Abstract
Purpose of the Review
In the present review, we discuss the very recent findings that the gut microbiota composition can modulate cell-based plasticity in the brain, namely, adult hippocampal neurogenesis, and thereby alter hippocampal dependent behavior.
Recent Findings
Absence of gut microbiota from birth or antibiotic-induced dysbiosis in adults leads to an aberrant metabolite production and immune functions. Both scenarios compromise a proper postnatal brain development, or brain wiring in adults, including aberrant neurogenesis. This in turn leads to a hippocampal mismanagement of environmental cues and renders the animals to be more susceptible to stress and less cognitively flexible which contribute to general impairments in learning and memory functions and social behavior.
Summary
Mounting evidence indicates that certain behavior aberrances in germ-free and dysbiotic mice are mediated by changes in neurogenesis. The mechanisms and the relevance of this complex regulation remain to be elucidated by future research.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1965;124(3):319–35.
Altman J, Das GD. Postnatal neurogenesis in the guinea-pig. Nature. 1967;214(5093):1098–101.
Kaplan MS, Hinds JW. Neurogenesis in the adult rat: electron microscopic analysis of light radioautographs. Science. 1977;197(4308):1092–4.
Corotto FS, Henegar JA, Maruniak JA. Neurogenesis persists in the subependymal layer of the adult mouse brain. Neurosci Lett. 1993;149(2):111–4.
Luskin MB. Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron. 1993;11(1):173–89.
Seki T, Arai Y. Highly polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM-H) is expressed by newly generated granule cells in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. J Neurosci. 1993;13(6):2351–8.
Kaplan MS, Bell DH. Neuronal proliferation in the 9-month-old rodent-radioautographic study of granule cells in the hippocampus. Exp Brain Res. 1983;52(1):1–5.
Kaplan MS, Bell DH. Mitotic neuroblasts in the 9-day-old and 11-month-old rodent hippocampus. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci. 1984;4(6):1429–41.
Cameron HA, Woolley CS, McEwen BS, Gould E. Differentiation of newly born neurons and glia in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Neuroscience. 1993;56(2):337–44.
Kempermann G, Kuhn HG, Gage FH. More hippocampal neurons in adult mice living in an enriched environment. Nature. 1997;386(6624):493–5.
Kuhn HG, Dickinson-Anson H, Gage FH. Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J Neurosci. 1996;16(6):2027–33.
Kornack DR, Rakic P. Continuation of neurogenesis in the hippocampus of the adult macaque monkey. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(10):5768–73.
Gould E, Vail N, Wagers M, Gross CG. Adult-generated hippocampal and neocortical neurons in macaques have a transient existence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(19):10910–7.
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, et al. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med. 1998;4(11):1313–7.
Spalding KL, Bergmann O, Alkass K, Bernard S, Salehpour M, Huttner HB, et al. Dynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult humans. Cell. 2013;153(6):1219–27.
Gage FH. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science. 2000;287(5457):1433–8.
Reynolds BA, Weiss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1992;255(5052):1707–10.
Kempermann G, editor. Adult neurogenesis. Stem cells and neuronal development in the adult brain. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2006.
Altman J. Autoradiographic and histological studies of postnatal neurogenesis. IV. Cell proliferation and migration in the anterior forebrain, with special reference to persisting neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol. 1969;137(4):433–57.
Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A. Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science. 1994;264(5162):1145–8.
Kempermann G. Why new neurons? Possible functions for adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci. 2002;22(3):635–8.
Kempermann G, Jessberger S, Steiner B, Kronenberg G. Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27(8):447–52.
Markakis EA, Gage FH. Adult-generated neurons in the dentate gyrus send axonal projections to field CA3 and are surrounded by synaptic vesicles. J Comp Neurol. 1999;406(4):449–60.
Song HJ, Stevens CF, Gage FH. Neural stem cells from adult hippocampus develop essential properties of functional CNS neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5(5):438–45.
Stanfield BB, Trice JE. Evidence that granule cells generated in the dentate gyrus of adult rats extend axonal projections. Exp Brain Res. 1988;72(2):399–406.
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, Toni N, Palmer TD, Gage FH. Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature. 2002;415(6875):1030–4.
Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim DA. For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron. 2004;41(5):683–6.
Gould E, Gross CG. Neurogenesis in adult mammals: some progress and problems. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci. 2002;22(3):619–23.
Deng W, Aimone JB, Gage FH. New neurons and new memories: how does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11(5):339–50.
Bruel-Jungerman E, Rampon C, Laroche S. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity and memory: facts and hypotheses. Rev Neurosci. 2007;18(2):93–114.
Sahay A, Scobie KN, Hill AS, O'Carroll CM, Kheirbek MA, Burghardt NS, et al. Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve pattern separation. Nature. 2011;472(7344):466–70.
