Abstract
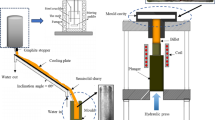
Semisolid casting using the cooling slope plate method (CSP) is known to refine the microstructure of hypereutectic aluminum alloys and enhance their mechanical properties. The current research investigates the combined effect of casting using the CSP and mechanical vibration of the mold on microstructure and wear behavior of A390 alloy. After pouring the alloy on the CSP, the mold (sand/metallic) was vibrated mechanically at 50 Hz during filling and up to solidification. Conventional casting with the same mold vibration conditions was also done for comparison. During CSP casting with mechanical vibration of the mold, the crystal nucleus multiplication inhibits the grain growth, and the dendrite break-up takes place simultaneously, leading to refinement of the microstructure. The double effect of the shear force by melt flow and vibrational turbulence is responsible for fragmentation of the particles. This finding was more pronounced in case of using the sand mold. The quantitative measurements showed that the size of primary Si reduced from ~ 184 μm for the conventional casting in the sand mold without vibration to ~ 70 μm when the mold was vibrated and from ~ 30 μm in case of CSP down to ~ 20 μm when CSP was followed by mechanical vibration of the mold. However, applying the mechanical vibration after CSP in case of the metallic mold increased the size of primary Si from ~ 21 to 36 μm. Accordingly, the improvement in the hardness and wear resistance of the CSP samples due to vibration was more significant in case of using the sand mold.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Lasa, J.M. Rodriguez-Ibab, Wear behaviour of eutectic and hypereutectic Al–Si–Cu–Mg casting alloys tested against a composite brake pad. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 363, 193–202 (2003)
H. Tahiri, A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty et al., Effect of Sr–Grain Refiner–Si interactions on the microstructure characteristics of Al–Si hypereutectic alloys. Int. J. Metalcast. 12, 307–320 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-017-0164-5
Q. Li, B. Li, J. Liu et al., Modification of hypereutectic Al–20 wt% Si alloy based on the addition of yttrium and Al–5Ti–1B modifiers mixing melt. Int. J. Metalcast. 13, 367–383 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-0242-3
R.G. Guan, D. Tie, A Review on grain refinement of aluminum alloys: progress, challenges and prospects. Acta Metall. Sin. 30, 409–432 (2017)
C. Limmaneevichitr, S. Pongananpanya, J. Kajornchaiyakul, Metallurgical structure of A356 aluminum alloy solidified under mechanical vibration: an investigation of alternative semi-solid casting routes. Mater. Des. 30, 3925 (2009)
F. Taghavi, H. Saghafian, Y.H.K. Kharrazi, Study on the effect of prolonged mechanical vibration on the grain refinement and density of A356 aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 30, 1604 (2009)
H.M. Guo, A.S. Zhang, X.J. Yang, M.M. Yan, Grain refinement of Al–5%Cu aluminum alloy under mechanical vibration using melt able vibrating probe. Trans. Nonferrous Metal. Soc. 24, 2489 (2014)
N.K. Kund, Effect of tilted plate vibration on solidification and microstructural and mechanical properties of semisolid cast and heat-treated A356 Al alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 97, 1617–1626 (2018)
S.G. Shabestari, M. Ghanbari, Effect of plastic deformation and semisolid forming on iron–manganese rich intermetallic in Al–8Si–3Cu–4Fe–2Mn alloy. Alloys Compd. 508, 315–319 (2010)
W. Khalifa, S. El-Hadad, Y. Tsunekawa, Microstructure and wear behavior of solidification sonoprocessed B390 hyper-eutectic Al–Si alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44, 5817–5824 (2013)
K. Liu, X. Cao, X.G. Chen, Solidification of iron-rich intermetallic phases in Al–4.5Cu–0.3Fe cast alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 42, 2004–2016 (2011)
D.N. Miller, L. Lu, A.K. Dahle, The role of oxides in the formation of primary iron intermetallics in an Al–11.6Si–0.37 Mg alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 37, 873–878 (2006)
J. Barbosa, H. Puga, J. Oliveira, S. Ribeiro, M. Prokic, Physical modification of intermetallic phases in Al–Si–Cu alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 148, 1163–1170 (2014)
W. Khalifa, Y. Tsunekawa, S. El-Hadad, Ultrasonic rheo-die casting of A383 aluminum alloy. Solid State Phenom. 256, 282–287 (2016)
S. Wu, S. Lu, P. An, Z. Zhu, Preparation and rheocasting of semi-solid aluminum alloy slurry with indirect ultrasonic vibration process. MRS Proc. 1380, 1380 (2012)
W. Khalifa, S. El-Hadad, Ultrasonication effects on the microstructure characteristics of the A380 die cast alloy. Int. J. Metalcast. 13, 865–879 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-00296-8
S. Wu, S. Lu, P. An, H. Nakae, Microstructure and property of rheo-casting aluminium alloy made with indirect ultrasonic vibration process. Mater. Lett. 73, 150–153 (2012)
