Abstract
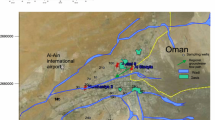
Groundwater is one of the most valuable natural resources in Peddavagu in Central Telangana (PCT). Most of the PCT region population rely on groundwater for especially drinking purposes. For this reason a thirty-five groundwater samples were collected, analysed various physico-chemical parameters including F−. The range of fluoride concentration 0.6–3.6 mg/L in Zone-I and 1–3.5 mg/L in Zone-II. pH of groundwater is from 7.1 to 8.4 and 7.3 to 8.3 in Zone-I and Zone-II respectively. Fluoride shows a significant correlation with pH, HCO3−, and Na+, which may leads to enhance the fluoride content in groundwater. Insignificant relationship between F− and NO3− suggests no influence of anthropogenic sources for F− content in groundwater. The results of the relationship between Na++K+ versus total cations (TZ+), Ca2++Mg2+ versus HCO3−+SO42− describes silicate weathering is prevails in the groundwater chemistry. The dominance of the water types Na+-HCO3−> Ca2+-Mg2+-HCO3−> Ca2+-Mg2+-SO42−Cl−>Na+-Cl−. Gibbs plot employed to differentiate the controlling mechanisms of hydrochemistry, which showed that rock water interaction is the governing process. Na+-HCO3−, alkaline nature water and rock water interaction can leads to elevate fluoride content into groundwater in the study region. Thereby, most of the region people suffer with fluorosis problem, due to intake of higher fluoride content of drinking water. Therefore, the study region population may avoid such untreated water for drinking and adopt a suitable method to reduce the fluorosis problem in future.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adimalla N, Venkatayogi S (2017) Mechanism of fluoride enrichment in groundwater of hard rock aquifers in Medak, Telangana State, South India. Environ Earth Sci 76:45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6362-2
Adimalla N, Venkatayogi S (2018) Geochemical characterization and evaluation of groundwater suitability for domestic and agricultural utility in semi-arid region of Basara, Telangana State, South India. App Water Sci 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0682-1
Apambire WB, Boyle DR, Michel FA (1997) Geochemistry, genesis, and health implications of fluoriferous groundwaters in the upper regions of Ghana. Environ Geol 33:13–24
APHA (1999) Standard methods for estimation of water and waste water, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Ayoob S, Gupta AK (2006) Fluoride in drinking water: a review on the status and stress effects. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 36(6):433–487
Brindha K, Rajesh R, Murugan R, Elango L (2011) Fluoride contamination in groundwater in parts of Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Monit Assess 172:481–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1348-0
CGWB (2013) Groundwater Brochure, Karimnagar district, Telangana, India. Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water resources, Government of India
Chin HI, Chon HT, Min KW (1995) Geochemical data analysis of the granitic rocks potentially related to fluorite mineralization in the Geumsan district. Econ Environ Geol 28:369–379
Coinly HH (1945) Cyanosis in infants caused by nitrates in well water. J Am Med Assoc 129:112
David LO (2009) Fluoride and environmental health: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 8:59–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-008-9136-9
Davis SN, De Wiest RJM (1966) Hydrogeology. Wiley, New York
Domenico PA, Schwartz FW (1990) Physical and chemical hydrogeology. Wiley, New York, p 824
Ehteshami M, Salari M, Zaresefat M (2016) Sustainable development analyses to evaluate groundwater quality and quantity management. Model Earth Syst Environ 2:133. doi.https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0196-5
Faten H, Azouzi R, Charef A Be´dir M (2016) Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical mechanisms evolution in Northeastern, Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 75:746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5441-8
Fetter CW (1990) Applied hydrogeology. CBS Publishers and Distributors, New Delhi
Freeze RA, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Garwood EA, Ryden JC (1986) Nitrate loss through leaching and surface runoff from grassland: effects of water supply, soil type and management. In: Van der Meer HG, Ryden JC, Ennik GC (eds) Nitrogen fluxes in intensive grassland systems. Martinus Nijhoff Dordrecht, pp 99–113
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 17:1088–1090
Handa BK (1975) Geochemistry and genesis of fluoride containing groundwaters in India. Groundwater 13:275–281
He X, Ma T, Wang Y, Shan H, Deng Y (2013) Hydrogeochemistry of high fluoride groundwater in shallow aquifers, Hangjinhouqi, Hetao Plain. J Geochem Explor 135:63–70
Hem JD (1991) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water; U.S. Geological Survey Water Supply Paper 2254. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur, p 264
Karro E, Uppin M (2013) The occurrence and hydrochemistry of fluoride and boron in carbonate aquifer system, central and western Estonia. Environ Monit Assess 185:3735–3748
Kim SH, Kim K, Ko KS, Kim Y, Lee KS (2012) Co-contamination of arsenic and fluoride in the groundwater of unconsolidated aquifers under reducing environments. Chemosphere 87:851–856
Li P, Qian H, Wu J, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2014) Occurrence and hydrogeochemistry of fluoride in alluvial aquifer of Weihe River, China. Environ Earth Sci 71:3133–3145
