Abstract
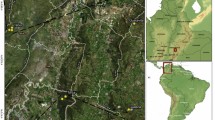
Andrographis is a medicinally important genus of 26 species native to India, with greatest species diversity occurring in southern India. The present study provides the natural range of eleven species of Andrographis in Andhra Pradesh. Of these, nine species show narrow distributional range and are vulnerable to unsustainable harvesting and land use changes. As the first step towards the conservation and prioritization of the valuable taxa, this study presents data on diversity, spatial distribution and habitats of Andrographis species in the state of Andhra Pradesh.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akerele O (1992) WHO guideline for assessment of herbal medicines. Fitoterapia 63:99–118
Huxley A (1984) Green Inheritance: The World Wildlife Fund Book of India. Collins/Harvel, London
Abhyankar G, Reddy VD (2007) Rapid micropropagation via axillary bud proliferation of Adhatoda vasica Nees from nodal segments. Indian J Exp Biol 45:268–271
Karthikeyan S, Sanjappa M, Moorthy S (2009) Flowering Plants of India-Dicotyledons. Publ Bot Surv India 1:1–4
Pattanaik C, Reddy CS, Reddy KN (2009) Ethno-medicinal survey of threatened plants in Eastern Ghats, India. Our Nat 7:122–128
Pullaiah T, Ali-Moulali D (1997) Flora of Andhra Pradesh, vol 2. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur, pp 691–694
Das B, Ramu R, Rao YK, Reddy MR, Harish H, Reddy VS, Ramakrishna KVS (2006) Acylated 5, 7, 2′, 6′-oxygenated flavone glycosides from Andrographis alata. Phytochemistry 67:978–983
Alagesaboopathi C (2011) Antimicrobial activity and phytochemical analysis of Andrographis alata Nees from Southern India. Int J Pharm Tech Res 3:1322–1328
Walter KS, Gillett HJ (1998) The 1997 IUCN Red list of Threatened Plants. IUCN, World Conservation Union, Cambridge
Jayaprakasam B, Damu AG, Gunasekar D, Blond A, Bodo B (1999) Dihydroechioidinin, a flavanone from Andrographis echioides. Phytochemistry 52:935–937
Neelima M, Prasad GP, Pratap GP, Jyothi B (2011) Ethnobotanical studies in Rapur forest division of Nellore district in Andhra Pradesh. Life Sci Leafl 11:333–345
Alagesaboopathi C (2013) Evaluation of antibacterial properties of leaf and stem extracts of Andrographis elongata T. And. – an endemic medicinal plant of India. Int J Pharm Bio Sci 4:503–510
Sangameswaran B, Reddy TC, Jayakar B (2008) Hepatoprotective effect of leaf extracts of Andrographis lineata Nees on liver damage caused by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Phytother Res 22:124–126
Renugadevi G, Ramanathan T, Shanmuga PR, Thirunavukkarasu P (2013) Studies on effects of Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) and Andrographis lineata Nees (Family: acanthaceae) extracts against two mosquitoes Culex quinquefasciatus (Say.) and Aedes aegypti (Linn.). Asian Pac J Trop Med 6:176–179
Subbarao GV, Kumari GR (2008) Flora of Visakhapatnam District. Publ Bot Surv India 2:22
Venkatasubbaiah KP, Savithramma N (2012) Bio-prospecting and documentation of traditional medicinal plants used to treat selected skin diseases by ethnic groups of Kurnool district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Int J Adv Pharm Res 3:790–797
Padma Y, Venakataraju RR (2013) Phytochemical screening and evaluation of antimicrobial activity of Andrographis nallamalayana Ellis, a rare and endangered species. Am J PharmTech Res 3:957–962
Alagesaboopathi C (2010) Vegetative propagation of Andrographis ovata. J Trop Med Plants 11:215–217
Alagesaboopathi C (2011) Phytochemical screening and antimicrobial potential of Andrographis ovata Clarke. Afr J Biotechnol 10:5033–5036
Chao WW, Lin BF (2010) Isolation and identification of bioactive compounds in Andrographis paniculata. Chin Med 5:17
Parixit B, Bharath Ch, Rajarajeshwari N, Ganapaty S (2012) The genus Andrographis - A review. Int J Pharm Sci 4:1835–1856
Srivastava N, Akhila A (2010) Biosynthesis of Andrographolide in Andrographis paniculata. Phytochemistry 71:1298–1304
Roy S, Kiranmayee R, Bhuvaneswari Ch, Archana G, Narasu ML (2010) Phytochemical analysis of Andrographis paniculata extract and its antimicrobial activity. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:85–91
Sule A, Ahmed QU, Latip J, Samah OA, Omar MN, Umar A, Dogarai BB (2011) Antifungal activity of Andrographis paniculata extracts and active principles against skin pathogenic fungal strains in vitro. Pharm Biol 50:850–856
Dua VK, Verma G, Dash AP (2009) In vitro antiprotozoal activity of some xanthones isolated from the roots of Andrographis paniculata. Phytother Res 23:126–128
Nagalekshmi R, Menon A, Chandrasekharan DK, Nair CK (2011) Hepatoprotective activity of Andrographis paniculata and Swertia chirayita. Food Chem Toxicol 49:3367–3373
Jain PK, Khurana N, Pounikar Y, Gajbhiye A, Kharya MD (2013) Enhancement of absorption and hepatoprotective potential through soya-phosphatidylcholine-andrographolide vesicular system. J Liposome Res 23:110–118
Alagesabhoopathi C (2013) Ethnomedicinal plants used for the treatment of snake bites by Malayali tribal’s and rural people in Salem district, Tamilnadu, India. Int J Biosci 3:42–53
Govindachari TR, Parthasarathy PC (1968) Chemical investigation of Andrographis serpyllifolia: isolation and structure of serpyllin, a new flavones. Tetrahedron 24:7027–7031
Vasu K, Govardhan P, Reddy CHS, Nath AR, Reddy RR (2012) In-vitro and in- vivo anti-inflammatory activity of Andrographis serpyllifolia (Rottl. ex Vahl) Wt. Int Curr Pharm J 1:199–204
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Dr. P. V. Prasanna, Scientist E, Deccan Circle, Botanical survey of India, Prof. V. S. Raju, Depatment of Botany, Kakatiya University and Dr. C.S. Jha, Head, Forestry and Ecology Group, NRSC for their advice. Thanks are due to University Grants Commission, New Delhi for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neeraja, C., Krishna, P.H., Reddy, C.S. et al. Distribution of Andrographis species in Different Districts of Andhra Pradesh. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 85, 601–606 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-014-0364-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-014-0364-1