Abstract
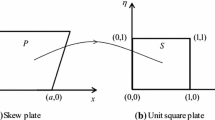
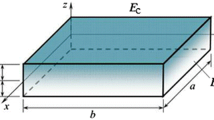
This paper deals with the vibration and buckling analysis of skew functionally graded material (FGM) plates. A finite element mathematical model is developed based on higher order shear deformation theory. The model is based on an eight noded isoparametric element with seven degrees of freedom per node. The material properties are graded along thickness direction obeying simple power-law distribution. The general displacement equation provides \(\hbox {C}^{0}\) continuity. The transverse shear strain undergoes parabolic variation through the thickness of the plate. Hence, there is no requirement of a shear correction factor in this theory. The governing equation for the skew FGM plate is obtained using Hamilton’s principle. The obtained results are compared with the published results to determine the accuracy of the method. The effect of various parameters like aspect ratio, side-thickness ratio, volume fraction index, boundary conditions and skew angle on the natural frequencies and buckling loads has been investigated.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar, A., Panda, S.K., Kumar, R.: Buckling behaviour of laminated composite skew plates with various boundary conditions subjected to linearly varying in-plane edge loading. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 100, 136–144 (2015)
Wang, X., Wang, Y., Yuan, Z.: Accurate vibration analysis of skew plates by the new version of the differential quadrature method. Appl. Math. Model. 38, 926–937 (2014)
Joodaky, A., Joodaky, I.: A semi-analytical study on static behavior of thin skew plates on Winkler and Pasternak foundations. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 100, 322–327 (2015)
Bardell, N.S.: Free vibration analysis of a flat plate using the hierarchical finite element method. J. Sound Vib. 151, 263–289 (1991)
Asemi, K., Salami, S., Slaehi, M., Sadighi, M.: Dynamic and static analysis of FGM skew plates with 3D elasticity based graded finite element modeling. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 11, 504–533 (2014)
Butalia, T.S., Kant, T., Dixit, V.D.: Performance of heterosis element for bending of skew rhombic plates. Comput. Struct. 34, 23–49 (1990)
Duan, M., Mahendran, M.: Large deflection analyses of skew plates using hybrid/mixed finite element method. Comput. Struct. 81, 1415–1424 (2003)
Liew, K.M., Han, J.-B.: Bending analysis of simply supported shear deformable skew plates. J. Eng. Mech. 123, 214–221 (1997)
Chen, C.C., Kitipornchai, S., Lim, C.W., Liew, K.M.: Free vibration of symmetrically laminated thick-perforated plates. J. Sound Vib. 230, 111–132 (2000)
Zhou, L., Zheng, W.X.X.: Vibration of skew plates by the MLS-Ritz method. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 50, 1133–1141 (2008)
Mizusawa, T., Kajita, T., Naruoka, M.: Vibration of skew plates by using B-spline functions. J. Sound Vib. 62, 301–308 (1979)
Mizusawa, T., Kajita, T., Naruoka, M.: Analysis of skew plate problems with various constraints. J. Sound Vib. 73, 575–584 (1980)
Singh, B., Chakraverty, S.: Flexural vibration of skew plates using boundary characteristic orthogonal polynomials in two variables. J. Sound Vib. 173, 157–178 (1994)
Liew, K.M., Xiang, Y., Kitipornchai, S., Wang, C.W.: Vibration of thick skew plates based on mindlin shear deformation plate theory. J. Sound Vib. 168, 39–69 (1993)
Malekzadeh, P., Karami, G.: Differential quadrature nonlinear analysis of skew composite plates based on FSDT. Eng. Struct. 28, 1307–1318 (2006)
Muhammad, T., Singh, A.V.: A p-type solution for the bending of rectangular, circular, elliptic and skew plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41, 3977–3997 (2004)
Nair, P.S., Durvasula, S.: Vibration of skew plates. J. Sound Vib. 26, 1–19 (1973)
Bishop, R.E.D.: The Mechanics of Vibration. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1979)
Zhao, X., Lee, Y.Y., Liew, K.M.: Free vibration analysis of functionally graded plates using the element-free kp-Ritz method. J. Sound Vib. 319(3–5), 918–939 (2009)
Xiang, Y., Wang, C.M., Kitipornchai, S.: Buckling of skew mindlin plates subjected to in-plane shear loadings. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 37, 1089–1101 (1995)
Li, Q., Iu, V.P., Kou, K.P.: Three-dimensional vibration analysis of functionally graded material plates in thermal environment. J. Sound Vib. 324, 733–750 (2009)
Chen, P., Peng, J., Yu, L., Yang, Y.: The interfacial analysis of a film bonded to a finite thickness graded substrate. Int. J. Solids Struct. 120, 57–66 (2017)
Chen, P., Chen, S., Peng, J.: Interface behaviour of a thin-film bonded to a graded layer coated elastic half-plane. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 115–116, 489–500 (2016)
Petyt, M.: Introduction to finite element vibration analysis, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Bhavikatti, S.S.: Finite element analysis. New age international (P) Limited, Publishers, New Delhi (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
A.1
The strain-displacement matrix [B]
A.2
The inertia matrix [I]
Shape function Matrix \(\left[ N \right] \)
where, \(N_i \) is the shape function at each node \((i=1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8)\).
A.3
The stress matrix [S]
where,
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parida, S., Mohanty, S.C. Vibration and Stability Analysis of Functionally Graded Skew Plate Using Higher Order Shear Deformation Theory. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 4, 22 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-017-0440-3
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-017-0440-3