Abstract
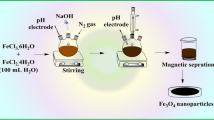
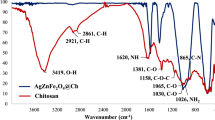
In this study, a novel magnetic nanocomposite adsorbent was prepared from carbon nanotube with chitosan and cross-linked with citric acid using a facile sonochemical technique. This nanocomposite was characterized using VSM, FTIR, FESEM, HRTEM, and XRD analyses and then examined for Cu(II) ions removal from water solution. The results showed that it has excellent Cu(II) ions’ adsorption efficiency in almost 20-min contact time. The batch equilibrium experiments revealed that the most suitable pH for copper adsorption was ranged between 5.8 and 6.0. The experimental results were subjected to kinetic and isotherm analyses. The Langmuir isotherm was fitted well to the experimental data with the theoretical maximum adsorption capacity (12.12 mg g–1), which was close to the experimental value (11.77 mg g–1). Pseudo-second-order kinetic models were fitted well to the experimental data with R2 near to unity. Rapid removal of Cu(II) ions and easy separation of the adsorbent from the water make the proposed composite more applicable for treating Cu(II) ions containing water.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A (2017) Health and environmental impacts of dyes: mini review. Am J Environ Sci Eng 1(3):64–67
El Nemr A (ed) (2012) Non-conventional textile waste water treatment. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., Hauppauge p 267 (Hard cover ISBN: 978-1-62100-079-2, e-book ISBN: 978-1-62100-228-4)
Sadegh H, Shahryari-ghoshekandi R, Agarwal S, Tyagi I, Asif M, Gupta VK (2015) Microwave-assisted removal of malachite green by carboxylate functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes: kinetics and equilibrium study. J Mol Liq 206:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.02.007
Sadegh H, Shahryari-Ghoshekandi R, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2015) Kinetic and thermodynamic studies for alizarin removal from liquid phase using poly-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (PHEMA). J Mol Liq 207:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.03.014
Sadegh H, Ali GA, Gupta VK, Makhlouf ASH, Shahryari-ghoshekandi R, Nadagouda MN, Sillanpää M, Megiel E (2017) The role of nanomaterials as effective adsorbents and their applications in wastewater treatment. J Nanostruct Chem 7(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-017-0219-4
El Nemr A, Eleryan A, Mashaly M, Khaled A (2020) Comparative study of synthesis of cellulose propionate from different sources using NIS as a new catalyst. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03313-1
El Nemr A, Eleryan A, Mashaly M, Khaled A (2020) Rapid synthesis of cellulose propionate and its conversion to cellulose nitrate propionate. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03317-x
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A, Madkour FF (2016) Application of ozonation and UV assisted ozonation for decolorization of direct yellow 50 in sea water. Pharm Chem J 3(2):131–138
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A, Madkour FF (2017) Testing the advanced oxidation processes on the degradation of direct blue 86 dye in wastewater. Egypt J Aquat Res 43:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2016.09.006
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A, Madkour FF (2017) advanced oxidation processes of mordant violet 40 dye in freshwater and seawater. Egypt J Aquat Res 43:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2016.09.004
Alghamdi MM, El-Zahhar AA, Idris AM, Sadi TO, Sahlabji T, El Nemr A (2019) Synthesis, characterization and application of a new polymeric-clay-magnetite composite resin for water softening. Sep Purif Technol 224:356–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.05.037
Ismael MNM, El Nemr A, El Ashry ESH, Abdel Hamid H (2020) Removal of hexavalent chromium by cross-linking chitosan and N, N’-methylene bis-acrylamide. Environ Proc 7:911–930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-020-00447-2
Ismail MNM, El El Nemr A, El Ashry ESH, Abdel Hamid H (2020) Novel simple modification of chitosan as adsorptive agent for removal of Cr6+ from aqueous solution. Egypt J Chem 63(4):1219–1240. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejchem.2019.11157.1716
Gupta VK, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Sadegh H, Shahryari-ghoshekandi R, Yari M, Yousefi-nejat O (2015) Experimental study of surfaces of hydrogel polymers HEMA, HEMA–EEMA–MA, and PVA as adsorbent for removal of azo dyes from liquid phase. J Mol Liq 206:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.02.015
Yang ZF, Li LY, Hsieh CT, Juang RS (2018) Co-precipitation of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles onto carbon nanotubes for removal of copper ions from aqueous solution. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 82:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.11.009
