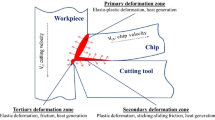
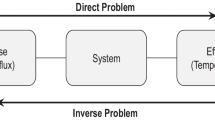
Abstract
Higher rate of production and better surface quality are major driving forces for modern machining systems. Higher cutting speeds can be used to achieve higher production rates. The generation of heat puts a limit on cutting speeds, thus reducing production rates. Almost all energy spent in machining operations is converted into heat. The plastic deformation of metals during machining is concentrated in a narrow zone and thus very high temperature is expected in this zone. These high temperatures are responsible for reduction in tool life and degradation of surface quality. The complex coupling between plastic deformation and temperature fields is an area of research for many years. The techniques like numerical, analytical and experimental were used for the prediction of the cutting temperatures accurately. Milling is one of the most versatile machining processes used in modern industries. As the industries are focusing more on reducing the use of cutting fluids because of their harmful effects to the operators and environment, dry milling is used as an alternative. Measurement and prediction of the cutting temperature during milling is challenging because of the variation in the high-speed rotating cutter and chip thickness. In this paper, the literature on experimental measurement of the cutting temperatures and prediction of cutting temperatures using numerical, analytical and experimental techniques for dry milling operations is reviewed. The methodology used for modelling and the novelty in the work are highlighted. Initially, a brief review of the temperature measurement techniques is taken to bring out their relative merits and demerits. The paper is aimed to highlight the latest work in this field and also, the areas needed to be addressed are discussed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fernandez-Valdivielso A, Lopez de Lacalle LN, Urbikain G, Rodriguez A (2015) Detecting the key geometrical features and grades of carbide inserts for the turning of nickel-based alloys concerning surface integrity. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C J Mech Eng Sci 0(0):1–18
Fata A (2011) Temperature measurement during machining depending on cutting conditions. J P&A Sci Technol 2:16–21
Bacci M, Wallbank J (1999) Cutting temperature: prediction and measurement methods—a review. J Mater Process Technol 88:195–202
Norouzifard V, Hamedi M (2014) A three-dimensional heat conduction inverse procedure to investigate tool—chip thermal interaction in machining process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74(9–12):1637–1648
Aydın M (2016) Cutting temperature analysis considering the improved Oxley’ s predictive machining theory. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. doi:10.1007/s40430-016-0514-x
Astakhov VP (2006) Improvements of tribological conditions. In: Astakhov VP (ed) Tribology of metal cutting, vol. 52. Elsevier B. V., pp 326–390
Shokrani A, Dhokia V, Newman ST (2012) Environmentally conscious machining of difficult-to-machine materials with regard to cutting fluids. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 57:83–101
Sreejith PS, Ngoi BKA (2000) Dry machining: Machining of the future. J Mater Process Technol 101(1):287–291
Astakhov VP (2008) Ecological machining: near-dry machining’. In: Machining: fundamentals and recent advances. Springer, London, pp 195–223
Gandarias A, de Lacalle LNL, Lamikiz A, Aizpitarte X (2008) Study of the performance of the turning and drilling of austenitic stainless steels using two coolant techniques. Int J Mach Mach Mater 3(1/2):1–17
Yap TC, El-tayeb NSM, Von Brevern P (2013) Cutting forces, friction coefficient and surface roughness in machining Ti-5Al-4V-0. 6Mo-0. 4Fe using carbide tool K313 under low pressure liquid nitrogen. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 35:11–15
Pereira O, Català P, Rodríguez A, Ostra T, Vivancos J, Rivero A (2015) The use of hybrid CO2 + MQL in machining operations. Proc Eng 132:492–499
Pereira O, Rodríguez A, Barreiro J, De Lacalle LNL (2016) Cryogenic and minimum quantity lubrication for an eco-efficiency turning of AISI 304. J Clean Prod. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.030
Palazzc G, Pasquino R, Bellomo N, Torino P (2002) Temperature fields in machining processes and heat transfer models. Math Comput Model 35:101–109
Cooke AL, Science E (2007) On The measurement of temperature in material removal processes 1. Ann CIRP 56(2):581–604
Landeta JF, Valdivielso AF, de Lacalle LNL, Girot F (2015) Wear of form taps in threading of steel cold forged parts. J Manuf Sci Eng 137:1–11