Jessberger S, Toni N, Clemenson GD Jr, Ray J, Gage FH. Directed differentiation of hippocampal stem/progenitor cells in the adult brain. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11(8):888–93.
Aimone JB, Deng W, Gage FH. Resolving new memories: a critical look at the dentate gyrus, adult neurogenesis, and pattern separation. Neuron. 2011;70(4):589–96.
Aimone JB, Wiles J, Gage FH. Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9(6):723–7.
Aimone JB, Wiles J, Gage FH. Computational influence of adult neurogenesis on memory encoding. Neuron. 2009;61(2):187–202.
Appleby PA, Wiskott L. Additive neurogenesis as a strategy for avoiding interference in a sparsely-coding dentate gyrus. Network. 2009;20(3):137–61.
Wiskott L, Rasch MJ, Kempermann G. A functional hypothesis for adult hippocampal neurogenesis: avoidance of catastrophic interference in the dentate gyrus. Hippocampus. 2006;16(3):329–43.
Garthe A, Behr J, Kempermann G. Adult-generated hippocampal neurons allow the flexible use of spatially precise learning strategies. PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5464.
Kempermann G. Regulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis—implications for novel theories of major depression. Bipolar Disord. 2002;4(1):17–33.
Wolf SA, Steiner B, Akpinarli A, Kammertoens T, Nassenstein C, Braun A, et al. CD4-positive T lymphocytes provide a neuroimmunological link in the control of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J Immunol. 2009;182(7):3979–84.
Bloom FE. Modern concepts in electrophysiology for psychiatry. Psychopharmacol Commun. 1975;1(6):579–85.
Holsboer F. Implications of altered limbic-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (LHPA)-function for neurobiology of depression. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1988;341:72–111.
Mirescu C, Peters JD, Gould E. Early life experience alters response of adult neurogenesis to stress. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7(8):841–6.
Lu L, Bao G, Chen H, Xia P, Fan X, Zhang J, et al. Modification of hippocampal neurogenesis and neuroplasticity by social environments. Exp Neurol. 2003;183(2):600–9.
Pham K, Nacher J, Hof PR, McEwen BS. Repeated restraint stress suppresses neurogenesis and induces biphasic PSA-NCAM expression in the adult rat dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;17(4):879–86.
Nixon K, Crews FT. Binge ethanol exposure decreases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J Neurochem. 2002;83(5):1087–93.
Schoenfeld TJ, Gould E. Differential effects of stress and glucocorticoids on adult neurogenesis. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2013;15:139–64.
Jacobs BL, Praag H, Gage FH. Adult brain neurogenesis and psychiatry: a novel theory of depression. Mol Psychiatry. 2000;5(3):262–9.
Reif A, Schmitt A, Fritzen S, Lesch KP. Neurogenesis and schizophrenia: dividing neurons in a divided mind? Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2007;257(5):290–9.
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S, et al. Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science. 2003;301(5634):805–9.
Sahay A, Hen R. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in depression. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10(9):1110–5.
Wexler BE, Zhu H, Bell MD, Nicholls SS, Fulbright RK, Gore JC, et al. Neuropsychological near normality and brain structure abnormality in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166(2):189–95.
Arango C, Kirkpatrick B, Koenig J. At issue: stress, hippocampal neuronal turnover, and neuropsychiatric disorders. Schizophr Bull. 2001;27(3):477–80.
Kempermann G, Krebs J, Fabel K. The contribution of failing adult hippocampal neurogenesis to psychiatric disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2008;21(3):290–5.
Eisch AJ, Cameron HA, Encinas JM, Meltzer LA, Ming GL, Overstreet-Wadiche LS. Adult neurogenesis, mental health, and mental illness: hope or hype? J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci. 2008;28(46):11785–91.
Toro CT, Deakin JF. Adult neurogenesis and schizophrenia: a window on abnormal early brain development? Schizophr Res. 2007;90(1–3):1–14.
Pajonk FG, Wobrock T, Gruber O, Scherk H, Berner D, Kaizl I, et al. Hippocampal plasticity in response to exercise in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67(2):133–43.
• Franca TFA, Bitencourt AM, Maximilla NR, Barros DM, Monserrat JM. Hippocampal neurogenesis and pattern separation: a meta-analysis of behavioral data. Hippocampus. 2017;27(9):937–950
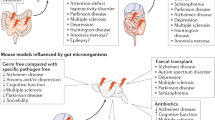
• Campos AC, Rocha NP, Nicoli JR, Vieira LQ, Teixeira MM, Teixeira AL. Absence of gut microbiota influences lipopolysaccharide-induced behavioral changes in mice. Behav Brain Res. 2016;312:186–94.
Clarke G, Grenham S, Scully P, Fitzgerald P, Moloney RD, Shanahan F, et al. The microbiome-gut-brain axis during early life regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent manner. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18(6):666–73.
