Abstract
Background and Objective
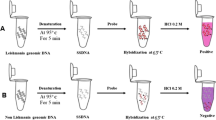
We describe here a nanodiagnostic colorimetric assay for 18S rRNA of Leishmania pathogens that uses nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA) and gold nanorods (GNRs).
Methods
NASBA primers targeting 18S rRNA were used for amplification of RNA in an isothermal process. The electrostatic interactions between the phosphate groups of the RNA amplicons and the cetyl trimethylammonium bromide layer on the GNRs resulting in their aggregation. This phenomenon changes the color of the GNR solution from red to purple.
Results
Our data showed 100 % sensitivity and 80 % specificity with the colorimetric assay compared with results using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
Conclusion
The nanodiagnostic method we describe simplifies the detection of NASBA amplicons without the need for gel electrophoresis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bates PA. Transmission of Leishmania metacyclic promastigote by Phlebotomine sand flies. Int J Parasitol. 2007;37(10):1097–9. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2007.04.003.
van der Meide WF, Schoone GJ, Faber WR, Zeegelaar JE, De Vries HJ, Ozbel Y, Lai A, Fat RF, Coelho LI, Kassi M, Schallig HD. Quantitative nucleic acid sequence-based assay as a new molecular tool for detection and quantification of Leishmania parasites in skin biopsy samples. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43(11):5560–6. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.11.5560-5566.2005.
Berman JD. Human leishmaniasis: clinical, diagnostic and chemotherapeutic developments in the last 10 years. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;24(4):684–703. doi:10.1093/clind/24.4.684.
Schallig HD, Oskam L. Molecular biological applications in the diagnosis and control of leishmaniasis and parasite identification. Trop Med Int. 2002;7(8):641–51. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3156.2002.00911.x.
Aransay AM, Scoulica E, Tselentis Y. Detection and identification of Leishmania DNA within naturally infected flies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002;66(5):1933–8. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.5.1933-1938.2000.
Faber WR, Oskam L, van Gool T, Kroong NCM, Knegt-Junk KJ, Hofwegenf H, van der Wal AC, Kager PA. Value of diagnostic techniques for cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49(1):70–4. doi:10.1067/mjd.2003.492.
Laskay T, Miko TL, Negesse Y, Solbach W, Rollinghoff M, Frommel D. Detection of cutaneous Leishmania infection in paraffin embedded skin biopsies using the polymerase chain reaction. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1995;89(3):273–5. doi:10.1016/0035-9203(95)90537-5.
Schubach AF, Haddad MP, Oliveira-Neto W. Detection of Leishmania DNA by PCR in scars of treated human patients. J Infect Dis. 1998;178(3):911–4. doi:10.1086/515355.
Mendonça MG, Brito MEF, Rodrigues EHG, Bandeira V, Jardim ML, Abath FGC. Persistence of Leishmania parasites in scars after clinical cure of American cutaneous Leishmaniasis: is there a sterile cure? J Infect Dis. 2004;189(6):1018–23. doi:10.1086/382135.
Omar SA, Mens PF, Schoone GJ, Yusuf A, Mwangi J, Kaniaru S. Plasmodium falciparum: evaluation of a quantitative nucleic acid sequence-based amplification assay to predict the outcome of sulfadoxine pyrimethamine treatment of uncomplicated malaria. Exp Parasitol. 2005;110(1):73–9. doi:10.1016/j.exppara.2005.02.001.
Compton J. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification. Nature. 1991;350(6313):91–2. doi:10.1038/350091a0.
Deiman B, van Aarle P, Sillekens P. Characteristics and applications of nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA). Appl Biochem Biotechnol B Mol Biotechnol. 2002;20(2):163–79. doi:10.1385/MB:20:2:163.
Gill P, Ghaemi A. Nucleic acid isothermal amplification technologies: a review. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2008;27(3):224–43. doi:10.1080/15257770701845204.
Malek L, Sooknanan R, Compton J. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification. In: Isaac PG, editor. Methods in molecular biology, vol 28, protocols for nucleic acid analysis by nonradioactive probes. Totowa: Humana Press; 1994. p. 253–60.
Gill P, Ramezani R, Amiri MV, Ghaemi A, Hashempour T, Eshraghi N, Ghalami M, Tehrani HA. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of nucleic acid sequence-based amplification for molecular detection of M. tuberculosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;347(4):1151–7. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.039.
van Gemen B, van Beuningen R, Nabbe A, van Strijp D, Jurriaans S, Lens P, Kievits T. A one-tube quantitative HIV-1 RNA NASBA nucleic acid amplification assay using electrochemiluminescent (ECL) labeled probes. J Virol Methods. 1994;49(2):157–67. doi:10.1016/0166-0934(94)90040-X.
