Abstract
Purpose
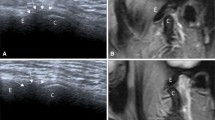
To assess pattern of articular disc displacement in patients with internal derangement (ID) of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) with ultrasound.
Materials and methods
Prospective study was conducted upon 40 TMJ of 20 patients (3 male, 17 female with mean age of 26.1 years) with ID of TMJ. They underwent high-resolution ultrasound and MR imaging of TMJ. The MR images were used as the gold standard for calculating sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive likelihood ratio (PLR), and negative likelihood ratio (NLR) of ultrasound for diagnosis of anterior or sideway displacement of the disc.
Results
The anterior displaced disc was seen in 26 joints at MR and 22 joints at ultrasound. The diagnostic efficacy of ultrasound for anterior displacement has sensitivity of 79.3 %, specificity of 72.7 %, accuracy of 77.5 %, PPV of 88.5 %, NPV of 57.1 %, PLR of 2.9 and NLR of 0.34. The sideway displacement of disc was seen in four joints at MR and three joints at ultrasound. The diagnostic efficacy of ultrasound for sideway displacement has a sensitivity of 75 %, specificity of 63.6 %, accuracy of 66.7 %, PPV of 42.8, NPV of 87.5 %, PLR of 2.06, and NLR of 0.39.
Conclusion
We concluded that ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging modality used for assessment of anterior and sideway displacement of the articular disc in patients with ID of TMJ.
Riassunto
Scopo
Valutare i pattern della dislocazione del disco articolare nei pazienti con squilibrio interno (ID) dell’articolazione temporo-mandibolare (ATM) con l’ecografia.
Materiale e metodi
E’ stato condotto uno studio prospettico su 40 ATM di 20 pazienti (3 maschi, 17 femmine, con età media di 26,1 anni) con ID della TMJ. Tutti sono stati sottoposti ad ecografia ad alta risoluzione e RM della TMJ. La RM è stati utilizzata come il gold standard per il calcolo di sensibilità, specificità, accuratezza, valore predittivo positivo (PPV), valore predittivo negativo (NPV), rapporto di probabilità positivo (PLR) e rapporto di probabilità negativo (NLR) dell’ecografia nella la diagnosi di dislocazione anteriore o lateralmente del disco.
Risultati
Il disco appariva dislocato anteriormente in 26 ATM con la MR e in 22 con l’ecografia. L’efficacia diagnostica dell’ecografia nella diagnosi di dislocazione anteriore aveva sensibilità del 79,3 %, specificità del 72,7 %, accuratezza del 77,5 %, valore predittivo positivo del 88,5 %, NPV di 57,1 %, PLR di 2,9 e NLR di 0,34. Il dislocamento laterale del disco è stata osservato in 4 casi con MR e 3 con ecografia. L’efficacia diagnostica dell’ecografia per lo spostamento laterale aveva sensibilità del 75 %, specificità del 63,6 %, accuratezza del 66,7 %, PPV di 42,8, NPV di 87,5 %, PLR di 2.06 e NLR di 0,39.
Conclusioni
Abbiamo concluso che l’ecografia è una metodica di imaging non invasiva che può essere utilizzata per la valutazione delle dislocazioni anteriori e laterali del disco articolare nei pazienti con ID di TMJ.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunter A, Kalathingal S (2013) Diagnostic imaging for temporomandibular disorders and orofacial pain. Dent Clin N Am 57:405–418
de Leeuw R (2008) Internal Derangements of the temporomandibular joint. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin N Am 20:159–168
Vilanova J, Barceló J, Puig J, Remollo S, Nicolau C, Bru C (2007) Diagnostic imaging: magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, and ultrasound. Semin Ultrasound CT MRI 28:184–191
Aiken A, Bouloux G, Hudgins P (2012) MR imaging of the temporomandibular joint. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 20:397–412
Rao VM, Liem M, Farole A, Razek AA (1993) Elusive “stuck” disk in the temporomandibular joint: diagnosis with MR imaging. Radiology 189:823–827
Whyte AM, McNamara D, Rosenberg I, Whyte AW (2006) Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of temporomandibular joint disc displacement—a review of 144 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35:696–703
Eberhard L, Giannakopoulos NN, Rohde S, Schmitter M (2013) Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disc position in patients with TMJ pain assessed by coronal MRI. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 42:20120199
Kirk WS Jr (2013) Lateral impingements of the temporomandibular joint: a classification system and MRI imaging characteristics. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42:223–228
Schmitter M, Kress B, Ludwig C, Koob A, Gabbert O, Rammelsberg P (2005) Temporomandibular joint disk position assessed at coronal MR imaging in asymptomatic volunteers. Radiology 236:559–564
Chen YJ, Gallo LM, Meier D, Palla S (2000) Individualized oblique-axial magnetic resonance imaging for improved visualization of mediolateral TMJ disc displacement. J Orofac Pain 14:128–139
Razek AA, Fouda NS, Elmetwaley N, Elbogdady E (2009) Sonography of the knee joint. J Ultrasound 12:53–60