Komanduri R, Hou Z (2001) A review of the experimental techniques for the measurement of heat and temperatures generated in some manufacturing processes and tribology. Tribol Int 34(10):653–682
Abukhshim NA, Mativenga PT, Sheikh MA (2006) Heat generation and temperature prediction in metal cutting: a review and implications for high speed machining. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 46(7–8):782–800
Sullivan DO, Cotterell M (2002) Workpiece temperature measurement in machining. Proc Inst Mech Eng 216(Part B):135–139
Longbottom JM, Lanham JD (2008) Cutting temperature measurement while machining—a review. Aircr Eng Aerosp Technol 77(2):122–130
Goyal A, Dhiman S, Kumar S, Sharma R (2014) A study of experimental temperature measuring techniques used in metal cutting. Jordan J Mech Ind Eng 8(2):82–93
Conradie PJT, Oosthuizen GA, Treurnicht NF, Al Shaalane A (2012) Overview of work piece temperature measurement techniques for machining of Ti6Al4V. S Afr J Ind Eng 23(July):116–130
Lo LN, De Lacalle Â, Celaya A, Lamikiz A, Bravo U (2008) Effect of coatings and tool geometry on the dry milling of wrought aluminium alloys. Int J Mater Prod Technol 32(1):41–55
Ulutan D, Lazoglu I, Dinc C (2009) Three-dimensional temperature predictions in machining processes using finite difference method. J Mater Process Technol 209(2):1111–1121
Riza M, Adesta EYT (2016) Investigation of cutting temperature for AISI H13 in high speed end milling. Int J Eng Mater Manuf 1(1):27–34
Ghafarizadeh S, Lebrun G (2016) Experimental investigation of the cutting temperature and surface quality during milling of unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced plastic. J Compos Mater 50(8):1059–1071
Sun Y, Sun J, Li J, Xiong Q (2014) An experimental investigation of the influence of cutting parameters on cutting temperature in milling Ti6Al4V by applying semi-artificial thermocouple. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70(5–8):765–773
Yang Y, Zhu W (2014) Study on cutting temperature during milling of titanium alloy based on FEM and experiment. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73(9–12):1511–1521
Le Coz G, Dudzinski D (2014) Temperature variation in the workpiece and in the cutting tool when dry milling Inconel 718. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74(5–8):1133–1139
Aspinwall DK, Mantle AL, Kok W, Hood R, Leung S (2013) Cutting temperatures when ball nose end milling g-TiAl intermetallic alloys. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 62(1):75–78
Yashiro T, Ogawa T, Sasahara H (2013) Temperature measurement of cutting tool and machined surface layer in milling of CFRP. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 70:63–69
Ueda T, Sato M, Hosokawa A, Ozawa M (2008) Development of infrared radiation pyrometer with optical fibers—two-color pyrometer with non-contact fiber coupler. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 57:69–72
Ueda T, Hosokawa A, Oda K, Yamada K (2001) Temperature on flank face of cutting tool in high speed milling. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 50(1):37–40
Sato M, Ueda T, Tanaka H (2007) An experimental technique for the measurement of temperature on CBN tool face in end milling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47:2071–2076
Le Coz G, Marinescu M, Devillez A, Dudzinski D, Velnom L (2012) Measuring temperature of rotating cutting tools: Application to MQL drilling and dry milling of aerospace alloys. Appl Therm Eng 36(1):434–441
Suprock CA, Nichols JS, Jerard RB, Fussell BK (2009) Calibration and implementation of a torque and temperature sensor-integrated tooling system for end milling. In: CIRP conference on modeling machining operations, pp 403–409
Toh CK (2005) Comparison of chip surface temperature between up and down milling orientations in high speed rough milling of hardened steel. J Mater Process Technol 167:110–118
Ngl E, Lee DW, Sharmanl ARC, Dewes RC, Aspinwal DK (2000) High speed ball nose end milling of Inconel718. Ann CIRP 49(1):41–46
Dewes RC, Ng E, Chua KS, Newton PG, Aspinwall DK (1999) Temperature measurement when high speed machining hardened mould/die steel. J Mater Process Technol 93–93:293–301
Fernandes MGA, Fonseca EMM, Natal RJ (2016) Thermal analysis during bone drilling using rigid polyurethane foams: numerical and experimental methodologies. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. doi:10.1007/s40430-016-0560-4
Tay AAO (1993) A review of methods of calculating machining temperature. J Mater Process Technol 36:225–257
Ali MH, Basim MNMA (2014) Simulation machining of titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) based on the finite element modeling. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. doi:10.1007/s40430-013-0084-0