El-Nemr MA, Ismail IMA, Abdelmonem NM, Ragab S, El Nemr A (2020) Ozone and ammonium hydroxide modification of biochar prepared from Pisum sativum peels improves the adsorption of copper(II) from an aqueous medium. Environ Proc 7:973–1007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-020-00455-2
El-Nemr MA, Ismail IMA, Abdelmonem NM, El Nemr A, Ragab S (2020) Amination of biochar derived from watermelon peel by triethylenetetramine and ammonium hydroxide for toxic chromium removal enhancement. Chin J Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2020.08.020 (In press)
El-Nemr MA, Abdelmonem NM, Ismail IMA, Ragab S, El Nemr A (2020) The efficient removal of the hazardous azo dye acid orange 7 from water using modified biochar from Pea peels. Desal Water Treat. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.26190
El-Nemr MA, Abdelmonem NM, Ismail IMA, Ragab S, El Nemr A (2020) Removal of acid yellow 11 dye using novel modified biochar derived from watermelon peels. Desal Water Treat. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.26207
Hosain ANA, El Nemr A, El Sikaily A, Mahmoud ME, Amira MF (2020) Surface modifications of nanochitosan coated magnetic nanoparticles and their applications in Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) removal. J Environ Chem Eng 8(5):104316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104316
Salem DMSA, Khaled A, El Nemr A, El-Sikaily A (2014) Comprehensive risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments along the Egyptian Red Sea coast. Egypt J Aquat Res 40:349–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2014.11.004
Khaled A, El Nemr A, El Sikaily A, El-Sarraf WM (2010) Assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of the Mediterranean Coast of Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Res 36(1):43–53
Ngah WW, Teong L, Hanafiah M (2011) Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: a review. Carbohydr Polym 83(4):1446–1456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.11.004
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A, Madkour FF (2016) Environmental assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk. Am J Water Sci Eng 2(3):14–19. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajwse.20160203.11
Wang J, Zhao G, Jing L, Peng X, Li Y (2015) Facile self-assembly of magnetite nanoparticles on three-dimensional graphene oxide–chitosan composite for lipase immobilization. Biochem Eng J 98:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2014.11.013
Shen C, Chen C, Wen T, Zhao Z, Wang X, Xu A (2015) Superior adsorption capacity of g-C3N4 for heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. J Coll Interface Sci 456:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.06.004
Zeng G, Liu X, Liu M, Huang Q, Xu D, Wan Q, Huang H, Deng F, Zhang X, Wei Y (2016) Facile preparation of carbon nanotubes based carboxymethyl chitosan nanocomposites through combination of mussel inspired chemistry and Michael addition reaction: characterization and improved Cu2+ removal capability. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 68:446–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.09.008
Theophanides T, Anastassopoulou J (2002) Copper and carcinogenesis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 42(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1040-8428(02)00007-0
Awual MR, Ismael M, Khaleque MA, Yaita T, Chemistry E (2014) Ultra-trace copper(II) detection and removal from wastewater using novel meso-adsorbent. J Indust Eng Chem 20(4):2332–2340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.10.009
Awual MR, Yaita T, Okamoto YJS, Chemical AB (2014) A novel ligand based dual conjugate adsorbent for cobalt(II) and copper(II) ions capturing from water. Sens Actuators B Chem 203:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.06.088
WHO (1971) International standards for drinking water, 3rd edn. Geneva
Lai YL, Thirumavalavan M, Lee JF (2010) Effective adsorption of heavy metal ions (Cu2+, Pb2+, Zn2+) from aqueous solution by immobilization of adsorbents on Ca-alginate beads. Toxicol Environ Chem 92(4):697–705. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772240903057382
Awual MR, Eldesoky GE, Yaita T, Naushad M, Shiwaku H, AlOthman ZA, Suzuki S (2015) Schiff based ligand containing nano-composite adsorbent for optical copper(II) ions removal from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 279:639–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.049
Aziz HA, Adlan MN, Ariffin KSJBT (2008) Heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Zn, Ni, Cu and Cr(III)) removal from water in Malaysia: post treatment by high quality limestone. Bioresour Technol 99(6):1578–1583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.04.007