•• Diaz Heijtz R, Wang S, Anuar F, Qian Y, Bjorkholm B, Samuelsson A, et al. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(7):3047–52.
Neufeld KM, Kang N, Bienenstock J, Foster JA. Reduced anxiety-like behavior and central neurochemical change in germ-free mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil : Off J Eur Gastrointest Motil Soc. 2011;23(3):255–64. e119
Sudo N, Chida Y, Aiba Y, Sonoda J, Oyama N, Yu XN, et al. Postnatal microbial colonization programs the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system for stress response in mice. J Physiol. 2004;558(Pt 1):263–75.
•• Zheng P, Zeng B, Zhou C, Liu M, Fang Z, Xu X, et al. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21(6):786–96.
Crumeyrolle-Arias M, Jaglin M, Bruneau A, Vancassel S, Cardona A, Dauge V, et al. Absence of the gut microbiota enhances anxiety-like behavior and neuroendocrine response to acute stress in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014;42:207–17.
Schoenfeld TJ, Gould E. Stress, stress hormones, and adult neurogenesis. Exp Neurol. 2012;233(1):12–21.
Lyons DM, Buckmaster PS, Lee AG, Wu C, Mitra R, Duffey LM, et al. Stress coping stimulates hippocampal neurogenesis in adult monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(33):14823–7.
Hill AS, Sahay A, Hen R. Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to reduce anxiety and depression-like behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40(10):2368–78.
Levone BR, Cryan JF, O'Leary OF. Role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in stress resilience. Neurobiol Stress. 2015;1:147–55.
•• Revest JM, Dupret D, Koehl M, Funk-Reiter C, Grosjean N, Piazza PV, et al. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is involved in anxiety-related behaviors. Mol Psychiatry. 2009;14(10):959–67.
Seo DO, Carillo MA, Chih-Hsiung Lim S, Tanaka KF, Drew MR. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis modulates fear learning through associative and nonassociative mechanisms. J Neurosci. 2015;35(32):11330–45.
Snyder JS, Soumier A, Brewer M, Pickel J, Cameron HA. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis buffers stress responses and depressive behaviour. Nature. 2011;476(7361):458–61.
Schloesser RJ, Manji HK, Martinowich K. Suppression of adult neurogenesis leads to an increased hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis response. Neuroreport. 2009;20(6):553–7.
Surget A, Tanti A, Leonardo ED, Laugeray A, Rainer Q, Touma C, et al. Antidepressants recruit new neurons to improve stress response regulation. Mol Psychiatry. 2011;16(12):1177–88.
•• Arentsen T, Raith H, Qian Y, Forssberg H, Diaz HR. Host microbiota modulates development of social preference in mice. Microb Ecol Health Dis. 2015;26:29719.
• Ogbonnaya ES, Clarke G, Shanahan F, Dinan TG, Cryan JF, O'Leary OF. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is regulated by the microbiome. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;78(4):e7–9.
Dash PK, Mach SA, Moore AN. Enhanced neurogenesis in the rodent hippocampus following traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci Res. 2001;63(4):313–9.
Lu D, Mahmood A, Zhang R, Copp M. Upregulation of neurogenesis and reduction in functional deficits following administration of DEtA/NONOate, a nitric oxide donor, after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurosurg. 2003;99(2):351–61.
Rice AC, Khaldi A, Harvey HB, Salman NJ, White F, Fillmore H, et al. Proliferation and neuronal differentiation of mitotically active cells following traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2003;183(2):406–17.
Arvidsson A, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated increase of neurogenesis in adult rat dentate gyrus following stroke. Eur J Neurosci. 2001;14(1):10–8.
Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O. Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med. 2002;8(9):963–70.
Parent JM, Vexler ZS, Gong C, Derugin N, Ferriero DM. Rat forebrain neurogenesis and striatal neuron replacement after focal stroke. Ann Neurol. 2002;52(6):802–13.
Jin K, Sun Y, Xie L, Peel A, Mao XO, Batteur S, et al. Directed migration of neuronal precursors into the ischemic cerebral cortex and striatum. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003;24(1):171–89.
Parent JM, Yu TW, Leibowitz RT, Geschwind DH, Sloviter RS, Lowenstein DH. Dentate granule cell neurogenesis is increased by seizures and contributes to aberrant network reorganization in the adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1997;17(10):3727–38.
Jessberger S, Romer B, Babu H, Kempermann G. Seizures induce proliferation and dispersion of doublecortin-positive hippocampal progenitor cells. Exp Neurol. 2005;196(2):342–51.
Bick-Sander A, Steiner B, Wolf SA, Babu H, Kempermann G. Running in pregnancy transiently increases postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in the offspring. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(10):3852–7.