Mkaddem A, Zain-ul-abdein M, Demirci I, Bin Mahfouz AS (2016) A pure thermal model to evaluate heat-affected zone when milling E-glass fiber-reinforced polyester composites. J Compos Mater. 1–12. doi:10.1177/0021998316640059
Liu Z, Peng W, Guo L, Dong F, Ma J (2015) Thermal-mechanical coupled finite element analysis of aluminum alloy grid sheet in high-speed milling. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 8:1–10
Pittalà GM, Monno M (2011) A new approach to the prediction of temperature of the workpiece of face milling operations of Ti-6Al-4V. Appl Therm Eng 31(2–3):173–180
Sölter J, Gulpak M (2012) Heat partitioning in dry milling of steel. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 61(1):87–90
Bhattacharya SN, Chakraborty G, Bose D (2011) 3-dimensional thermal mapping of workpiece during dry milling using finite element methods. Int J Technol Eng Syst 2(2):183–187
Rai JK, Xirouchakis P (2009) FEM-based prediction of workpiece transient temperature distribution and deformations during milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 42:429–449
Rai JK, Xirouchakis P (2008) Finite element method based machining simulation environment for analyzing part errors induced during milling of thin-walled components. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48:629–643
Deng WJ, Xia W, Zhao XL, Tang Y (2008) Modelling of temperature history during machining of cast aluminium alloy. In: Advanced design and manufacture to gain a competitive edge, pp 231–240
Brandão LC, Coelho RT, Rodrigues AR (2008) Experimental and theoretical study of workpiece temperature when end milling hardened steels using (TiAl)N-coated and PcBN-tipped tools. J Mater Process Technol 199(1):234–244
Feng Y, Zheng L, Wang M, Wang B (2015) Research on cutting temperature of work-piece in milling process based on WPSO. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79:427–435
Liu L, Cheng Y, Wang T, Han Y, Xu M (2015) Investigations of the high-temperature deformation behaviour and fatigue mechanisms of cemented carbide inserts during cutting 508III steel. Int J Manuf Res 10(4):299–312
Liu G, Tan G, Li G (2009) Experiment, modeling, and analysis for temperature field of milling insert. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40:67–73
Liu G, Li G, Song H, Rong Y(K) (2008) Analysis of temperature field of milling insert with 3D complex groove using Cellular Automata. Int J Manuf Res 3(2):188–197
Tan G, Liu G, Li G, Rong Y (2004) Study on 3D temperature distribution of milling insert with complex groove. In: Proceedings of the ASME applied mechanics division, pp 479–483
Ozel T, Altan T (2000) Process simulation using finite element method—prediction of cutting forces, tool stresses and temperatures in high-speed flat end milling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 40(5):713–738
Li A, Zhao J, Pei Z, Zhu N (2014) Simulation-based solid carbide end mill design and geometry optimization. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71(9–12):1889–1900
Soo SL, Aspinwall DK, Dewes RC (2004) Three-dimensional finite element modelling of high-speed milling of Inconel 718. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 218:1555–1561
Nasri A, Tsoumarev O (2011) Numerical simulation of temperature distribution in a 3D ball end milling model. Int J Mach Mach 9(November 1998):209–222
Ming C, Fanghong S, Haili W, Renwei Y, Zhenghong Q, Shuqiao Z (2003) Experimental research on the dynamic characteristics of the cutting temperature in the process of high-speed milling. J Mater Process Technol 138(1–3):468–471
Lazoglu I, Altintas Y (2002) Prediction of tool and chip temperature in continuous and interrupted machining. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42(9):1011–1022
Dinc C, Lazoglu I, Serpenguzel A (2008) Analysis of thermal fields in orthogonal machining with infrared imaging. J Mater Process Technol 198(1–3):147–154
Wernsing H, Gulpak M (2014) Enhanced method for the evaluation of the thermal impact of dry machining processes. Product Eng 8(3):291–300
Wernsing H (2015) Parameter identification for finite element based models in dry machining applications. In: 15th CIRP conference on modeling of machining operations (CIRP CMMO), vol 31, pp 328–333
Liu J, Chen G, Ji C, Qin X, Li H, Ren C (2014) An investigation of workpiece temperature variation of helical milling for carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP). Int J Mach Tools Manuf 86:89–103
Lin S, Peng F, Wen J, Liu Y, Yan R (2013) An investigation of workpiece temperature variation in end milling considering flank rubbing effect. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 73:71–86
Sugita N, Osa T, Mitsuishi M (2009) Analysis and estimation of cutting-temperature distribution during end milling in relation to orthopedic surgery. Med Eng Phys 31:101–107
