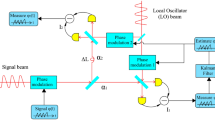
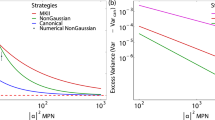
Abstract
We examine the effect of different sources of technical noise on inverse weak value-based precision phase measurements. We find that this type of measurement is similarly robust to technical noise as related experiments in the weak value regime. In particular, the measurements considered here are robust to additive Gaussian white noise and angular jitter noise commonly encountered in optical experiments. Additionally, we show the same techniques used for precision phase measurement can be used with the same technical advantages for optical frequency measurements.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonov, Y., Albert, D.Z., Vaidman, L.: How the result of a measurement of a component of the spin of a spin-1/2 particle can turn out to be 100. Phys. Rev. Lett. Am. Phys. Soc. 60, 1351 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.60.1351
Hosten, O., Kwiat, P.: Observation of the spin hall effect of light via weak measurements. Science 319, 787 (2008)
Dixon, P.B., Starling, D.J., Jordan, A.N., Howell, J.C.: Ultrasensitive beam deflection measurement via interferometric weak value amplification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 173601 (2009)
Starling, D.J., Dixon, P.B., Jordan, A.N., Howell, J.C.: Optimizing the signal-to-noise ratio of a beam-deflection measurement with interferometric weak values. Phys. Rev. A 80, 041803 (2009)
Starling, D.J., Dixon, P.B., Jordan, A.N., Howell, J.C.: Precision frequency measurements with interferometric weak values. Phys. Rev. A 82, 063822 (2010)
Starling, D.J., Dixon, P.B., Williams, N.S., Jordan, A.N., Howell, J.C.: Continuous phase amplification with a Sagnac interferometer. Phys. Rev. A 82, 011802(R) (2010)
Howell, J.C., Starling, D.J., Dixon, P.B., Vudyasetu, P.K., Jordan, A.N.: Interferometric weak value deflections: quantum and classical treatments. Phys. Rev. A 81, 033813 (2010)
Hogan, J.M., Hammer, J., Chiow, S.-W., Dickerson, S., Johnson, D.M.S., Kovachy, T., Sugarbaker, A., Kasevich, M.A.: Precision angle sensor using an optical lever inside a Sagnac interferometer. Opt. Lett. 36, 1698 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.36.001698
Pfeifer, M., Fischer, P.: Instrumentation, measurement, and metrology; Refraction; Birefringence; Chiral media. Opt. Express 19, 16508 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.19.016508
Egan, P., Stone, J.A.: Weak-value thermostat with 0.2 mK precision. Opt. Lett. 37, 4991 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.37.004991
Gorodetski, Y., Bliokh, K.Y., Stein, B., Genet, C., Shitrit, N., Kleiner, V., Hasman, E., Ebbesen, T.W.: Weak measurements of light chirality with a plasmonic slit, experimental observation of the spin hall effect of light on a nanometal film via weak measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett 109, 013901 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.013901
Zhou, X., Xiao, Z., Luo, H., Wendoi, S.: Experimental observation of the spin Hall effect of light on a nanometal film via weak measurements. Phys. Rev. A 85, 043809 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.85.043809
Strübi, G., Bruder, C.: Measuring ultrasmall time delays of light by joint weak measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 083605 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.083605
Viza, G.I., Martínez-Rincón, J., Howland, G.A., Frostig, H., Shomroni, I., Dayan, B., Howell, J.C.: Weak-values technique for velocity measurements. Opt. Lett. 38, 2949 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.38.002949
Xu, X.-Y., Kedem, Y., Sun, K., Vaidman, L., Li, C.-F., Guo, G.-C.: Phase estimation with weak measurement using a white light source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 033604 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.033604
Zhou, L., Turek, Y., Sun, C.P., Nori, F.: Weak-value amplification of light deflection by a dark atomic ensemble. Phys. Rev. A 88, 053815 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.88.053815
Magaña Loaiza, O.S., Mirhosseini, M., Rodenburg, B., Boyd, R.W.: Amplification of angular rotations using weak measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 200401 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.200401
Salazar-Serrano, L.J., Janner, D., Brunner, N., Pruneri, V., Torres, J.P.: Measurement of sub-pulse-width temporal delays via spectral interference induced by weak value amplification. Phys. Rev. A 89, 012126 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.89.012126
