthikeyan et al., Thermal properties and morphology of MgO–PVA nanocomposite film. J. Nanostruct. Polym. Nanocompos. 5(4), 83–88 (2009)
Z.-X. Tang, B.-F. Lv, MgO nanoparticles as antibacterial agent: preparation and activity. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 31(3), 591–601 (2014)
F.L. Rashid et al., Novel phase change materials, MgO nanoparticles, and water based nanofluids for thermal energy storage and biomedical applications. J. Pharm. Phytopharm. Res. 8(1), 46–56 (2018)
D.K.M. Al-Nasrawy et al., The effect of SiC–particles–reinforced MgO composites. J. Kufa-Phys. 3(1), 75–81 (2011)
D.C. Young, A Practical Guide for Applying Techniques to Real-World Problems (2001)
Y.-R. Luo, Handbook of Bond Dissociation Energies in Organic Compounds (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2002)
P. Atkins, J. De Paula, Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2011)
C.C. DeMerlis, D.R. Schoneker, Review of the oral toxicity of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Food Chem. Toxicol. 41(3), 319–326 (2003)
I.R. Agool, K.J. Kadhim, A. Hashim, Fabrication of new nanocomposites: (PVA–PEG–PVP) blend-zirconium oxide nanoparticles) for humidity sensors. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 21(2), 397 (2017)
A. Hadi, A. Hashim, Development of a new humidity sensor based on (carboxymethyl cellulose–starch) blend with copper oxide nanoparticles. Ukr. J. Phys. 62(12), 1044 (2017)
A. Hashim, Q. Hadi, Structural, electrical and optical properties of (biopolymer blend/titanium carbide) nanocomposites for low cost humidity sensors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 11598–11604 (2018)
A. Hashim, Q. Hadi, Synthesis of novel (polymer blend-ceramics) nanocomposites: structural, optical and electrical properties for humidity sensors. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28(4), 1394–1401 (2018)
A.P. Indolia, M.S. Gaur, Optical properties of solution grown PVDF ZnO nanocomposite thin films. J. Polym. Res. 20(1), 43 (2013)
P. Phukan, D. Saikia, Optical and structural investigation of CdSe quantum dots dispersed in PVA matrix and photovoltaic applications. Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 728280 (2013)
S. Salman, N. Bakr, M.H. Mahmood, Preparation and study of some optical properties of (PVA-Ni (CH3COO)2) composites. Int. J. Curr. Res. 6(11), 9638–9643 (2014)
M.R. Islam, J. Podder, Optical properties of ZnO nano fiber thin films grown by spray pyrolysis of zinc acetate precursor. Cryst. Res. Technol. J. Exp. Ind. Crystallogr. 44(3), 286–292 (2009)
C.J. Mathai et al., Effect of iodine doping on the bandgap of plasma polymerized aniline thin films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 35(17), 2206 (2002)
E. Kavitha, N. Sundaraganesan, S. Sebastian, Molecular structure, vibrational spectroscopic and HOMO, LUMO studies of 4-nitroaniline by density functional method (2010)
Q. Fan et al., Mechanical and electronic properties of Ca1−xMgxO alloys. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 40, 676–684 (2015)
A.M. El Sayed, W.M. Morsi, α-Fe2O3/(PVA + PEG) nanocomposite films; synthesis, optical, and dielectric characterizations. J. Mater. Sci. 49(15), 5378–5387 (2014)
B. Singh Rathore et al., Optical and dielectric properties of 55 MeV carbon beam-irradiated polycarbonate films. Radiat. Effects Defects Solids 167(2), 131–140 (2012)
M.A.M. Khan, M. Zulfequar, M. Husain, Optical investigation of a-Se100−xBix alloys. Opt. Mater. 22(1), 21–29 (2003)
G. Attia, M.F.H. Abd El-Kader, Structural, optical and thermal characterization of PVA/2HEC polyblend films. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 8, 5672–5687 (2013)
A. Hashim, A. Jassim, Novel of biodegradable polymers-inorganic nanoparticles: structural, optical and electrical properties as humidity sensors and gamma radiation shielding for biological applications. J. Bionanosci. 12, 170 (2018)
A. Hashim, A. Hadi, Novel lead oxide polymer nanocomposites for nuclear radiation shielding applications. Ukr. J. Phys. 62(11), 978 (2017)
A. Hashim, A. Jassim, Novel of (PVA-ST-PbO2) Bio nanocomposites: preparation and properties for humidity sensors and radiation shielding applications. Sens. Lett. 15(12), 1003 (2017)
N.G. Imam, M.B. Mohamed, Environmentally friendly Zn0.75Cd0.25S/PVA heterosystem nanocomposite: UV-stimulated emission and absorption spectra. J. Mol. Struct. 1105, 80–86 (2016)
A. Hashim, I.R. Agool, K.J. Kadhim, Novel of (polymer blend-Fe3O4) magnetic nanocomposites: preparation and characterization for thermal energy storage and release, gamma ray shielding, antibacterial activity and humidity sensors applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29(12), 10369–10394 (2018)
A.J. Kadham, D. Hassan, N. Mohammad, A. Hashim, Fabrication of (polymer blend-magnesium oxide) nanoparticle and studying their optical properties for optoelectronic applications. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 7(1), 28 (2018)
M. Joshi, R.P. Singh, Cross linking polymers (PVA & PEG) with TiO2 nanoparticles for humidity sensing. Sens. Transducers 110(11), 105 (2009)
R. Srivastava, Effect of poly ethylene glycolon moisture sensing of copper ferrite nanocomposite. Am. J. Sens. Technol. 3(1), 1–4 (2015)
A. Hind, H.M. Abduljalil, A. Hashim, Analysis of structural, optical and electronic properties of polymeric nanocomposites/silicon carbide for humidity sensors. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-019-00100-2
A. Hashim, M.A. Habeeb, Synthesis and characterization of polymer blend-CoFe2O4 nanoparticles as a humidity sensors for different temperatures. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-018-0081-1
N.A. Elmarzugi et al., Spectroscopic characterization of PEG-DNA biocomplexes by FTIR. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 4(8), 6 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the University of Babylon–Iraq (College of Education for Pure Sciences, Department of Physics and College of Science, Department of Physics).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, H., Abduljalil, H.M. & Hashim, A. Structural, Optical and Electronic Properties of Novel (PVA–MgO)/SiC Nanocomposites Films for Humidity Sensors. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 20, 218–232 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-019-00111-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-019-00111-z