Bakhtiari N, Azizian S (2015) Adsorption of copper ion from aqueous solution by nanoporous MOF-5: a kinetic and equilibrium study. J Mol Liq 206:114–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.02.009
Guo LJ, Niu CG, Wang XY, Wen XJ, Zeng GM (2016) DTC-GO as effective adsorbent for the removal of Cu2+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution. Water Air Soil Pollut 227(6):169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2865-4
Serag E, El Nemr A, El-Maghraby A (2017) Synthesis of highly effective novel graphene oxide-polyethylene glycol-polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite hydrogel for copper removal. J Water Environ Nanotechnol 2(4):223–234
Serag E, El Nemr A, Abdel Hamid FF, Fathy SA, El-Maghraby A (2018) A novel three dimensional carbon nanotube-polyethylene glycol—polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite for Cu(II) removal from water. Egypt J Aquat Biol Fish 22(2):103–118
Sheng G, Li J, Shao D, Hu J, Chen C, Chen Y, Wang X (2010) Adsorption of copper(II) on multiwalled carbon nanotubes in the absence and presence of humic or fulvic acids. J Hazard Mater 178(1–3):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.084
Xie Y, He C, Liu L, Mao L, Wang K, Huang Q, Liu M, Wan Q, Deng F, Huang H (2015) Carbon nanotube based polymer nanocomposites: biomimic preparation and organic dye adsorption applications. RSC Adv 5(100):82503–82512. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA15626B
Ren X, Chen C, Nagatsu M, Wang X (2011) Carbon nanotubes as adsorbents in environmental pollution management: a review. Chem Eng J 170(2–3):395–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.08.045
Schaetz A, Zeltner M, Stark W (2012) Carbon modifications and surfaces for catalytic organic transformations. ACS Catal 2(6):1267–1284. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs300014k
Fathy SA, Abdel Hamid FF, El Nemr A, El-Maghraby A, Serag E (2018) Novel tyrosinase biosensor based on multiwall carbon nanotube–titanium oxide nanocomposite for catechol determination. Desalin Water Treat 130:98–108. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.22847
Guo B, Deng F, Zhao Y, Luo X, Luo S, Au C (2014) Magnetic ion-imprinted and –SH functionalized polymer for selective removal of Pb(II) from aqueous samples. Appl Surf Sci 292:438–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.11.156
Huang J, Xie H, Ye H, Xie T, Lin Y, Gong J, Jiang C, Wu Y, Liu S, Cui Y (2016) Effect of carboxyethylation degree on the adsorption capacity of Cu(II) by N-(2-carboxyethyl) chitosan from squid pens. Carbohydr Polym 138:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.037
Huang Q, Liu M, Chen J, Wang K, Xu D, Deng F, Huang H, Zhang X, Wei Y (2016) Mussel inspired preparation of functional silica nanocomposites for environmental adsorption applications. Appl Surf Sci 387:285–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.06.037
Jorgetto A, Silva R, Saeki M, Barbosa R, Martines M, Jorge S, Silva A, Schneider JF, Castro G (2014) Cassava root husks powder as green adsorbent for the removal of Cu(II) from natural river water. Appl Surf Sci 288:356–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.10.032
Lakouraj MM, Mojerlou F, Zare EN (2014) Nanogel and superparamagnetic nanocomposite based on sodium alginate for sorption of heavy metal ions. Carbohydr Polym 106:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.092
Mi FL, Wu SJ, Chen YC (2015) Combination of carboxymethyl chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles and chitosan-citrate complex gel beads as a novel magnetic adsorbent. Carbohydr Polym 131:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.031
Sargın İ, Arslan G, Kaya M (2016) Microfungal spores (Ustilago maydis and U. digitariae) immobilised chitosan microcapsules for heavy metal removal. Carbohydr Polym 138:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.065
Eldeeb TM, El Nemr A, Khedr MH, El-Dek SI, Imam NG (2020) Novel three-dimensional chitosan-carbon nanotube–PVA nanocomposite hydrogel for removal of Cr6+ from wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 184:163–177. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25366
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag 92(3):407–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011
Shoaib AGM, El Sikaily A, El Nemr A, Mohamed AE-DA, Hassan AA (2020) Preparation and characterization of highly surface area activated carbons followed Type IV from marine red alga (Pterocladia capillacea) by zinc chloride activation. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00760-8