Wolf SA, Melnik A, Kempermann G. Physical exercise increases adult neurogenesis and telomerase activity, and improves behavioral deficits in a mouse model of schizophrenia. Brain Behav Immun. 2011;25(5):971–80.
Fabel K, Wolf SA, Ehninger D, Babu H, Leal-Galicia P, Kempermann G. Additive effects of physical exercise and environmental enrichment on adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Front Neurosci. 2009;3:50.
van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH. Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2(3):266–70.
van Praag H, Fleshner M, Schwartz MW, Mattson MP. Exercise, energy intake, glucose homeostasis, and the brain. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci. 2014;34(46):15139–49.
Kronenberg G, Bick-Sander A, Bunk E, Wolf C, Ehninger D, Kempermann G. Physical exercise prevents age-related decline in precursor cell activity in the mouse dentate gyrus. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27(10):1505–13.
•• Desbonnet L, Clarke G, Traplin A, O'Sullivan O, Crispie F, Moloney RD, et al. Gut microbiota depletion from early adolescence in mice: implications for brain and behaviour. Brain Behav Immun. 2015;48:165–73.
Mohle L, Mattei D, Heimesaat MM, Bereswill S, Fischer A, Alutis M, et al. Ly6C(hi) monocytes provide a link between antibiotic-induced changes in gut microbiota and adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Cell Rep. 2016;15(9):1945–56.
•• Wohleb ES, McKim DB, Sheridan JF, Godbout JP. Monocyte trafficking to the brain with stress and inflammation: a novel axis of immune-to-brain communication that influences mood and behavior. Front Neurosci. 2014;8:447.
• Dorrestein PC, Mazmanian SK, Knight R. Finding the missing links among metabolites, microbes, and the host. Immunity. 2014;40(6):824–32.
• Rogers GB, Keating DJ, Young RL, Wong ML, Licinio J, Wesselingh S. From gut dysbiosis to altered brain function and mental illness: mechanisms and pathways. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21(6):738–48.
Bruch JD. Intestinal infection associated with future onset of an anxiety disorder: results of a nationally representative study. Brain Behav Immun. 2016;57:222–6.
Yassa MA, Stark CE. Pattern separation in the hippocampus. Trends Neurosci. 2011;34(10):515–25.
•• Bercik P, Collins SM. The effects of inflammation, infection and antibiotics on the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;817:279–89.
Noble EE, Hsu TM, Kanoski SE. Gut to brain dysbiosis: mechanisms linking western diet consumption, the microbiome, and cognitive impairment. Front Behav Neurosci. 2017;11:9.
•• Frohlich EE, Farzi A, Mayerhofer R, Reichmann F, Jacan A, Wagner B, et al. Cognitive impairment by antibiotic-induced gut dysbiosis: analysis of gut microbiota-brain communication. Brain Behav Immun. 2016;56:140–55.
Gareau MG, Wine E, Rodrigues DM, Cho JH, Whary MT, Philpott DJ, et al. Bacterial infection causes stress-induced memory dysfunction in mice. Gut. 2011;60(3):307–17.
•• Wang T, Hu X, Liang S, Li W, Wu X, Wang L, et al. Lactobacillus fermentum NS9 restores the antibiotic induced physiological and psychological abnormalities in rats. Benef Microbes. 2015;6(5):707–17.
Lieberwirth C, Pan Y, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Wang Z. Hippocampal adult neurogenesis: its regulation and potential role in spatial learning and memory. Brain Res. 2016;1644:127–40.
•• Mostafa S, Miller BJ. Antibiotic-associated psychosis during treatment of urinary tract infections: a systematic review. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014;34(4):483–90.
•• Opendak M, Briones BA, Gould E. Social behavior, hormones and adult neurogenesis. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2016;41:71–86.
Rubin RD, Watson PD, Duff MC, Cohen NJ. The role of the hippocampus in flexible cognition and social behavior. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014;8:742.
• Desbonnet L, Clarke G, Shanahan F, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Microbiota is essential for social development in the mouse. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19(2):146–8.
•• Buffington SA, Di Prisco GV, Auchtung TA, Ajami NJ, Petrosino JF, Costa-Mattioli M. Microbial reconstitution reverses maternal diet-induced social and synaptic deficits in offspring. Cell. 2016;165(7):1762–75.
Niculescu MD, Lupu DS. High fat diet-induced maternal obesity alters fetal hippocampal development. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2009;27(7):627–33.
•• de Theije CG, Wopereis H, Ramadan M, van Eijndthoven T, Lambert J, Knol J, et al. Altered gut microbiota and activity in a murine model of autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav Immun. 2014;37:197–206.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Brain and Microbiome
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolf, S.A., Mattei, D. You Need Guts to Make New Neurons. Curr Behav Neurosci Rep 4, 353–360 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40473-017-0127-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40473-017-0127-4