Sakellariou G, Iagnocco A, Filippucci E, Ceccarelli F, Di Geso L, Carli L et al (2013) Ultrasound imaging for the rheumatologist XLVIII. Ultrasound of the shoulders of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 31:837–842
Abdel Razek A, Fouda N, Elmetwaly N, Elbogdady E (2008) Sonography of the knee joint–technique and normal anatomy. Eur Med Imaging Rev 1:66–68
Li C, Su N, Yang X, Yang X, Shi Z, Li L (2012) Ultrasonography for detection of disc displacement of temporomandibular joint: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70:1300–1309
Manfredini D (2012) Ultrasonography has an acceptable diagnostic efficacy for temporomandibular disc displacement. Evid Based Dent 13:84–85
Dupuy-Bonafé I, Picot MC, Maldonado IL, Lachiche V, Granier I, Bonafé A (2012) Internal derangement of the temporomandibular joint: is there still a place for ultrasound? Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 113:832–840
Manfredini D, Guarda-Nardini L (2009) Ultrasonography of the temporomandibular joint: a literature review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38:1229–1236
Melis M, Secci S, Ceneviz C (2007) Use of ultrasonography for the diagnosis of temporomandibular joint disorders: a review. Am J Dent 20:73–78
Bas B, Yılmaz N, Gökce E, Akan H (2011) Diagnostic value of ultrasonography in temporomandibular disorders. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:1304–1310
Cakir-Ozkan N, Sarikaya B, Erkorkmaz U, Aktürk Y (2010) Ultrasonographic evaluation of disc displacement of the temporomandibular joint compared with magnetic resonance imaging. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1075–1080
Kaya K, Dulgeroglu D, Unsal-Delialioglu S, Babadag M, Tacal T, Barlak A et al (2010) Diagnostic value of ultrasonography in the evaluation of the temporomandibular joint anterior disc displacement. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 38:391–395
Byahatti SM, Ramamurthy BR, Mubeen M, Agnihothri PG (2010) Assessment of diagnostic accuracy of high-resolution ultrasonography in determination of temporomandibular joint internal derangement. Indian J Dent Res 21:189–194
Landes C, Sader R (2007) Sonographic evaluation of the ranges of condylar translation and of temporomandibular joint space as well as first comparison with symptomatic joints. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 35:374–381
Rudisch A, Emshoff R, Maurer H, Kovacs P, Bodner G (2006) Pathologic–sonographic correlation in temporomandibular joint pathology. Eur Radiol 16:1750–1756
Jank S, Emshoff R, Norer B, Missmann M, Nicasi A, Strobl H et al (2005) Diagnostic quality of dynamic high-resolution ultrasonography of the TMJ—a pilot study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34:132–137
Emshoff R, Jank S, Bertram S, Rudisch A, Bodner G (2002) Disk displacement of the temporomandibular joint: sonography versus MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 178:1557–1562
Uysal S, Kansu H, Akhan O, Kansu O (2002) Comparison of ultrasonography with magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of temporomandibular joint internal derangements: a preliminary investigation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 94:115–121
Emshoff R, Jank S, Rudisch A, Walch C, Bodner G (2002) Error patterns and observer variations in the high-resolution ultrasonography imaging evaluation of the disk position of the temporomandibular joint. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 93:369–375
Truelove EL, Sommers EE, LcResch L, Dworkin SF, Von Korff M (1992) Clinical diagnostic criteria for TMD: new classification permits multiple diagnoses. J Am Dent Assoc 123:47
Ahmad M, Hollender L, Anderson Q, Kartha K, Ohrbach R, Truelove EL et al (2009) Research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders (RDC/TMD): development of image analysis criteria and examiner reliability for image analysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107:844–860
Landes CA, Goral WA, Sader R, Mack MG (2007) Three-dimensional versus two-dimensional sonography of the temporomandibular joint in comparison to MRI. Eur J Radiol 61:235–244
Conflict of interest
The authors (Abdel Razek A, Al Belasy F, Ahmed W, Haggag M) have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000 (5). All patients provided written informed consent to enrolment in the study and to the inclusion in this article of information that could potentially lead to their identification.
Human and animal studies
The study conducted in accordance with all institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razek, A.A.K.A., Al Mahdy Al Belasy, F., Ahmed, W.M.S. et al. Assessment of articular disc displacement of temporomandibular joint with ultrasound. J Ultrasound 18, 159–163 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-014-0133-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-014-0133-2