Shoaib AGM, El-Sikaily A, El Nemr A, Mohamed AE-DA, Hassan AA (2020) Testing the carbonization condition for high surface area preparation of activated carbon followed Type IV from green alga Ulva lactuca. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00823-w
Lim S, Chen JP (2007) Synthesis of an innovative calcium-alginate magnetic sorbent for removal of multiple contaminants. Appl Surf Sci 253(13):5772–5775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.12.049
Tian Y, Wu M, Lin X, Huang P, Huang Y (2011) Synthesis of magnetic wheat straw for arsenic adsorption. J Hazard Mater 193:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.093
Yao T, Guo S, Zeng C, Wang C, Zhang L (2015) Investigation on efficient adsorption of cationic dyes on porous magnetic polyacrylamide microspheres. J Hazard Mater 292:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.014
Naushad M, Ahamad T, Al-Maswari BM, Alqadami AA, Alshehri SM (2017) Nickel ferrite bearing nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon as efficient adsorbent for the removal of highly toxic metal ion from aqueous medium. Chem Eng J 330:1351–1360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.08.079
Kefeni KK, Mamba BB, Msagati TA (2017) Application of spinel ferrite nanoparticles in water and wastewater treatment: a review. Sep Purif Technol 188:399–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.07.015
Rocher V, Siaugue J-M, Cabuil V, Bee A (2008) Removal of organic dyes by magnetic alginate beads. Water Res 42(4–5):1290–1298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.09.024
El Sikaily A, El Nemr A, Khaled A (2011) Copper sorption onto dried red alga Pterocladia capillacea and its activated carbon. Chem Eng J 168:707–714
El Nemr A, El Sikaily A, Khaled A, Abdelwahab O (2015) Removal of toxic chromium from aqueous solution, wastewater and saline water by marine red alga Pterocladia capillacea and its activated carbon. Arab J Chem 8:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2011.01.016
Ahmed AESI, Moustafa HY, El-Masry AM, Hassan SA (2014) Natural and synthetic polymers for water treatment against dissolved pharmaceuticals. J Appl Polym Sci 131:40458. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.40458
Laus R, Costa TG, Szpoganicz B, Fávere VT (2010) Adsorption and desorption of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions using chitosan crosslinked with epichlorohydrin-triphosphate as the adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 183(1–3):233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.07.016
Liu D, Li Z, Zhu Y, Li Z, Kumar R (2014) Recycled chitosan nanofibril as an effective Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) ionic chelating agent: adsorption and desorption performance. Carbohydr Polym 111:469–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.04.018
Wang J, Chen C (2014) Chitosan-based biosorbents: modification and application for biosorption of heavy metals and radionuclides. Bioresour Technol 160:129–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.110
Wang T, Song Y, Li B, Zhou XG (2010) Crosslinked carboxymethyl modified starch for treatment of heavy metals water by technique of chelating-ultrafiltration. Adv Mater Res 113–116:877–880. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.113-116.877
Reddy DHK, Lee SM (2013) Application of magnetic chitosan composites for the removal of toxic metal and dyes from aqueous solutions. Adv Coll Interface Sci 201:68–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2013.10.002
Bagheri M, Younesi H, Hajati S, Borghei SM (2015) Application of chitosan-citric acid nanoparticles for removal of chromium(VI). Int J Biol Macromol 80:431–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.07.022
Bibi S, Yasin T, Hassan S, Riaz M, Nawaz M (2015) Chitosan/CNTs green nanocomposite membrane: synthesis, swelling and polyaromatic hydrocarbons removal. Mater Sci Eng C 46:359–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.10.057
García-Díaz I, López F, Alguacil F (2018) Carbon nanofibers: a new adsorbent for copper removal from wastewater. Metals 28:914. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110914
Gu SY, Hsieh CT, Gandomi YA, Yang ZF, Li L, Fu CC, Juang RS (2019) Functionalization of activated carbons with magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for removal of copper ions from aqueous solution. J Mol Liq 277:499–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.12.018
Neto OM, Bellato CR, de Castro SD (2019) Iron oxide/carbon nanotubes/chitosan magnetic composite film for chromium species removal. Chemosphere 218:391–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.080
Ouni L, Ramazani A, Fardood ST (2019) An overview of carbon nanotubes role in heavy metals removal from wastewater. Front Chem Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-018-1765-0