S. Gencalp, N. Saklakoglu, “effect of low frequency mechanical vibration and casting temperatures on microstructure of semisolid AlSi8Cu3Fe alloy. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 37, 2255–2267 (2012)
P. Das, S.K. Samanta, P. Dutta, Microstructure evolution and rheological behavior of cooling slope processed Al–Si–Cu–Fe alloy slurry. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. ASM Int. 47, 2243–2246 (2016)
S.D. Kumar, A. Mandal, M. Chakraborty, Cooling slope casting process of semisolid aluminum alloys: a review. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 3, 269–283 (2014)
R.G. Guan, Z.Y. Zhao, H. Zhang, C. Lian, C.S. Lee, C.M. Liu, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 212, 1430 (2012)
M.M. Shehata, S. El-Hadad, M.E. Moussa, M. EL-Shennawy, Optimizing the pouring temperature for semisolid casting of a hypereutectic Al–Si alloy using the cooling slope plate method. Int. J. Metalcast. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00465-8
M. Ramadan, N. Fathy. Solidification microstructure of rheocast hyper-eutectic Al–18Si alloy. J. Metall. Eng. 2, 149–154 (2013)
Z. Hu, G. Wu, J. Xu, Dry wear behavior of rheo-casting Al − 16Si − 4Cu − 0.5 Mg alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26, 2818–2829 (2016)
M. Qi, J. Li, Correlation between segregation behavior and wall thickness in a rheological high pressure die-casting AC46000 aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 3565–3579 (2019)
M.N. Mohammed, M.Z. Omar, M.S. Salleh, K.S. Alhawari, P. Kapranos, Semisolid metal processing techniques for non-dendritic feedstock production. Sci. World J. 2013, 752175 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/752175
K.S. Alhawari, M.Z. Omar, M.J. Ghazali, M.S. Salleh, M.N. Mohammed, Evaluation of the microstructure and dry sliding wear behaviour of thixoformed A319 aluminium alloy. Mater. Des. 76, 169–180 (2015)
W. Khalifa, S. El-Hadad, Y. Tsunekawa, Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of sono processed-Thixo cast AC4C Billets, in 71st World Foundry Congress on Advanced Sustainable Energy, 19–21 May, Bilbao-Spain (2014)
C. Cui, A. Schulz, K. Schimanski, H.W. Zoch, Spray forming of hypereutectic Al–Si alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 5220–5228 (2009)
R.A. Flemings, M.C. Martinez, Principles of microstructural formation in semi-solid metal processing. Solid State Phenom. 116–117, 1–8 (2006)
L.N. Yu, X.F. Liu, H.M. Ding, X.F. Bia, A new nucleation mechanism of primary Si by like-peritectic coupling of AlP and Al4C3 in near eutectic Al–Si alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 429, 119–125 (2007)
R.G. Guana, F.R. Caoa, L.Q. Chenb, J.P. Lib, C. Wanga, Dynamical solidification behaviors and microstructural evolution during vibrating wavelike sloping plate process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 2592–2601 (2009)
R.G. Guan, Z.Y. Zhao, C.S. Lee, Q.S. Zhang, C.M. Liu, Effect of wavelike sloping plate rheo-casting on microstructures of hypereutectic Al-18% Si-5% Fe alloys. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. ASM Int. (2011)
J. Deshpande, The Effect of mechanical mold vibration on the characteristics of aluminum alloys. M.Sc Thesis, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Manufacturing Engineering, September (2006)
J. Campbell, Grain refinement of solidifying metals by vibration: a review, in Proceedings of the Solidification Technology in the Foundry and Cast House, Coventry, UK, 15–17 September (1980), pp. 61–64
J. Campbell, Effects of vibration during solidification. Int. Mater. Rev. 2, 71–106 (1981)
R.D. Doherty, Comments on mechanical deformation of dendrites by fluid flow during the solidification of undercooled melts. Scripta Mater. 49, 1219–1222 (2003)
M. Harun, I.A. Talib, A.R. Daud, Effect of element additions on wear property of eutectic aluminium–silicon alloys. Wear 194, 54–59 (1996)
K.V. Ojha, A. Tomar, D. Singh, G.C. Kaushal, Shape, microstructure and wear of spray formed hypoeutectic Al–Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 487, 591–596 (2008)
A.S. Anasyida, A.R. Daud, M.J. Ghazali, Dry sliding wear behavior of Al–12Si–4 Mg alloy with cerium addition. Mater. Des. 31, 365–371 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the financial support from The Central Metallurgical Research and Development Institute, Grant No. 146/2019. The corresponding author would like to acknowledge the partial support from the Science and Technology Development Fund (Egypt) through the Grant No. 26565.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shehata, M.M., El-Hadad, S., Moussa, M.E. et al. The Combined Effect of Cooling Slope Plate Casting and Mold Vibration on Microstructure, Hardness and Wear Behavior of Al–Si Alloy (A390). Inter Metalcast 15, 763–779 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00497-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00497-0