Richardson DJ, Keavey MA, Dailami F (2006) Modelling of cutting induced workpiece temperatures for dry milling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 46(10):1139–1145
Lazoglu I, Bugdayci B (2014) Thermal modelling of end milling. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 63:113–116
Yan S, Zhu D, Zhuang K, Zhang X, Ding H (2014) Modeling and analysis of coated tool temperature variation in dry milling of Inconel 718 turbine blade considering flank wear effect. J Mater Process Technol 214(12):2985–3001
Sun Y, Sun J, Li J (2015) Modeling and experimental study of temperature distributions in end milling Ti6Al4V with solid carbide tool. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 231(2):217–227
Jiang F, Liu Z, Wan Y, Shi Z (2013) Analytical modeling and experimental investigation of tool and workpiece temperatures for interrupted cutting 1045 steel by inverse heat conduction method. J Mater Process Technol 213(6):887–894
Palanisamy P, Rajendran I, Shanmugasundaram S, Saravanan R (2006) Prediction of cutting force and temperature rise in the end-milling operation. Proc IMechE Part B J Eng Manuf 220:1577–1587
Zaghbani I, Songmene V (2009) A force-temperature model including a constitutive law for dry high speed milling of aluminium alloys. J Mater Process Technol 209:2532–2544
Santhanakrishnan M, Sivasakthivel PS, Sudhakaran R (2015) Modeling of geometrical and machining parameters on temperature rise while machining Al 6351 using response surface methodology and genetic algorithm. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. doi:10.1007/s40430-015-0378-5
Sivasakthivel PS, Sudhakaran R (2013) Optimization of machining parameters on temperature rise in end milling of Al 6063 using response surface methodology and genetic algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67(9–12):2313–2323
Patel B, Nayak H, Araniya K, Champaneri G (2014) Parametric optimization of temperature during CNC end milling of mild steel using RSM. Int J Eng Res Technol (IJERT) 3(1):69–73
Tamilarasan A, Marimuthu K, Renugambal A (2016) Investigations and optimization for hard milling process parameters using hybrid method of RSM and NSGA-II. Rev Téc Ing Univ Zulia 39(2012):41–54
Tamilarasan A, Rajamani D (2015) Multi-objective optimization of hard milling process using evolutionary computation techniques. Int J Adv Eng Res Appl (IJAERA) 1(7):264–275
Tamilsaran A, Rajamani D (2015) An approach on fuzzy and regression modeling for hard milling process. Appl Mech Mater 813–814:498–504
Tamilarasan A, Marimuthu K (2014) Multi-response optimization of hard milling process: RSM coupled with grey relational analysis. Int J Eng Technol 5(6):4903–4913
Tamilarasan A, Marimuthu K (2014) Multi-response optimisation of hard milling process parameters based on integrated Box-Behnken design with desirability function approach. Int J Mach Machin Mater 15(3/4):300–320
Chawale SB, Bhoyar VV, Ghawade PS, Kathoke TB (2013) Effect of machining parameters on temperature at cutter-work piece interface in milling. Int J Eng Innov Technol 2(12):85–88
Al Hazza MHF, Adesta EYT, Superianto MY, Riza M (2013) Cutting temperature and surface roughness optimization in cnc end milling using multi objective genetic algorithm. In: Proceedings—2012 international conference on advanced computer science applications and technologies, ACSAT 2012, pp 275–278
Adesta YT, Al Hazza MHF, Suprianto M, Riza M (2012) Prediction of cutting temperatures by using back propagation neural network modeling when cutting hardened H-13 steel in CNC end milling. Adv Mater Res 576:91–94
Spânu P, Iliescu M (2008) Mathematical model of temperature in milling glass fiber reinforced polymeric composites. U.P.B. Sci Bull Ser B 70(1):63–72
Mzad H (2015) A simple mathematical procedure to estimate heat flux in machining using measured surface temperature with infrared laser. Case Stud Therm Eng 6:128–135
Pabst R, Fleischer J, Michna J (2010) Modelling of the heat input for face-milling processes. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 59(1):121–124
Laxmikant R, Karthik M, Arun MCR, Shettigar K (2016) Application of particle swarm optimization and response surface methodology for machining parameters optimization of aluminium matrix composites in milling operation. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. doi:10.1007/s40430-016-0675-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Márcio Bacci da Silva.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhirud, N.L., Gawande, R.R. Measurement and prediction of cutting temperatures during dry milling: review and discussions. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39, 5135–5158 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-017-0869-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-017-0869-7