Tao HC, Li S, Zhang LJ, Chen YZ, Deng LP (2019) Magnetic chitosan/sodium alginate gel bead as a novel composite adsorbent for Cu(II) removal from aqueous solution. Environ Geochem Health 41(1):297–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0137-5
Hui M, Shengyan P, Yaqi H, Rongxin Z, Anatoly Z, Wei C (2018) A highly efficient magnetic chitosan “fluid” adsorbent with a high capacity and fast adsorption kinetics for dyeing wastewater purification. Chem Eng J 345:556–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.115
Jiang Y, Gong JL, Zeng GM, Ou XM, Chang YN, Deng CH, Zhang J, Liu HY, Huang SY (2016) Magnetic chitosan–graphene oxide composite for anti-microbial and dye removal applications. Int J Biol Macromol 82:702–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.11.021
Zhou C, Zhu H, Wang Q, Wang J, Cheng J, Guo Y, Zhou X, Bai R (2017) Adsorption of mercury(II) with an Fe3O4 magnetic polypyrrole–graphene oxide nanocomposite. RSC Adv 7(30):18466–18479. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA01147D
Abbasi M (2017) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanocomposite of chitosan/SiO2/carbon nanotubes and its application for dyes removal. J Clean Prod 145:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.046
Saleh TA (2020) Characterization, determination and elimination technologies for sulfur from petroleum: toward cleaner fuel and a safe environment. Trends Environ Anal Chem 25:e00080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teac.2020.e00080
Wang J, Shi Z, Fan J, Ge Y, Yin J, Hu G (2012) Self-assembly of graphene into three-dimensional structures promoted by natural phenolic acids. J Mater Chem 22:22459–22466
Ali I, AL-Hammadi SA, Saleh TA, (2018) Simultaneous sorption of dyes and toxic metals from waters using synthesized titania-incorporated polyamide. J Mol Liq 269:564–571
Ali I, Saleh TA (2018) Synthesis of polyamide grafted carbon microspheres for removal of rhodamine B dye and heavy metals. J Environ Chem Eng 6(4):5361–5368
Saleh TA (2020) Nanomaterials: classification, properties, and environmental toxicities. Environ Technol Innov 20:101067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101067
Saleh TA (2020) Trends in the sample preparation and analysis of nanomaterials as environmental contaminants. Trends Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teac.2020.e00101
Fan L, Luo C, Sun M, Li X, Qiu HJC, Biointerfaces SB (2013) Highly selective adsorption of lead ions by water-dispersible magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composites. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 103:523–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.11.006
Shawky HA, El-Aassar AHM, Abo-Zeid DE (2012) Chitosan/carbon nanotube composite beads: preparation, characterization, and cost evaluation for mercury removal from wastewater of some industrial cities in Egypt. J Appl Polym Sci 125(S1):E93–E101
Duman O, Tunç S, Polat TG, Bozoğlan BK (2016) Synthesis of magnetic oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotube-κ-carrageenan-Fe3O4 nanocomposite adsorbent and its application in cationic methylene blue dye adsorption. Carbohydr Polym 147:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.03.099
Fayazi M, Taher MA, Afzali D, Mostafavi A, Ghanei-Motlagh M (2016) Synthesis and application of novel ion-imprinted polymer coated magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective solid phase extraction of lead(II) ions. Mater Sci Eng C 60:365–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.11.060
Taghizadeh M, Hassanpour S (2017) Selective adsorption of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions using a Cr(VI)-imprinted polymer supported by magnetic multiwall carbon nanotubes. Water Air Soil Pollut 132:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4181-2
Saleh TA (2015) Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies on Hg(II) adsorption from aqueous solution by silica-multiwall carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16721–16731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4866-z
Saleh TA, Gupta VK (2012) Characterization of the chemical bonding between Al2O3 and nanotube in MWCNT/Al2O3 nanocomposite. Curr Nanosci 8(5):739–743
Saleh T (2016) Nanocomposite of carbon nanotubes/silica nanoparticles and their use for adsorption of Pb(II): from surface properties to sorption mechanism. Desalin Water Treat 57(23):10730–10744
Saleh TA (2016) Mercury sorption by silica/carbon nanotubes and silica/activated carbon: a comparison study. J Water Supply Res Tech-AQUA 64(8):892–903
Pang BW, Jiang CH, Yeung M, Ouyang Y, Xi J (2017) Removal of dissolved sulfides in aqueous solution by activated sludge: mechanism and characteristics. J Hazard Mater 324:732–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.11.048
