Abstract
Background and aims
Whether intensity or other characteristics of physical activity can better promote the release of nitric oxide (NO) and reduction of blood pressure in hypertensive older-adults is still unknown. In this study, the post-exercise blood pressure (BP) response and NO release after different intensities of aerobic exercise in elderly women were analyzed.
Methods
Blood pressure response and NO were analyzed in 23 elderly mildly hypertensive women. Participants underwent (1) high-intensity incremental exercise (IT); (2) moderate-intensity 20 min exercise at 90 % of the anaerobic threshold (AT), and (3) control (CONT) session. BP was measured before and after interventions; volunteers remained seated for 1 h. NO estimates were made through NO2 − analyses.
Results
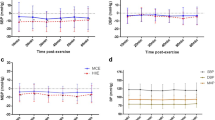
After CONT session, both diastolic BP and mean arterial pressure (MAP) were significantly higher than during pre-exercise resting. Post-exercise hypotension (PEH) was observed after exercise at IT and 90 % of AT. Although exercise in both sessions lowered SBP and MAP compared with CONT, exercise at the highest intensity (IT) was more effective on lowering systolic BP after exercise. In comparison with pre-exercise resting, NO2 − increased significantly only after IT, but both exercise sessions caused NO2 − to increase compared with CONT.
Conclusion
Exercise intensity and NO release may exert a role in eliciting PEH in mildly hypertensive elderly women.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR et al (2003) Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension 42:1206–1252
Pereira AC, Sposito AC, Mota GF et al (2006) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene variant modulates the relationship between serum cholesterol levels and blood pressure in the general population: new evidence for a direct effect of lipids in arterial blood pressure. Atherosclerosis 184:193–200
Arnal JF, Fontaine C, Billon-Gales A et al (2010) Estrogen receptors and endothelium. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30:1506–1512
Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Spiegelhalter DJ, Georgakopoulos D, Robinson J, Deanfield JE (1994) Aging is associated with endothelial dysfunction in healthy men years before the age-related decline in women. J Am Coll Cardiol 24:471–476
Reckelhoff JF (2001) Gender differences in the regulation of blood pressure. Hypertension 37:1199–1208
Kenney MJ, Seals DR (1993) Postexercise hypotension. Key features, mechanisms, and clinical significance. Hypertension 22:653–664
Goto C, Nishioka K, Umemura T et al (2007) Acute moderate-intensity exercise induces vasodilation through an increase in nitric oxide bioavailability in humans. Am J Hypertens 20:825–830
Lauer T, Heiss C, Balzer J et al (2008) Age-dependent endothelial dysfunction is associated with failure to increase plasma nitrite in response to exercise. Basic Res Cardiol 103:291–297
Duncan GE, Anton SD, Sydeman SJ et al (2005) Prescribing exercise at varied levels of intensity and frequency: a randomized trial. Arch Intern Med 165:2362–2369
Pescatello LS, Franklin BA, Fagard R, Farquhar WB, Kelley GA, Ray CA (2004) American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Exercise and hypertension. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:533–553
Lima LC, Assis GV, Hiyane W et al (2008) Hypotensive effects of exercise performed around anaerobic threshold in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 81:216–222
Nobrega OT, Faleiros VP, Telles JL (2009) Gerontology in the developing Brazil: achievements and challenges in public policies. Ger Gerontol Intern 9:135–139
Borg GA (1982) Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc 14:377–381
Cordova C, Silva VC, Moraes CF, Simoes HG, Nobrega OT (2009) Acute exercise performed close to the anaerobic threshold improves cognitive performance in elderly females. Braz J Med Biol Res 42:458–464
Tsikas D (2007) Analysis of nitrite and nitrate in biological fluids by assays based on the Griess reaction: appraisal of the Griess reaction in the l-arginine/nitric oxide area of research. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 851:51–70
Crecelius AR, Kirby BS, Voyles WF, Dinenno FA (2010) Nitric oxide, but not vasodilating prostaglandins, contributes to the improvement of exercise hyperemia via ascorbic acid in healthy older adults. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 299:H1633–H1641
Toda N, Imamura T, Okamura T (2010) Alteration of nitric oxide-mediated blood flow regulation in diabetes mellitus. Pharmacol Ther 127:189–209
Lauer T, Preik M, Rassaf T et al (2001) Plasma nitrite rather than nitrate reflects regional endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity but lacks intrinsic vasodilator action. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12814–12819
Chen X, Niroomand F, Liu Z et al (2006) Expression of nitric oxide related enzymes in coronary heart disease. Basic Res Cardiol 101:346–353
Freitas WM, Quaglia LA, Santos SN et al (2011) Association of systemic inflammatory activity with coronary and carotid atherosclerosis in the very elderly. Atherosclerosis 216:212–216
Huang X, Yang P, Du Y, Zhang J, Ma A (2007) Age-related down-regulation of HCN channels in rat sinoatrial node. Basic Res Cardiol 102:429–435
Turcato S, Turnbull L, Wang GY et al (2006) Ischemic preconditioning depends on age and gender. Basic Res Cardiol 101:235–243
Weinsaft JW, Edelberg JM (2001) Aging-associated changes in vascular activity: a potential link to geriatric cardiovascular disease. Am J Geriatr Cardiol 10:348–354
Seals DR, Desouza CA, Donato AJ, Tanaka H (2008) Habitual exercise and arterial aging. J Appl Physiol 105:1323–1332
Galetta F, Franzoni F, Plantinga Y et al (2006) Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and endothelium-dependent vasodilation in the elderly athletes. Biomed Pharmacother 60:443–447
Pescatello LS, Guidry MA, Blanchard BE et al (2004) Exercise intensity alters postexercise hypotension. J Hypertens 22:1881–1888
Miyado T, Tanaka Y, Nagai H et al (2004) Simultaneous determination of nitrate and nitrite in biological fluids by capillary electrophoresis and preliminary study on their determination by microchip capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 1051:185–191
Tanaka H, Dinenno FA, Monahan KD, Clevenger CM, DeSouza CA, Seals DR (2000) Aging, habitual exercise, and dynamic arterial compliance. Circulation 102:1270–1275
Gaspar A, Juhasz P, Bagyi K (2005) Application of capillary zone electrophoresis to the analysis and to a stability study of nitrite and nitrate in saliva. J Chromatogr A 1065:327–331
Proteggente AR, Pannala AS, Paganga G et al (2002) The antioxidant activity of regularly consumed fruit and vegetables reflects their phenolic and vitamin C composition. Free Radic Res 36:217–233
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by CNPq grants (#484318/2006-3 to O.T. Nóbrega and #478946/2008-2 to H.G. Simões). Drs. H.G. Simões, O.T. Nóbrega and A.C. Sposito were supported by fellowships for productivity in research from CNPq. The authors would like to thank Vanessa Neves de Oliveira (Department of Morphology, UFJF and Institute of Genetics and Biochemistry, UFU) for helping in the analyses.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santana, H.A.P., Moreira, S.R., Asano, R.Y. et al. Exercise intensity modulates nitric oxide and blood pressure responses in hypertensive older women. Aging Clin Exp Res 25, 43–48 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-013-0017-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-013-0017-x
Keywords
Profiles
- Hugo A. P. Santana View author profile