Leone G, van Gemen B, Schoen CD, van Schijndel H, Kramer FR. Molecular beacon probes combined with amplification by NASBA enable homogeneous, real-time detection of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998;26(9):2150–5. doi:10.1093/nar/26.9.2150.
Gill P, Ghalami M, Ghaemi A, Mosavari N, Abdul-Tehrani H, Sadeghizadeh M. Nanodiagnostic method for colorimetric detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis 16S rRNA. Nanobiotechnology. 2008;4(1–4):28–35. doi:10.1007/s12030-009-9021-9.
Wilson IG. Inhibition and facilitation of nucleic acid amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1997;63(10):3741–51. doi:63/10/3741.
Lee KS, El-Sayed MA. Dependence of the enhanced optical scattering efficiency relative to that of absorption for gold metal nanorods on aspect ratio, size, end-cap shape, and medium refractive index. J Phys Chem B. 2006;109(43):20331–8. doi:10.1021/jp054385p.
Chen CD, Cheng SF, Chau LK, Wang CRC. Sensing capability of the localized surface plasmon resonance of gold nanorods. Biosens Bioelectron. 2007;22(6):926–32. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2006.03.021.
Murphy CJ, Gole AM, Hunyadi SE, Stone JW, Sisco PN, Alkilany A, Kinard BE, Hankins P. Chemical sensing and imaging with metallic nanorods. Chem Commun. 2008;8(5):544–57. doi:10.1039/b711069c.
Ma Z, Tian L, Wang T, Wang C. Optical DNA detection based on gold nanorods aggregation. Anal Chim Acta. 2010;673(2):179–84. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2010.05.036.
Saber R, Shakoori Z, Sarkar S, Tavoosidana G, Kharrazi S, Gill P. Spectroscopic and microscopic analyses of rod-shaped gold nanoparticles interacted with ssDNA oligomers. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2013;7(2):1–8. doi:10.1049/iet-nbt.2012.0009.
Saad AA, Ahmed NG, Osman OS, Al-Basheer AA, Hamad A, Deborggraeve S, Büscher P, Schoone GJ, Schallig HD, Laurent T, Haleem A, Osman OF, Eltom AM, Elbashir MI, El-Safi S. Diagnostic accuracy of the Leishmania oligoC-tesT and NASBA oligochromatography for diagnosis of leishmaniasis in Sudan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010;4(8):1–5. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000776.
Moskowitz CS, Pepe MS. Comparing the predictive values of diagnostic tests: sample size and analysis for paired study designs. Clin Trials. 2006;3(3):272–9. doi:10.1191/1740774506cn147oa.
Schoone GJ, Oskam L, Kroon NCM, Schallig HDFH, Omar SA. Detection and quantification of Plasmodium falciparum in blood samples using quantitative nucleic acid sequence-based amplification. J Clin Microbiol. 1993;38(11):4072–5. doi:38/11/4072.
Ming-Cheng M, Cuda G, Bunimovich YL, Gaspari M, Heath JR, Hill HD, Mirkin CA, Nijdam J, Terracciano R, Thundat T, Ferrari M. Nanotechnologies for biomolecular detection and medical diagnostics. Cur Opin Chem Biol. 2006;10(1):11–9. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.01.006.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Vice-Chancellor in Research and Technology Affairs, Golestan University of Medical Sciences. The Iran Nanotechnology Initiative (INI) also supported partially this project. The authors thank Fatemeh Ghaffarifar, Fatemeh Mesgarian, Sareh Zhand, and Mohammad Shariati for their help in the laboratory experiments.
Author Contributions
P. Gill conceived and designed the experiments. A. Niazi and H. Nikbakht performed the experiments. P. Gill and O-N Jorjani analyzed the data. O-N. Jorjani and P. Gill contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. A. Niazi and P. Gill wrote the paper.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niazi, A., Jorjani, ON., Nikbakht, H. et al. A Nanodiagnostic Colorimetric Assay for 18S rRNA of Leishmania Pathogens using Nucleic Acid Sequence-Based Amplification and Gold Nanorods. Mol Diagn Ther 17, 363–370 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-013-0044-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-013-0044-5