Abstract
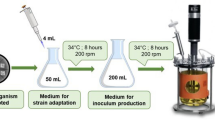
Bacterial poly3-hydroxyalkanotes are the polyesters that are accumulated in conditions of un-balanced nutrients. Soil samples were collected from Hilly areas of Muzaffarabad, and oil processing area of Lahore, Pakistan to isolate PHA producing bacteria. The bacteria were screened on Sudan black B and Nile blue A staining methodologies. An efficient PHA producing strain AZR-1 was isolated and characterized morphologically and biochemically. The strain was identified as Bacillus sp. AZR-1 on the genetic basis of 16S rRNA gene sequence. Bacillus sp. AZR-1 produced 40% PHA contents when grown on N-limited mineral salt medium supplemented with glucose in shake flasks. Starch and sodium gluconate were found to be other putative carbon sources for PHA production as the bacterium produced 22 and 17% PHA on these sources. FTIR confirmed the presence of scl-PHA monomers in the polymer extracted from the bacterium. The PHA synthase gene (phaC) was partially amplified and sequenced which showed maximum similarity with the PHA synthase of Bacillus weihenstephanensis KBAB4.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali I, Jamil N (2014) Enhanced biosynthesis of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) from potato starch by Bacillus cereus strain 64-INS in a laboratory-scale fermenter. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 44:822–833
Ali I, Jamil N (2016) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: current applications in the medical field. Front Bio 11:19–27
Anderson AJ, Dawes EA (1990) Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol Rev 54:450–472
Ataei SA, Vasheghani-Farahani E, Shojaosadati SA, Tehrani HA (2008) Isolation of PHA–producing bacteria from date syrup waste. Macromol Symp 269:11–16
Ausubel FM (2002) Short protocols in molecular biology: a compendium of methods from current protocols in molecular biology, vol 2. Wiley, New York, USA
Cappuccino JG, Sherman N (2008) Microbiology: a laboratory manual. Pearson/Benjamin Cummings, San Francisco, USA
Chaudhry WN, Jamil N, Ali I, Ayaz MH, Hasnain S (2011) Screening for polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-producing bacterial strains and comparison of PHA production from various inexpensive carbon sources. Ann Microbiol 61:623–629
Ciesielski S, Gorniak D, Mozejko J, Swiątecki A, Grzesiak J, Zdanowski M (2014) The diversity of bacteria isolated from Antarctic freshwater reservoirs possessing the ability to produce polyhydroxyalkanoates. Curr Microbiol 69:594–603
Dalal J, Sarma PM, Lavania M, Mandal AK, Lal B (2010) Evaluation of bacterial strains isolated from oil-contaminated soil for production of polyhydroxyalkanoic acids (PHA). Pedobiologia 54:25–30
Full T, Jung D, Madigan M (2006) Production of poly-β-hydroxyalkanoates from soy molasses oligosaccharides by new, rapidly growing Bacillus species. Lett Appl Microbiol 43:377–384
Hahn SK, Chang YK, Kim BS, Chang HN (1994) Optimization of microbial poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) recover using dispersions of sodium hypochlorite solution and chloroform. Biotechnol Bioeng 44:256–261
Halami PM (2008) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoate from starch by the native isolate Bacillus cereus CFR06. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:805–812
Kansiz M, Billman-Jacobe H, McNaughton D (2000) Quantitative determination of the biodegradable polymer poly (β-hydroxybutyrate) in a recombinant Escherichia coli strain by use of mid-infrared spectroscopy and multivariative statistics. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3415–3420
Lee W-H, Loo C-Y, Nomura CT, Sudesh K (2008) Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymers from mixtures of plant oils and 3-hydroxyvalerate precursors. Bioresour Technol 99:6844–6851
Madison LL, Huisman GW (1999) Metabolic engineering of poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates): from DNA to plastic. Microbiol Mol Bio Rev 63:21–53
Mizuno K, Ohta A, Hyakutake M, Ichinomiya Y, Tsuge T (2010) Isolation of polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing bacteria from a polluted soil and characterization of the isolated strain Bacillus cereus YB-4. Polym Degrad Stab 95:1335–1339
Mohapatra S, Mohanta P, Sarkar B, Daware A, Kumar C, Samantaray D (2015) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) by Bacillus strain isolated from waste water and its biochemical characterization. Proc Nat Acad Sci India B Biol Sci 1–8. doi:10.1007/s40011-015-0626-6
Naheed N, Jamil N, Hasnain S, Abbas G (2012) Biosynthesis of polyhydroxybutyrate in Enterobacter sp. SEL2 and Enterobacteriaceae bacterium sp. PFW1 using sugar cane molasses as media. Afr J Biotechnol 11:3321–3332
Obruca S, Marova I, Melusova S, Mravcova L (2011) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from cheese whey employing Bacillus megaterium CCM 2037. Ann Microbiol 61:947–953
Park SJ, Park JP, Lee SY (2002) Production of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) from whey by fed-batch culture of recombinant Escherichia coli in a pilot-scale fermenter. Biotechnol Lett 24:185–189
Phukon P, Saikia JP, Konwar BK (2011) Enhancing the stability of colloidal silver nanoparticles using polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) from Bacillus circulans (MTCC 8167) isolated from crude oil contaminated soil. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 86:314–318
Rehm B (2003) Polyester synthases: natural catalysts for plastics. Biochem J 376:15–33
Saadoun I (2002) Isolation and characterization of bacteria from crude petroleum oil contaminated soil and their potential to degrade diesel fuel. J B Microbiol 42:420–428
Shamala T, Chandrashekar A, Vijayendra S, Kshama L (2003) Identification of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) producing Bacillus spp. using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). J Appl Microbiol 94:369–374
Spiekermann P, Rehm BH, Kalscheuer R, Baumeister D, Steinbüchel A (1999) A sensitive, viable-colony staining method using Nile red for direct screening of bacteria that accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and other lipid storage compounds. Arch Microbiol 171:73–80
Steinbuchel A, Lütke-Eversloh T (2003) Metabolic engineering and pathway construction for biotechnological production of relevant polyhydroxyalkanoates in microorganisms. Biochem Eng J 16:81–96
Tajima K, Igari T, Nishimura D, Nakamura M, Satoh Y, Munekata M (2003) Isolation and characterization of Bacillus sp. INT005 accumulating polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) from gas field soil. J Biosci Bioeng 95:77–81
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Bio Evol 28:2731–2739
Verlinden RA, Hill DJ, Kenward M, Williams CD, Radecka I (2007) Bacterial synthesis of biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Appl Microbiol 102:1437–1449
Xu K, Xu P (2014) Efficient production of L-lactic acid using co-feeding strategy based on cane molasses/glucose carbon sources. Bioresour Technol 153:23–29
Younas T, Ali I, Jamil N (2015) Polyhydroxyalkanoates production using canola oil by bacteria isolated from paper pulp industry. Kuwait J Sci 42:236–249
Yu J (2001) Production of PHA from starchy wastewater via organic acids. J Biotechnol 86:105–112
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the University of the Punjab, Pakistan and Higher Education Commission of Pakistan for providing the funds to conduct this research work. Funding was provided by University of the Punjab and Higher Education Commission, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, I., Jamil, N. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Poly3-hydroxyalkanote (PHA) from Newly Isolated Bacterium Bacillus sp. AZR-1. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 42, 371–378 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-016-0132-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-016-0132-6