Abstract
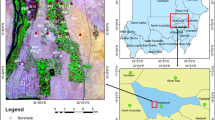
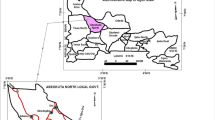
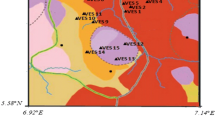
The growing demand for multifaceted and interdisciplinary techniques to analyze subterranean water quality inspired the use of electrical resistivity in assessing the research area's underground water quality. Scholars in the area have been concerned about the area's subterranean water quality. The current study is a contribution to geophysics and geophysical instruments in offering insight into the quality of the area's underground water. As a geophysical tool, the electrical sounding technique incorporates surface measurement of physical parameters and does not require the boring of a borehole to examine subsurface water. As a result, despite the amount of information it offers from deep inside the earth, the technology can be highly cost-effective. The computer-modeled interpretation approaches aided in determining the true aquifer thickness, resistivity, and electrical conductivity of the area's aquiferous zone, which are usually needed to refer to direct the ground water quality of the research area. According to the Vertical Electrical Sounding data interpretation, the entire area is made up of excellent aquifers with water quality that is considered standard and acceptable for domestic use. Nevertheless, there are some unique communities with extraordinarily high electrical conductivity values, such as Ogbodinibe. This is mostly due to the aquifer's high concentration of dissolved ions, which makes the underground water dangerous.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Abdulrazzaq, Z. T., Agbasi, O. E., Aziz, N. A., & Etuk, S. E. (2020). Identification of potential groundwater locations using geophysical data and fuzzy gamma operator model in Imo, Southeastern Nigeria. Applied Water Science, 10(8), 188.
Agbasi, O. E., Aziz, N. A., Abdulrazzaq, Z. T., & Etuk, S. E. (2019). Integrated geophysical data and GIS technique to forecast the potential groundwater locations in part of South Eastern Nigeria. Iraqi Journal of Science, 60(5), 1013–1022.
Ajah, N. J., Akaolisa, C. Z., Okeke, O. C., & Kalu, Q. A. (2019). Evaluation of groundwater potential of Owerri west and environs, southeastern Nigeria using resistivity method. International Journal of Engineering Science Invention, 8(6), 31–43.
Akaolisa, C. C. (2006). Aquifer transmissivity and basement structure determination using resistivity sounding at Jos Plateau State Nigeria. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 114, 27–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1075-8
Aladeboyeje, A. I., Coker, J., Agbasi, O. E., & Inyang, N. J. (2021). Integrated hydrogeophysical assessment of groundwater potential in the Ogun Drainage Basin, Nigeria. International Journal of Energy and Water Resources, 5(5), 461–475.
Chukwu, G. U. (2008). Water quality assessment of boreholes in Umuahia South local government area of Abia State, Nigeria. Pacific Journal of Science and Technology, 9(2), 592–598.
Dioha, E. C., Okeke, O. C., Akaolisa, C. C. Z., Opara, A. I., Shiru, M. S., & Eigbike, O. C. (2017). Correlation of 1-D geoelectrical data to delineate groundwater potential of Uli and environment, Southeastern Nigeria. International Journal of Advanced Academic Research, 3(3), 1–13.
Dixon, B. (2005). Groundwater vulnerability mapping, a GIS and fuzzy rule based integrated tool. Applied Geography, 25(4), 327–347.
Eke, D. U., Opara, A. I., Inayng, G. E., Emberga, T. T., Echetama, H. N., Ugwuegbu, C. A., Onwe, R. M., Onyema, J. C., & Chinaka, J. C. (2015). Hydrogeolophysical evaluation and vulnerability assessment of shallow aquifers of the upper Imo River Basin, South Eastern Nigeria. American Journal of Environmental Protection, 3(4), 125–136.
Ekwe, A. C., Onu, N. N., & Onuoha, K. M. (2006). Estimation of aquifer hydraulic characteristics from electric sounding data: the case study of middle Imo River Basin aquifers, South Eastern Nigeria. Journal of Spatial Hydrology, 6(2), 121–132.
Ibe, K. M., & Uzoukwu, S. C. (2004). An appraisal of subsurface Geology and Groundwater Resources of Owerri and Enirons based on electrical resistivity survey and borehole data evaluation. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 70(3), 303–321.
Ibe, K. K. (2017). Report on pre-drilling geophysical survey of Ogbuoji Farm Along Owutu-Ogbu Edda Road, Afikpo South Area of Southeastern Nigeria, pp. 1–9.
Igboekwe, M. U., Okwueze, E. E., & Okereke, C. S. (2006). Delineation of aquifer zones from geoelectric sounding in Kwa Ibo River Watershed. Southeastern Journal of Engineering and Applied Science, 1(4), 410–421.
Mbonu, P. D. C., Ebeniro, J. O., Ofoegbu, C. O., & Ekine, A. E. (1991). Geoelectric sounding for the determination of aquifer characteristics in parts of the Umuahia area of Nigeria. Geophysics, 56, 284–291.
Onuoha, K. M., & Mbazi, F. C. (1988). Aquifer transmissivity from electrical sounding data: The case study of Ajali sandstone aquifers, south-west of Enugu. In C. O. Ofegbu (Ed.), Ground Water and mineral Resources of Nigeria (pp. 17–29). Fried-vieweng and Sohn.
Opara, A. I., Eke, D. R., Onu, N. N., Ekwe, A. C., Akaolisa, C. Z., Okoli, A. E., & Inyang, G. E. (2021). Geo-hydraulic evaluation of aquifers of the Upper Imo River Basin, Southeastern Nigeria using Dar-Zarrouk parameters. International Journal of Energy and Water Resources, 5, 259–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-020-00099-w
Oseji, J. O., Atakpo, A., & Okolie, E. C. (2005). Geoelectric investigation of the aquifer characteristics and groundwater potential in Kwale, Delta state, Nigeria. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 9(1), 157–160.
Rahman, A. (2008). A GIS based DRASTIC model for assessing ground water vulnerability in shallow aquifer in Aligarh India. Applied Geography, 28, 32–53.
Rumaih, A. I. F., & Ali, H. O. (1986). Resistivity measurements for groundwater investigation in the Umm Al-Aish Area Northern Kuwait. Hydrology, 88, 185–198.
Schwarz, S. D. (1988). Application of Geophysical Methods to Ground water exploration in the Tolt River Basin, Washington State. Geotechnical Environment and Engineering (pp. 9–12). Geophysical society and European section, E.E.G.S.
Shaw, E. M. (1994). Hydrology in practice (3rd Edition) (pp. 165–169). Chapman and Hall.
Ugada, U., Ibe, K. K., Akaolisa, C. Z., & Opara, A. I. (2014). Hydrogeophysical evaluation of aquifer hydraulic characteristics using surface geophysical data: A case study of Umuahia and environs, Southeastern Nigeria. Arabian Journal of Geoscience, 7, 5397–5408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1150-8
US EPA. (1985). DRASTIC: A standard system for evaluating ground water potential using hydrogeology settings, Ada, Oklahoma WA/EPA series p. 163.
Zohdy, A. A. R. (1976). Application of surface Geophysics (Electrical methods of Ground Water Investigation). In Techniques for water Resources investigations in the United States. Section D, Book 2, pp. 5–55
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Editor and reviewers for their input.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akaolisa, C.C., Ibeneche, W., Ibeneme, S. et al. Enhance groundwater quality assessment using integrated vertical electrical sounding and physio-chemical analyses in Umuahia South, Nigeria. Int J Energ Water Res 9, 133–144 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-022-00219-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-022-00219-8