Low K, Lee C, Mak S (2004) Sorption of copper and lead by citric acid modified wood. Wood Sci Technol 38(8):629–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-003-0201-9
Sankararamakrishnan N, Dixit A, Iyengar L, ad Sanghi R, (2006) Removal of hexavalent chromium using a novel cross linked xanthated chitosan. Bioresour Technol 97(18):2377–2382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.10.024
Juang RS, Shao HJ (2002) A simplified equilibrium model for sorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions on chitosan. Water Res 36(12):2999–3008. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00537-1
Huang G, Chuo Y, Zhang K, Jeffrey S (2009) Adsorptive removal of copper ions from aqueous solution using cross-linked magnetic chitosan beads. Chin J Chem Eng 17(6):960–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1004-9541(08)60303-1
Ngah WW, Ab Ghani S, Kamari A (2005) Adsorption behaviour of Fe(II) and Fe(III) ions in aqueous solution on chitosan and cross-linked chitosan beads. Bioresour Technol 96(4):443–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.05.022
El Nemr A, El-Sikaily A, Khaled A (2010) Modeling of adsorption isotherms of Methylene Blue onto rice husk activated carbon. Egypt J Aquat Res 36(3):403–425
Lagergren S (1898) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar 24:1–39
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-0032(17)90938-X
Ho Y, McKay G, Wase D, Forster C (2000) Study of the sorption of divalent metal ions on to peat. Adsorpt Sci Technol 18(7):639–650. https://doi.org/10.1260/0263617001493693
Khraisheh MM, Al-Degs Y, Allen S, Ahmad M (2002) Elucidation of controlling steps of reactive dye adsorption on activated carbon. Ind Eng Chem Res 41(6):1651–1657. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie000942c
Lei C, Zhu X, Zhu B, Jiang C, Le Y, Yu J (2017) Superb adsorption capacity of hierarchical calcined Ni/Mg/Al layered double hydroxides for Congo red and Cr(VI) ions. J Hazard Mater 321:801–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.070
Holan Z, Volesky B, Prasetyo I (1993) Biosorption of cadmium by biomass of marine algae. Biotechnol Appl Microbiol 41(8):819–825. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260410808
Zhao H, Ye Y, Cao S, Dai J, Li L (2014) Synthesis and properties of cadmium(II)-imprinted polymer supported by magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Acc Chem Res 6(23):9313–9320. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar010151m
El-Sikaily A, El Nemr A, Khaled A, Abdelwehab O (2007) Removal of toxic chromium from wastewater using green alga Ulva lactuca and its activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 148(1–2):216–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.146
El Nemr A, Helmy ET, Arafa E, Eldafrawy S, Mousa M (2019) Photocatalytic and biological activities of undoped and doped TiO2 prepared by Green method for water treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 7(5):103385
Chen X, Chen G, Chen L, Chen Y, Lehmann J, McBride MB, Hay AG (2011) Adsorption of copper and zinc by biochars produced from pyrolysis of hardwood and corn straw in aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 102(19):8877–8884
Wang X, Liang X, Wang Y, Wang X, Liu M, Yin D, Zhang Y (2011) Adsorption of Copper(II) onto activated carbons from sewage sludge by microwave-induced phosphoric acid and zinc chloride activation. Desalination 278(1–3):231–237
Han Y, Boateng AA, Qi PX, Lima IM, Chang J (2013) Heavy metal and phenol adsorptive properties of biochars from pyrolyzed switchgrass and woody biomass in correlation with surface properties. J Environ Manag 118:196–204
Yang G-X, Jiang H (2014) Amino modification of biochar for enhanced adsorption of copper ions from synthetic wastewater. Water Res 48:396–405
Trakal L, Šigut R, Hanašillerová FD, Komárek M (2014) Copper removal from aqueous solution using biochar: effect of chemical activation. Arab J Chem 7:43–52
Xiao F, Cheng J, Cao W, Yang C, Chen J, Luo Z (2019) Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution using chitosan-combined magnetic biochars. J Colloid Interface Sci 540:579–584
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mr. Tarek M. Eldeeb conducted the practical part and wrote the original draft. Professor Dr. Ahmed El Nemr supervised the practical work, corrected the manuscript, and submitted the manuscript. Professor Dr. M. H. Khedr and Professor Dr. S. I. El-Dek supervised the work and read the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eldeeb, T.M., El Nemr, A., Khedr, M.H. et al. Efficient removal of Cu(II) from water solution using magnetic chitosan nanocomposite. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 6, 34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41204-021-00129-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41204-021-00129-w