Salazar-Serrano, L., Barrera, D., Amaya, W., Sales, S., Pruneri, V., Capmany, J., Torres, J.: Enhancement of the sensitivity of a temperature sensor based on fiber Bragg gratings via weak value amplification. Opt. Lett. 40, 3962 (2015)
Martínez-Rincón, J., Mullarkey, C.A., Viza, G.I., Liu, W.-T., Howell, J.C.: Ultrasensitive inverse weak-value tilt meter. Opt. Lett. 42, 2479 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.42.002479
Dressel, J., Malik, M., Miatto, F.M., Jordan, A.N., Boyd, R.W.: Colloquium: understanding quantum weak values: basics and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 86, 307 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.86.307
Pang, S., Dressel, J., Brun, T.A.: Entanglement-assisted weak value amplification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 030401 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.030401
Pang, S., Brun, T.A.: Improving the precision of weak measurements by postselection measurement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 120401 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.120401
Jordan, A.N., Martínez-Rincón, J., Howell, J.C.: Technical advantages for weak-value amplification: when less is more. Phys. Rev. X 4, 011031 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.4.011031
Knee, G.C., Gauger, E.M.: When amplification with weak values fails to suppress technical noise. Phys. Rev. X 4, 011032 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.4.011032
Viza, G.I., Martínez-Rincón, J., Alves, G.B., Jordan, A.N., Howell, J.C.: Experimentally quantifying the advantages of weak-value-based metrology. Phys. Rev. A 92, 032127 (2015)
Alves, G.B., Escher, B.M., de Matos Filho, R.L., Zagury, N., Davidovich, L.: Weak-value amplification as an optimal metrological protocol. Phys. Rev. A 91, 062107 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.91.062107
Torres, J.P., Salazar-Serrano, L.J.: Weak value amplification: a view from quantum estimation theory that highlights what it is and what isn’t. Sci. Rep. 6, 19702 (2016)
Harris, J., Boyd, R.W., Lundeen, J.S.: Weak value amplification can outperform conventional measurement in the presence of detector saturation (2016). arXiv preprint. arXiv:1612.04327
Pang, S., Alonso, J.R.G., Brun, T.A., Jordan, A.N.: Protecting weak measurements against systematic errors. Phys. Rev. A 94, 012329 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.94.012329
Dressel, J., Lyons, K., Jordan, A.N., Graham, T.M., Kwiat, P.G.: Strengthening weak-value amplification with recycled photons. Phys. Rev. A 88, 023821 (2013)
Lyons, K., Dressel, J., Jordan, A.N., Howell, J.C., Kwiat, P.G.: Power-recycled weak-value-based metrology. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 170801 (2015)
Byard, C., Graham, T., Jordan, A., Kwiat, P.G.: Pulse recycling and weak value metrology. In: Frontiers in Optics 2015. Optical Society of America, Paper JW2A-69 (2015)
Wang, Y.-T., Tang, J.-S., Hu, G., Wang, J., Yu, S., Zhou, Z.-Q., Cheng, Z.-D., Xu, J.-S., Fang, S.-Z., Wu, Q.-L., et al.: Experimental demonstration of higher precision weak-value-based metrology using power recycling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 230801 (2016)
Dressel, J., Lyons, K., Jordan, A.N., Graham, T., Kwiat, P.: Strengthening weak values with recycled photons. Phys. Rev. A 88, 023821 (2013)
Lyons, K., Dressel, J., Jordan, A.N., Howell, J.C., Kwiat, P.G.: Power-recycled weak-value-based metrology. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 170801 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.170801
Kofman, A.G., Ashhab, S., Nori, F.: Nonperturbative theory of weak pre- and post-selected measurements. Phys. Rep. 520, 43 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2012.07.001
Starling, D.J., Bloch, S.M., Vudyasetu, P.K., Choi, J.S., Little, B., Howell, J.C.: Double Lorentzian atomic prism. Phys. Rev. A 86, 023826 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.86.023826
Boyd, R.W., Gauthier, D.J.: Slow and Fast Light. University of Rochester Institute of Optics, Technical Report (2001)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by DRS Technologies and Army Research Office Grant no. W911NF-13-1-0402.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyons, K., Howell, J.C. & Jordan, A.N. Noise suppression in inverse weak value-based phase detection. Quantum Stud.: Math. Found. 5, 579–588 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40509-017-0145-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40509-017-0145-7