Li P, Jianhua Wu, Qian H (2016) Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: a case study in and around Hua County, China. Arab J Geosci 9:15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2059-1
Narsimha A (2018) Elevated fluoride concentration levels in rural villages of Siddipet, Telangana State, South India. Data Brief 16:693–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2017.11.088
Narsimha A, Rajitha S (2018) Spatial distribution and seasonal variation in fluoride enrichment in groundwater and its associated human health risk assessment in Telangana State, South India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess: Int J. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1438176
Narsimha A, Sudarshan V (2013) Hydrogeochemistry of groundwater in Basara area, Adilabad District, Andhra Pradesh, India. J Appl Geochem 15(2):224–237
Narsimha A, Sudarshan V (2017a) Assessment of fluoride contamination in groundwater from Basara, Adilabad District, Telangana State, India. Appl Water Sci 7:2717–2725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0489-x
Narsimha A, Sudarshan V (2017b) Contamination of fluoride in groundwater and its effect on human health: a case study in hard rock aquifers of Siddipet, Telangana State, India. Appl Water Sci 7:2501–2512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0441-0
Narsimha A, Sudarshan V (2018) Drinking water pollution with respective of fluoride in the semi-arid region of Basara, Nirmal district, Telangana State, India. Data in Brief 16:752–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2017.11.087
Piper AM (1944) A graphical procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–923
Reddy AGS, Reddy DV, Rao PN, Prasad KMd (2010) Hydrogeochemical characterization of fluoride rich groundwater of Wailpalli watershed, Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Monit Assess 171:561–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1300-3
Sajil Kumar PJ (2017) Geostatistical modeling of fluoride enrichment and nitrate contamination in the groundwater of Lower Bhavani Basin in Tamil Nadu, India. Model Earth Syst Environ 3:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0260-1
Saravanan K, Srinivasamoorthy K, Gopinath S et al (2018) Geochemical evolution of groundwater along flow path in Upper Vellar sub basin, Tamilnadu, India: an integrated approach using hydrochemistry, modeling and statistical techniques. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0400-2
Seyedmohammadi J, Esmaeelnejad L, Shabanpour M (2016) Spatial variation modelling of groundwater electrical conductivity using geostatistics and GIS. Model Earth Syst Environ 2(4):169
Stallard RE, Edmond JM (1983) Geochemistry of Amazon River: the influence of the geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load. J Geophys Res 88:9671–9688
Subba Rao N, Marghade D, Dinakar A, Chandana I, Sunitha B, Ravindra B, Balaji T (2017) Geochemical characteristics and controlling factors of chemical composition of groundwater in a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Earth Sci 76:747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7093-8
Sudarshan V, Geeta S, Narsimha A, Shankar S, Ravi Kumar A (2014) Fluoride distribution in the groundwater of Narsampet Area, Warangal District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Int J Earth Sci Eng 7(1):203–212
Sudarshan V, Srinivas B, Shankar S, Narsimha A, Ravi Kumar A, Geetha S, Ashok K (2016) Fluoride distribution in the groundwater of Gangadhara area, Karimnagar district, Telangana, India. Int J Earth Sci Eng 9(2):572–577
Sudhakar A, Narsimha A (2013) Suitability and assessment of groundwater for irrigation purpose: a case study of Kushaiguda area, Ranga Reddy district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Adv Appl Sci Res 4(6):75–81
Sujatha D (2003) Fluoride levels in the groundwater of the southeastern part of Ranga Reddy district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 44(5):587–591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0795-0
Thomas KB, Opoku F, Acquaah SO Akoto O (2016) Groundwater quality assessment using statistical approach and water quality index in Ejisu-Juaben Municipality, Ghana. Environ Earth Sci 75:489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5105-0
Todd DK (1980) Groundwater hydrology. Wiley Publications, New York
Vithanage M, Bhattacharya P (2015) Fluoride in the environment: Sources, distribution and defluoridation. Environ Chem Lett 13:131–147
Wagh VM, Panaskar DB, Muley AA (2017) Estimation of nitrate concentration in groundwater of Kadava river basin-Nashik district, Maharashtra, India by using artificial neural network model. Model Earth Syst Environ 3:36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0290-3
Wedepohl KH (1969) Handbook of geochemistry, vol II-l. Springer, Berlin
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva
Acknowledgements
The first author (Narsimha Adimalla) gratefully acknowledges the Department of Science and Technology (DST) New Delhi, for financial assistance in the form of Young Scientists Project (Start-Up Research Grant; SR/FTP/ES-13/2013). The authors wish to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments which improved the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adimalla, N., Vasa, S.K. & Li, P. Evaluation of groundwater quality, Peddavagu in Central Telangana (PCT), South India: an insight of controlling factors of fluoride enrichment. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 4, 841–852 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0443-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0443-z